Reconstructing the “Martell” Delegation through Newspapers
November 2, 2013

Symbolic Petition of the Chippewa Chiefs: This pictographic petition was brought to Washington D.C. by a delegation of Ojibwe chiefs and their interpreter J.B. Martell. This one, representing the band of Chief Oshkaabewis, is the most famous, but their were several others copied from birch bark by Seth Eastman and published in the works of Henry Schoolcraft. For more, follow this link.
Henry Schoolcraft. William W. Warren. George Copway. These names are familiar to any scholar of mid-19th-century Ojibwe history. They are three of the most referenced historians of the era, and their works provide a great deal of historical material that is not available in any other written sources. Copway was Ojibwe, Warren was a mix-blood Ojibwe, and Schoolcraft was married to the granddaughter of the great Chequamegon chief Waabojiig, so each is seen, to some extent, as providing an insider’s point of view. This could lead one to conclude that when all three agree on something, it must be accurate. However, there is a danger in over-relying on these early historians in that we forget that they were often active participants in the history they recorded.
This point was made clear to me once again as I tried to sort out my lingering questions about the 1848-49 “Martell” Delegation to Washington. If you are a regular reader, you may remember that this delegation was the subject of the first post on this website. You may also remember from this post, that the group did not have money to get to Washington and had to reach out to the people they encountered along the way.
The goal of the Martell Delegation was to get the United States to cede back title to the lands surrounding the major Lake Superior Ojibwe villages. The Ojibwe had given this land up in the Treaty of 1842 with the guarantee that they could remain on it. However, by 1848 there were rumors of removal of all the bands east of the Mississippi to unceded land in Minnesota. That removal was eventually attempted, in 1850-51, in what is now called the Sandy Lake Tragedy.
The Martell Delegation remains a little-known part of the removal story, although the pictographs remain popular. Those petitions are remembered because they were published in Henry Schoolcrafts’ Historical and statistical information respecting the history, condition, and prospects of the Indian tribes of the United States (1851) along with the most accessible primary account of the delegation:
In the month of January, 1849, a delegation of eleven Chippewas, from Lake Superior, presented themselves at Washington, who, amid other matters not well digested in their minds, asked the government for a retrocession of some portion of the lands which the nation had formerly ceded to the United States, at a treaty concluded at Lapointe, in Lake Superior, in 1842. They were headed by Oshcabawiss, a chief from a part of the forest-country, called by them Monomonecau, on the head-waters of the River Wisconsin. Some minor chiefs accompanied them, together with a Sioux and two boisbrules, or half-breeds, from the Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan. The principal of the latter was a person called Martell, who appeared to be the master-spirit and prime mover of the visit, and of the motions of the entire party. His motives in originating and conducting the party, were questioned in letters and verbal representations from persons on the frontiers. He was freely pronounced an adventurer, and a person who had other objects to fulfil, of higher interest to himself than the advancement of the civilization and industry of the Indians. Yet these were the ostensible objects put forward, though it was known that he had exhibited the Indians in various parts of the Union for gain, and had set out with the purpose of carrying them, for the same object, to England. However this may be, much interest in, and sympathy for them, was excited. Officially, indeed, their object was blocked up. The party were not accredited by their local agent. They brought no letter from the acting Superintendent of Indian Affairs on that frontier. The journey had not been authorized in any manner by the department. It was, in fine, wholly voluntary, and the expenses of it had been defrayed, as already indicated, chiefly from contributions made by citizens on the way, and from the avails of their exhibitions in the towns through which they passed; in which, arrayed in their national costume, they exhibited their peculiar dances, and native implements of war and music. What was wanting, in addition to these sources, had been supplied by borrowing from individuals.
Martell, who acted as their conductor and interpreter, brought private letters from several persons to members of Congress and others, which procured respect. After a visit, protracted through seven or eight weeks, an act was passed by Congress to defray the expenses of the party, including the repayment of the sums borrowed of citizens, and sufficient to carry them back, with every requisite comfort, to their homes in the north-west. While in Washington, the presence of the party at private houses, at levees, and places of public resort, and at the halls of Congress, attracted much interest; and this was not a little heightened by their aptness in the native ceremonies, dancing, and their orderly conduct and easy manners, united to the attraction of their neat and well-preserved costume, which helped forward the object of their mission.
The visit, although it has been stated, from respectable sources, to have had its origin wholly in private motives, in the carrying out of which the natives were made to play the part of mere subordinates, was concluded in a manner which reflects the highest credit on the liberal feelings and sentiments of Congress. The plan of retrocession of territory, on which some of the natives expressed a wish to settle and adopt the modes of civilized life, appeared to want the sanction of the several states in which the lands asked for lie. No action upon it could therefore be well had, until the legislatures of these states could be consulted (pg. 414-416, pictographic plates follow).
I have always had trouble with Schoolcraft’s interpretation of these events. It wasn’t that I had evidence to contradict his argument, but rather that I had a hard time believing that all these chiefs would make so weighty a decision as to go to Washington simply because their interpreter was trying to get rich. The petitions asked for a permanent homeland in the traditional villages east of the Mississippi. This was the major political goal of the Lake Superior Ojibwe leadership at that time and would remain so in all the years leading up to 1854. Furthermore, chiefs continued to ask for, or go “uninvited” on, diplomatic missions to the president in the years that followed.
I explored some of this in the post about the pictograph, but a number of lingering questions remained:
What route did this group take to Washington?
Who was Major John Baptiste Martell?
Did he manipulate the chiefs into working for him, or was he working for them?
Was the Naaganab who went with this group the well-known Fond du Lac chief or the warrior from Lake Chetek with the same name?
Did any chiefs from the La Pointe band go?
Why was Martell criticized so much? Did he steal the money?
What became of Martell after the expedition?
How did the “Martell Expedition” of 1848-49 impact the Ojibwe removal of 1850-51?
Lacking access to the really good archives on this subject, I decided to focus on newspapers, and since this expedition received so much attention and publicity, this was a good choice. Enjoy:


Indiana Palladium. Vevay, IN. Dec. 2, 1848
Capt. Seth Eastman of the U.S. Army took note of the delegation as it traveled down the Mississippi from Fort Snelling to St. Louis. Eastman, a famous painter of American Indians, copied the birch bark petitions for publication in the works of his collaborator Henry Schoolcraft. At least one St. Louis paper also noticed these unique pictographic documents.
 Lafayette Courier. Lafayette, IN. Dec. 8, 1848.
Lafayette Courier. Lafayette, IN. Dec. 8, 1848.
The delegation made its way up the Ohio River to Cincinnati, where Gezhiiyaash’s illness led to a chance encounter with some Ohio Freemasons. I won’t repeat it here, but I covered this unusual story in this post from August.
At Cincinnati, they left the river and headed toward Columbus. Just east of that city, on the way to Pittsburgh, one of the Ojibwe men offered some sound advice to the women of Hartford, Ohio, but he received only ridicule in return.

Madison Weekly Courier. Madison, IN. Jan. 24, 1849

It’s unclear how quickly reports of the delegation came back to the Lake Superior country. William Warren’s letter to his cousin George, written in March after the delegation had already left Washington, still spoke of St. Louis:
William W. Warren (Wikimedia Images)
“…About Martells Chiefs. They were according to last accounts dancing the pipe dance at St. Louis. They have been making monkeys of themselves to fill the pockets of some cute Yankee who has got hold of them. Black bird returned from Cleveland where he caught scarlet fever and clap. He has behaved uncommon well since his return…” (Schenck, pg. 49)
From this letter, we learn that Blackbird, the La Pointe chief, was originally part of the group. In evaluating Warren’s critical tone, we must remember that he was working closely with the very government officials who withheld their permission. Of the La Pointe chiefs, Blackbird was probably the least accepting of American colonial power. However, we see in the obituary of Naaganab, Blackbird’s rival at the 1855 annuity payment, that the Fond du Lac chief was also there.
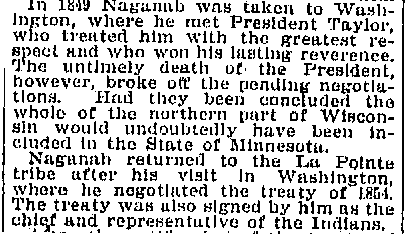
New York World. New York. July 22, 1894
Before finding this obituary, I had thought that the Naaganab who signed the petition was more likely the headman from Lake Chetek. Instead, this information suggests it was the more famous Fond du Lac chief. This matters because in 1848, Naaganab was considered the speaker for his cousin Zhingob, the leading chief at Fond du Lac. Blackbird, according to his son James, was the pipe carrier for Buffalo. While these chiefs had their differences with each other, it seems likely that they were representing their bands in an official capacity. This means that the support for this delegation was not only from “minor chiefs” as Schoolcraft described them, or “Martells Chiefs” as Warren did, from Lac du Flambeau and Michigan. I would argue that the presence of Blackbird and Naaganab suggests widespread support from the Lake Superior bands. I would guess that there was much discussion of the merits of a Washington delegation by Buffalo and others during the summer of 1848, and that the trip being a hasty money-making scheme by Martell seems much less likely.

Madison Daily Banner. Madison, IN. Jan. 3, 1849.
From Pittsburgh, the delegation made it to Philadelphia, and finally Washington. They attracted a lot of attention in the nation’s capital. Some of their adventures and trials: Oshkaabewis and his wife Pammawaygeonenoqua losing an infant child, the group hunting rabbits along the Potomac, and the chiefs taking over Congress, are included this post from March, so they aren’t repeated here.

Adams Sentinel. Gettysburg, PA. Feb. 5, 1849.
According to Ronald Satz, the delegation was received by both Congress and President Polk with “kindly feelings” and the expectation of “good treatment in the future” if they “behaved themselves (Satz 51).” Their petition was added to the Congressional Record, but the reservations were not granted at the time. However, Congress did take up the issue of paying for the debts accrued by the Ojibwe along the way.


George Copway (Wikimedia Commons)
Kah-Ge-Ga-Gah-Bowh (George Copway), a Mississauga Ojibwe and Methodist missionary, was the person “belonging to one of the Canada Bands of Chippewas,” who wrote the anti-Martell letter to Indian Commissioner William Medill. This is most likely the letter Schoolcraft referred to in 1851. In addition to being upset about the drinking, Copway was against reservations in Wisconsin. He wanted the government to create a huge pan-Indian colony at the headwaters of the Missouri River.

William Medill (Wikimedia Commons)

Iowa State Gazette. Burlington, IA. April 4, 1849
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 Weekly Wisconsin. Milwaukee. Feb. 28, 1849.
Weekly Wisconsin. Milwaukee. Feb. 28, 1849.
With $6000 (or did they only get $5000?), a substantial sum for the antebellum Federal Government, the group prepared to head back west with the ability to pay back their creditors.
It appears the chiefs returned to their villages by going back though the Great Lakes to Green Bay and then overland.
The Chippewa Delegation, who have been on a visit to see their “great fathers” in Washington, passed through this place on Saturday last, on their way to their homes near Lake Superior. From the accounts of the newspapers, they have been lionized during their whole journey, and particularly in Washington, where many presents were made them, among the most substantial of which was six boxed of silver ($6,000) to pay their expenses. They were loaded with presents, and we noticed one with a modern style trunk strapped to his back. They all looked well and in good spirits (qtd. in Paap, pg. 205).
Green Bay Gazette. April 4, 1849
So, it hardly seems that the Ojibwe chiefs returned to their villages feeling ripped off by their interpreter. Martell himself returned to the Soo, and found a community about to be ravaged by a epidemic of cholera.

Weekly Wisconsin. Milwaukee. Sep. 5, 1849.
Martell appears in the 1850 census on the record of those deceased in the past year. Whether he was a major in the Mexican War, whether he was in the United States or Canadian military, or whether it was even a real title, remains a mystery. His death record lists his birthplace as Minnesota, which probably connects him to the Martells of Red Lake and Red River, but little else is known about his early years. And while we can’t say for certain whether he led the group purely out of self-interest, or whether he genuinely supported the cause, John Baptiste Martell must be remembered as a key figure in the struggle for a permanent Ojibwe homeland in Wisconsin and Michigan. He didn’t live to see his fortieth birthday, but he made the 1848-49 Washington delegation possible.
So how do we sort all this out?
To refresh, my unanswered questions from the other posts about this delegation were:
1) What route did this group take to Washington?
2) Who was Major John Baptiste Martell?
3) Did he manipulate the chiefs into working for him, or was he working for them?
4) Was the Naaganab who went with this group the well-known Fond du Lac chief or the warrior from Lake Chetek with the same name?
5) Did any chiefs from the La Pointe band go?
6) Why was Martell criticized so much? Did he steal the money?
7) What became of Martell after the expedition?
8) How did the “Martell Expedition” of 1848-49 impact the Ojibwe removal of 1850-51?
We’ll start with the easiest and work our way to the hardest. We know that the primary route to Washington was down the Brule, St. Croix, and Mississippi to St. Louis, and from there up the Ohio. The return trip appears to have been via the Great Lakes.
We still don’t know how Martell became a major, but we do know what became of him after the diplomatic mission. He didn’t survive to see the end of 1849.
The Fond du Lac chief Naaganab, and the La Pointe chief Blackbird, were part of the group. This indicates that a wide swath of the Lake Superior Ojibwe leadership supported the delegation, and casts serious doubt on the notion that it was a few minor chiefs in Michigan manipulated by Martell.
Until further evidence surfaces, there is no reason to support Schoolcraft’s accusations toward Martell. Even though these allegations are seemingly validated by Warren and Copway, we need to remember how these three men fit into the story. Schoolcraft had moved to Washington D.C. by this point and was no longer Ojibwe agent, but he obviously supported the power of the Indian agents and favored the assimilation of his mother-in-law’s people. Copway and Warren also worked closely with the Government, and both supported removal as a way to separate the Ojibwe from the destructive influences of the encroaching white population. These views were completely opposed to what the chiefs were asking for: permanent reservations at the traditional villages. Because of this, we need to consider that Schoolcraft, Warren, and Copway would be negatively biased toward this group and its interpreter.
Finally there’s the question Howard Paap raises in Red Cliff, Wisconsin. How did this delegation impact the political developments of the early 1850s? In one sense the chiefs were clearly pleased with the results of the trip. They made many friends in Congress, in the media, and in several American cities. They came home smiling with gifts and money to spread to their people. However, they didn’t obtain their primary goal: reservations east of the Mississippi, and for this reason, the following statement in Schoolcraft’s account stands out:
The plan of retrocession of territory, on which some of the natives expressed a wish to settle and adopt the modes of civilized life, appeared to want the sanction of the several states in which the lands asked for lie. No action upon it could therefore be well had, until the legislatures of these states could be consulted.
“Kindly feelings” from President Polk didn’t mean much when Zachary Taylor and a new Whig administration were on the way in. Meanwhile, Congress and the media were so wrapped up in the national debate over slavery that they forgot all about the concerns of the Ojibwes of Lake Superior. This allowed a handful of Indian Department officials, corrupt traders, and a crooked, incompetent Minnesota Territorial governor named Alexander Ramsey to force a removal in 1850 that resulted in the deaths of 400 Ojibwe people in the Sandy Lake Tragedy.
It is hard to know how the chiefs felt about their 1848-49 diplomatic mission after Sandy Lake. Certainly their must have been a strong sense that they were betrayed and abandoned by a Government that had indicated it would support them, but the idea of bypassing the agents and territorial officials and going directly to the seat of government remained strong. Another, much more famous, “uninvited” delegation brought Buffalo and Oshogay to Washington in 1852, and ultimately the Federal Government did step in to grant the Ojibwe the reservations. Almost all of the chiefs who made the journey, or were shown in the pictographs, signed the Treaty of 1854 that made them.
Sources:
McClurken, James M., and Charles E. Cleland. Fish in the Lakes, Wild Rice, and Game in Abundance: Testimony on Behalf of Mille Lacs Ojibwe Hunting and Fishing Rights / James M. McClurken, Compiler ; with Charles E. Cleland … [et Al.]. East Lansing, MI: Michigan State UP, 2000. Print.
Paap, Howard D. Red Cliff, Wisconsin: A History of an Ojibwe Community. St. Cloud, MN: North Star, 2013. Print.
Satz, Ronald N. Chippewa Treaty Rights: The Reserved Rights of Wisconsin’s Chippewa Indians in Historical Perspective. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters, 1991. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and times of an Ojibwe Leader. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2007. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe, and Seth Eastman. Historical and Statistical Information Respecting the History, Condition, and Prospects of the Indian Tribes of the United States: Collected and Prepared under the Direction of the Bureau of Indian Affairs per Act of Congress of March 3rd, 1847. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo, 1851. Print.
Chief Buffalo Picture Search: Introduction
May 26, 2013
Click the question mark under the picture to see if it shows Chief Buffalo.
 ?
?
Buffalo, the 19th-century chief of the La Pointe Ojibwe, is arguably the most locally-famous person in history of the Chequamegon region. He is best known for his 1852 trip to Washington D.C., undertaken when he was thought to be over ninety years old. Buffalo looms large in the written records of the time, and makes many appearances on this website.
He is especially important to the people of Red Cliff. He is the founding father of their small community at the northern tip of Wisconsin in the sense that in the Treaty of 1854, he negotiated for Red Cliff (then called the Buffalo Estate or the Buffalo Bay Reservation) as a separate entity from the main La Pointe Band reservation at Bad River. Buffalo is a direct ancestor to several of the main families of Red Cliff, and many tribal members will proudly tell of how they connect back to him. Finally, Buffaloʼs fight to keep the Ojibwe in Wisconsin, in the face of a government that wanted to move them west, has served as an inspiration to those who try to maintain their cultural traditions and treaty rights. It is unfortunate, then, that through honest mistakes and scholarly carelessness, there is a lot of inaccurate information out there about him.
During the early twentieth century, the people of Red Cliff maintained oral traditions about about his life while the written records were largely being forgotten by mainstream historians. However, the 1960s and ʻ70s brought a renewed interest in American Indian history and the written records came back to light. With them came no fewer than seven purported images of Buffalo, some of them vouched for by such prestigious institutions as the State Historical Society of Wisconsin and the U.S. Capitol. These images, ranged from well-known lithographs produced during Buffaloʼs lifetime, to a photograph taken five years after he died, to a symbolic representation of a clan animal originally drawn on birch bark. These images continue to appear connected to Buffalo in both scholarly and mainstream works. However, there is no proof that any of them show the La Pointe chief, and there is clear evidence that several of them do not show him.
The problem this has created is not merely one of mistaken identity in pictures. To reconcile incorrect pictures with ill-fitting facts, multiple authors have attempted to create back stories where none exist, placing Buffalo where he wasnʼt, in order for the pictures to make sense. This spiral of compounding misinformation has begun to obscure the legacy of this important man, and therefore, this study attempts to sort it out.
Bizhikiwag
The confusion over the images stems from the fact that there was more than one Ojibwe leader in the mid-nineteenth century named Bizhiki (Buffalo). Because Ojibwe names are descriptive, and often come from dreams, visions, or life experiences, one can be lead to believe that each name was wholly unique. However, this is not the case. Names were frequently repeated within families or even outside of families. Waabojiig (White Fisher) and Bugone-Giizhig (Hole in the Day) are prominent examples of names from Buffaloʼs lifetime that were given to unrelated men from different villages and clans. Buffalo himself carried two names, neither of which was particularly unique. Whites usually referred to him as Buffalo, Great Buffalo, or LaBoeuf, translations of his name Bizhiki. In Ojibwe, he is just as often recorded by the name Gichi-Weshkii. Weshkii, literally “new one,” was a name often given to firstborn sons in Ojibwe families. Gichi is a prefix meaning “big” or “great,” both of which could be used to describe Buffalo.

Nichols and Nyholm translate Bizhiki (Besheke, Peezhickee, Bezhike, etc.) as both “cow” and “buffalo.” Originally it meant “buffalo” in Ojibwe. As cattle became more common in Ojibwe country, the term expanded to include both animals to the point where the primary meaning of the word today is “cow” in some dialects. These dialects will use Mashkodebizhiki (Prairie Cow) to mean buffalo. However, this term is a more recent addition to the language and was not used by individuals named Buffalo in the mid- nineteenth century. (National Park Service photo)
One glance at the 1837 Treaty of St. Peters shows three Buffalos. Pe-zhe-kins (Bizhikiins) or “Young Buffalo” signed as a warrior from Leech Lake. “Pe-zhe-ke, or the Buffalo” was the first chief to sign from the St. Croix region. Finally, the familiar Buffalo is listed as the first name under those from La Pointe on Lake Superior. It is these two other Buffalos, from St. Croix and Leech Lake, whose faces grace several of the images supposedly showing Buffalo of La Pointe. All three of these men were chiefs, all three were Ojibwe, and all three represented their people in Washington D.C. Because they share a name, their histories have unfortunately been mashed together.
Who were these three men?

Treaty of St. Peters (1837) For more on Dagwagaane (Ta-qua-ga-na), check out the People Index.
The familiar Buffalo was born at La Pointe in the middle of the 18th century. He was a member of the Loon Clan, which had become a chiefly clan under the leadership of his grandfather Andeg-wiiyas (Crowʼs Meat). Although he was already elderly by the time the Lake Superior Ojibwe entered into their treaty relationship with the United States, his skills as an orator were such that by the Treaty of 1854, one year before his death, Buffalo was the most influential leader not only of La Pointe, but of the whole Lake Superior country.

Treaty of St. Peters (1837) For more on Gaa-bimabi (Ka-be-ma-be), check out the People Index.
William Warren, describes the St. Croix Buffalo as a member of the Bear Clan who originally came to the St. Croix from Sault Ste. Marie after committing a murder. He goes on to declare that this Buffaloʼs chieftainship came only as a reward from traders who appreciated his trapping skills. Warren does admit, however, that Buffaloʼs influence grew and surpassed that of the hereditary St. Croix leaders.

Treaty of St. Peters (1837) For more on Flat Mouth, check out the People Index.
The “Young Buffalo,” of the Pillager or Leech Lake Ojibwe of northern Minnesota was a war chief who also belonged to the Bear Clan and was considerably younger than the other two Buffalos (the La Pointe and St. Croix chiefs were about the same age). As Biizhikiins grew into his later adulthood, he was known simply as Bizhiki (Buffalo). His mark on history came largely after the La Pointe Buffaloʼs death, during the politics surrounding the various Ojibwe treaties in Minnesota and in the events surrounding the US-Dakota War of 1862.
The Picture Search
In the coming months, I will devote several posts to analyzing the reported images of Chief Buffalo that I am aware of. The first post on this site can be considered the first in the series. Keep checking back for more.
Sources:
KAPPLER’S INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES. Ed. Charles J. Kappler. Oklahoma State University Library, n.d. Web. 21 June 2012. <http:// digital.library.okstate.edu/Kappler/>.
Nichols, John, and Earl Nyholm. A Concise Dictionary of Minnesota Ojibwe. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota, 1995. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry R. Personal Memoirs of a Residence of Thirty Years with the Indian Tribes on the American Frontiers: With Brief Notices of Passing Events, Facts, and Opinions, A.D. 1812 to A.D. 1842. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo and, 1851. Print.
Treuer, Anton. The Assassination of Hole in the Day. St. Paul, MN: Borealis, 2010. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
No Princess Zone: Hanging Cloud, the Ogichidaakwe
May 12, 2013

This image of Aazhawigiizhigokwe (Hanging Cloud) was created 35 years after the battle depicted by Marr and Richards Engraving of Milwaukee for use in Benjamin Armstrong’s Early Life Among the Indians (Wikimedia Images).
Here is an interesting story I’ve run across a few times. Don’t consider this exhaustive research on the subject, but it’s something I thought was worth putting on here.
In late 1854 and 1855, the talk of northern Wisconsin was a young woman from from the Chippewa River around Rice Lake. Her name was Ah-shaw-way-gee-she-go-qua, which Morse (below) translates as “Hanging Cloud.” Her father was Nenaa’angebi (Beautifying Bird) a chief who the treaties record as part of the Lac Courte Oreilles band. His band’s territory, however, was further down the Chippewa from Lac Courte Oreilles, dangerously close to the territories of the Dakota Sioux. The Ojibwe and Dakota of that region had a long history of intermarriage, but the fallout from the Treaty of Prairie du Chien (1825) led to increased incidents of violence. This, along with increased population pressures combined with hunting territory lost to white settlement, led to an intensification of warfare between the two nations in the mid-18th century.
As you’ll see below, Hanging Cloud gained her fame in battle. She was an ogichidaakwe (warrior). Unfortunately, many sources refer to her as the “Chippewa Princess.” She was not a princess. Her father was not a king. She did not sit in a palace waited on hand and foot. Her marriageability was not her only contribution to her people. Leave the princesses in Europe. Hanging Cloud was an ogichidaakwe. She literally fought and killed to protect her people.
 Americans have had a bizarre obsession with the idea of Indian princesses since Pocahontas. Engraving of Pocahontas by Simon van de Passe (1616) Wikimedia Images
Americans have had a bizarre obsession with the idea of Indian princesses since Pocahontas. Engraving of Pocahontas by Simon van de Passe (1616) Wikimedia ImagesIn An Infinity of Nations, Michael Witgen devotes a chapter to America’s ongoing obsession with the concept of the “Indian Princess.” He traces the phenomenon from Pocahontas down to 21st-century white Americans claiming descent from mythical Cherokee princesses. He has some interesting thoughts about the idea being used to justify the European conquest and dispossession of Native peoples. I’m going to try to stick to history here and not get bogged down in theory, but am going to declare northern Wisconsin a “NO PRINCESS ZONE.”
Ozhaawashkodewekwe, Madeline Cadotte, and Hanging Cloud were remarkable women who played a pivotal role in history. They are not princesses, and to describe them as such does not add to their credit. It detracts from it.
Anyway, rant over, the first account of Hanging Cloud reproduced here comes from Dr. Richard E. Morse of Detroit. He observed the 1855 annuity payment at La Pointe. This was the first payment following the Treaty of 1854, and it was overseen directly by Indian Affairs Commissioner George Manypenny. Morse records speeches of many of the most prominent Lake Superior Ojibwe chiefs at the time, records the death of Chief Buffalo in September of that year, and otherwise offers his observations. These were published in 1857 as The Chippewas of Lake Superior in the third volume of the State Historical Society’s Wisconsin Historical Collections. This is most of pages 349 to 354:
“The “Princess”–AH-SHAW-WAY-GEE-SHE-GO-QUA–The Hanging Cloud.
The Chippewa Princess was very conspicuous at the payment. She attracted much notice; her history and character were subjects of general observation and comment, after the bands, to which she was, arrived at La Pointe, more so than any other female who attended the payment.
She was a chivalrous warrior, of tried courage and valor; the only female who was allowed to participate in the dancing circles, war ceremonies, or to march in rank and file, to wear the plumes of the braves. Her feats of fame were not long in being known after she arrived; most persons felt curious to look upon the renowned youthful maiden.
 Nenaa’angebi as depicted on the cover of Benjamin Armstrong’s Early Life Among the Indians (Wikimedia Images).
Nenaa’angebi as depicted on the cover of Benjamin Armstrong’s Early Life Among the Indians (Wikimedia Images).She is the daughter of Chief NA-NAW-ONG-GA-BE, whose speech, with comments upon himself and bands, we have already given. Of him, who is the gifted orator, the able chieftain, this maiden is the boast of her father, the pride of her tribe. She is about the usual height of females, slim and spare-built, between eighteen and twenty years of age. These people do not keep records, nor dates of their marriages, nor of the birth of their children.
This female is unmarried. No warrior nor brave need presume to win her heart or to gain her hand in marriage, who cannot prove credentials to superior courage and deeds of daring upon the war-path, as well as endurance in the chase. On foot she was conceded the fleetest of her race. Her complexion is rather dark, prominent nose, inclining to the Roman order, eyes rather large and very black, hair the color of coal and glossy, a countenance upon which smiles seemed strangers, an expression that indicated the ne plus ultra of craft and cunning, a face from which, sure enough, a portentous cloud seemed to be ever hanging–ominous of her name. We doubt not, that to plunge the dagger into the heart of an execrable Sioux, would be more grateful to her wish, more pleasing to her heart, than the taste of precious manna to her tongue…
…Inside the circle were the musicians and persons of distinction, not least of whom was our heroine, who sat upon a blanket spread upon the ground. She was plainly, though richly dressed in blue broad-cloth shawl and leggings. She wore the short skirt, a la Bloomer, and be it known that the females of all Indians we have seen, invariably wear the Bloomer skirt and pants. Their good sense, in this particular, at least, cannot, we think, be too highly commended. Two plumes, warrior feathers, were in her hair; these bore devices, stripes of various colored ribbon pasted on, as all braves have, to indicate the number of the enemy killed, and of scalps taken by the wearer. Her countenance betokened self-possession, and as she sat her fingers played furtively with the haft of a good sized knife.
The coterie leaving a large kettle hanging upon the cross-sticks over a fire, in which to cook a fat dog for a feast at the close of the ceremony, soon set off, in single file procession, to visit the camp of the respective chiefs, who remained at their lodges to receive these guests. In the march, our heroine was the third, two leading braves before her. No timid air and bearing were apparent upon the person of this wild-wood nymph; her step was proud and majestic, as that of a Forest Queen should be.
The party visited the various chiefs, each of whom, or his proxy, appeared and gave a harangue, the tenor of which, we learned, was to minister to their war spirit, to herald the glory of their tribe, and to exhort the practice of charity and good will to their poor. At the close of each speech, some donation to the beggar’s fun, blankets, provisions, &c., was made from the lodge of each visited chief. Some of the latter danced and sung around the ring, brandishing the war-club in the air and over his head. Chief “LOON’S FOOT,” whose lodge was near the Indian Agents residence, (the latter chief is the brother of Mrs. Judge ASHMAN at the Soo,) made a lengthy talk and gave freely…
…An evening’s interview, through an interpreter, with the chief, father of the Princess, disclosed that a small party of Sioux, at a time not far back, stole near unto the lodge of the the chief, who was lying upon his back inside, and fired a rifle at him; the ball grazed his nose near his eyes, the scar remaining to be seen–when the girl seizing the loaded rifle of her father, and with a few young braces near by, pursued the enemy; two were killed, the heroine shot one, and bore his scalp back to the lodge of NA-NAW-ONG-GA-BE, her father.
At this interview, we learned of a custom among the Chippewas, savoring of superstition, and which they say has ever been observed in their tribe. All the youths of either sex, before they can be considered men and women, are required to undergo a season of rigid fasting. If any fail to endure for four days without food or drink, they cannot be respected in the tribe, but if they can continue to fast through ten days it is sufficient, and all in any case required. They have then perfected their high position in life.
This Princess fasted ten days without a particle of food or drink; on the tenth day, feeble and nervous from fasting, she had a remarkable vision which she revealed to her friends. She dreamed that at a time not far distant, she accompanied a war party to the Sioux country, and the party would kill one of the enemy, and would bring home his scalp. The war party, as she had dreamed, was duly organized for the start.
Against the strongest remonstrance of her mother, father, and other friends, who protested against it, the young girl insisted upon going with the party; her highest ambition, her whole destiny, her life seemed to be at stake, to go and verify the prophecy of her dream. She did go with the war party. They were absent about ten or twelve days, the had crossed the Mississippi, and been into the Sioux territory. There had been no blood of the enemy to allay their thirst or to palliate their vengeance. They had taken no scalp to herald their triumphant return to their home. The party reached the great river homeward, were recrossing, when lo! they spied a single Sioux, in his bark canoe near by, whom they shot, and hastened exultingly to bear his scalp to their friends at the lodges from which they started. Thus was the prophecy of the prophetess realized to the letter, and herself, in the esteem of all the neighboring bands, elevated to the highest honor in all their ceremonies. They even hold her in superstitious reverence. She alone, of the females, is permitted in all festivities, to associate, mingle and to counsel with the bravest of the braves of her tribe…”
 Benjamin Armstrong
Benjamin ArmstrongBenjamin Armstrong’s memoir Early Life Among the Indians also includes an account of the warrior daughter of Nenaa’angebi. In contrast to Morse, the outside observer, Armstrong was married to Buffalo’s niece and was the old chief’s personal interpreter. He lived in this area for over fifty years and knew just about everyone. His memoir, published over 35 years after Hanging Cloud got her fame, contains details an outsider wouldn’t have any way of knowing.
Unfortunately, the details don’t line up very well. Most conspicuously, Armstrong says that Nenaa’angebi was killed in the attack that brought his daughter fame. If that’s true, then I don’t know how Morse was able to record the Rice Lake chief’s speeches the following summer. It’s possible these were separate incidents, but it is more likely that Armstrong’s memories were scrambled. He warns us as much in his introduction. Some historians refuse to use Armstrong at all because of discrepancies like this and because it contains a good deal of fiction. I have a hard time throwing out Armstrong completely because he really does have the insider’s knowledge that is lacking in so many primary sources about this area. I don’t look at him as a liar or fraud, but rather as a typical northwoodsman who knows how to run a line of B.S. when he needs to liven up a story. Take what you will of it, these are pages 199-202 of Early Life Among the Indians.
“While writing about chiefs and their character it may not be amiss to give the reader a short story of a chief‟s daughter in battle, where she proved as good a warrior as many of the sterner sex.
In the ’50’s there lived in the vicinity of Rice Lake, Wis. a band of Indians numbering about 200. They were headed by a chief named Na-nong-ga-bee. This chief, with about seventy of his people came to La Point to attend the treaty of 1854. After the treaty was concluded he started home with his people, the route being through heavy forests and the trail one which was little used. When they had reached a spot a few miles south of the Namekagon River and near a place called Beck-qua-ah-wong they were surprised by a band of Sioux who were on the warpath and then in ambush, where a few Chippewas were killed, including the old chief and his oldest son, the trail being a narrow one only one could pass at a time, true Indian file. This made their line quite long as they were not trying to keep bunched, not expecting or having any thought of being attacked by their life long enemy.
The chief, his son and daughter were in the lead and the old man and his son were the first to fall, as the Sioux had of course picked them out for slaughter and they were killed before they dropped their packs or were ready for war. The old chief had just brought the gun to his face to shoot when a ball struck him square in the forehead. As he fell, his daughter fell beside him and feigned death. At the firing Na-nong-ga-bee’s Band swung out of the trail to strike the flanks of the Sioux and get behind them to cut off their retreat, should they press forward or make a retreat, but that was not the Sioux intention. There was not a great number of them and their tactic was to surprise the band, get as many scalps as they could and get out of the way, knowing that it would be but the work of a few moments, when they would be encircled by the Chippewas. The girl lay motionless until she perceived that the Sioux would not come down on them en-masse, when she raised her father‟s loaded gun and killed a warrior who was running to get her father‟s scalp, thus knowing she had killed the slayer of her father, as no Indian would come for a scalp he had not earned himself. The Sioux were now on the retreat and their flank and rear were being threatened, the girl picked up her father‟s ammunition pouch, loaded the rifle, and started in pursuit. Stopping at the body of her dead Sioux she lifted the scalp and tucked it under her belt. She continued the chase with the men of her band, and it was two days before they returned to the women and children, whom they had left on the trail, and when the brave little heroine returned she had added two scalps to the one she started with.
She is now living, or was, but a few years ago, near Rice Lake, Wis., the wife of Edward Dingley, who served in the war of rebellion from the time of the first draft of soldiers to the end of the war. She became his wife in 1857, and lived with him until he went into the service, and at this time had one child, a boy. A short time after he went to the war news came that all the party that had left Bayfield at the time he did as substitutes had been killed in battle, and a year or so after, his wife, hearing nothing from him, and believing him dead, married again. At the end of the war Dingley came back and I saw him at Bayfield and told him everyone had supposed him dead and that his wife had married another man. He was very sorry to hear this news and said he would go and see her, and if she preferred the second man she could stay with him, but that he should take the boy. A few years ago I had occasion to stop over night with them. And had a long talk over the two marriages. She told me the circumstances that had let her to the second marriage. She thought Dingley dead, and her father and brother being dead, she had no one to look after her support, or otherwise she would not have done so. She related the related the pursuit of the Sioux at the time of her father‟s death with much tribal pride, and the satisfaction she felt at revenging herself upon the murder of her father and kinsmen. She gave me the particulars of getting the last two scalps that she secured in the eventful chase. The first she raised only a short distance from her place of starting; a warrior she espied skulking behind a tree presumably watching for some one other of her friends that was approaching. The other she did not get until the second day out when she discovered a Sioux crossing a river. She said: “The good luck that had followed me since I raised my father‟s rifle did not now desert me,” for her shot had proved a good one and she soon had his dripping scalp at her belt although she had to wade the river after it.”
At this point, this is all I have to offer on the story of Hanging Cloud the ogichidaakwe. I’ll be sure to update if I stumble across anything else, but for now, we’ll have to be content with these two contradictory stories.
Sources:
Armstrong, Benj G., and Thomas P. Wentworth. Early Life among the Indians: Reminiscences from the Life of Benj. G. Armstrong : Treaties of 1835, 1837, 1842 and 1854 : Habits and Customs of the Red Men of the Forest : Incidents, Biographical Sketches, Battles, &c. Ashland, WI: Press of A.W. Bowron, 1892. Print.
Morse, Richard F. “The Chippewas of Lake Superior.” Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin. Ed. Lyman C. Draper. Vol. 3. Madison: State Historical Society of Wisconsin, 1857. 338-69. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Witgen, Michael J. An Infinity of Nations: How the Native New World Shaped Early North America. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania, 2012. Print.
…a donation of twenty-four sections of land covering the graves of our fathers, our sugar orchards, and our rice lakes and rivers…
March 29, 2013

Symbolic Petition of Chippewa Chiefs: Original birch bark petition of Oshkaabewis copied by Seth Eastman and printed in “Historical and statistical information respecting the history, condition, and prospects of the Indian tribes of the United States” by Henry Rowe Schoolcraft (1851). Digitized by University of Wisconsin Libraries Wisconsin Electronic Reader project (1998).
For the first post on Chequamegon History, I thought I’d share my research into an image that has been circulating around the area for several years now. The image shows seven Ojibwe chiefs by their doodemag (clan symbols), connected by heart and mind to Lake Superior and to some smaller lakes. The clans shown are the Crane, Marten, Bear, Merman, and Bullhead.
All the interpretations I’ve heard agree that this image is a copy of a birch bark pictograph, and that it represents a unity among the several chiefs and their clans against Government efforts to remove the Lake Superior bands to Minnesota.
While there is this agreement on the why question of this petition’s creation, the who and when have been a source of confusion. Much of this confusion stems from efforts to connect this image to the famous La Pointe chief, Buffalo (Bizhiki/Gichi-weshkii).
In 2007, the Great Lakes Indian Fish and Wildlife Commission (GLIFWC) released the short documentary Mikwendaagoziwag: They Are Remembered. While otherwise a very good overview of the Lake Superior Ojibwe in this era, it incorrectly uses this image to describe Buffalo going to Washington D.C. in 1849. Buffalo is famous for a trip to Washington in 1852, but he was not part of the 1849 group.
At the time the GLIFWC film was released, the Wisconsin Historical Society website referred to this pictograph as, “Chief Buffaloʼs Petition to the President,” and identified the crane as Buffalo. Citing oral history from Lac Courte Oreilles, the Society dated the petition after the botched 1850-51 removal to Sandy Lake, Minnesota that resulted in hundreds of Ojibwe deaths from disease and starvation due to negligence, greed, and institutional racism on the part of government officials. The Historical Society has since revised its description to re-date the pictograph at 1848-49, but it still incorrectly lists Buffalo, a member of the Loon Clan, as being depicted by the crane. The Sandy Lake Tragedy, has deservedly gained coverage by historians in recent years, but the pictographic petition came earlier and was not part of it.
If the Historical Society had contacted Chief Buffaloʼs descendants in Red Cliff, they would have known that Buffalo was from the Loon Clan. The relationship between the Loons and the Cranes, as far as which clan can claim the hereditary chieftainship of the La Pointe Band, is very interesting and covered extensively in Warrenʼs History of the Ojibwe People. It would make a good subject for a future post.
After looking into the history of this image, I can confidently say that Buffalo is not one of the chiefs represented. It was created before Sandy Lake and Buffalo’s journey, but it is related to those events. Here is the story:
In late 1848, a group of Ojibwe chiefs went to Washington. They wanted to meet directly with President James K. Polk to ask for a permanent reservations in Wisconsin and Michigan. At that time the Ojibwe did not hold title to any part of the newly-created state of Wisconsin or Upper Michigan, having ceded these lands in the treaties in 1837 and 1842. In signing the treaties, they had received guarantees that they could stay in their traditional villages and hunt, fish, and gather throughout the ceded territory. However, by 1848, rumors were flying of removal of all Ojibwe to unceded lands on the Mississippi River in Minnesota Territory. These chiefs were trying to stop that from happening.
John Baptist Martell, a mix-blood, acted as their guide and interpreter. The government officials and Indian agents in the west were the ones actively promoting removal, so they did not grant permission (or travel money) for the trip. The chiefs had to pay their way as they went by putting themselves on display and dancing as they went from town to town.
Martell was accused by government officials of acting out of self interest, but the written petition presented to congress asked for, “a donation of twenty-four sections of land covering the graves of our fathers, our sugar orchards, and our rice lakes and rivers, at seven different places now occupied by us at villages…” The chiefs claimed to be acting on behalf of the chiefs of all the Lake Superior bands, and there is reason to believe them given that their request is precisely what Chief Buffalo and other leaders continued to ask for up until the Treaty of 1854.

This written petition accompanied the pictographic petitions. It clearly states the goal of the the chiefs was to secure permanent reservations around the traditional villages east of the Mississippi.
The visiting Ojibwes made a big impression on the nationʼs capital and positive accounts of the chiefs, their families, and their interpreter appeared in the magazines of the day. Congress granted them $6000 for their expenses, which according to their critics was a scheme by Martell. However, it is likely they were vilified by government officials for working outside the colonial structure and for trying to stop the removal rather than for any ill-intentions of the part of their interpreter. A full scholarly study of the 1848-49 trip remains to be done, however.

Amid articles on the end of the slave trade, the California Gold Rush, and the benefits of the “passing away of the Celt” during the Great Irish Famine, two articles appeared in Littell’s Living Age magazine about the 1849 delegation. The first is tragic, and the second is comical.
Along with written letters and petitions supporting the Ojibwe cause, the chiefs carried not only the one, but several birchbark pictographs. The pictographs show the clan animals of several chiefs and leading men from several small villages from the mouth of the Ontonagon River to Lac Vieux Desert in Upper Michigan and smaller satellite communities in Wisconsin. After seeing these petitions, the artist Seth Eastman copied them on paper and gave them to Henry Schoolcraft who printed and explained them alongside his criticism of the trip. They appear in his 1851 Historical and statistical information respecting the history, condition, and prospects of the Indian tribes of the United States.

Kenisteno, and his Band of Trout Lake, Wisconsin

Okundekund, and his Band of Ontonagon, Michigan (Upper) Kakake-ogwunaosh, and his Band of the head of Wisconsin River (Lower)
According to Schoolcraft, the crane in the most famous pictograph is Oshkaabewis, a Crane-clan chief from Lac Vieux Desert, and the leader of the 1848-49 expedition. In the Treaty of 1854, he is listed as a first chief from Lac du Flambeau in nearby Wisconsin. It makes sense that someone named Oshkaabewis would lead a delegation since the word oshkaabewis is used to describe someone who carries messages and pipes for a civil chief.

Kaizheosh [Gezhiiyaash], and his band from Lake Vieu Desert, Michigan and Wisconsin (University of Nebraska Libraries)
Long Story Short…
This is not Chief Buffalo or anyone from the La Pointe Band, and it was created before the Sandy Lake Tragedy. However it is totally appropriate to use the image in connection with those topics because it was all part of the efforts of the Lake Superior Ojibwe to resist removal in the late 1840s and early 1850s. However, when you do, please remember to credit the Lac Vieux Desert/Ontonagon chiefs who created these remarkable documents.













 The Old Mission Church, La Pointe, Madeline Island. (Wisconsin Historical Society Image ID: 24827)
The Old Mission Church, La Pointe, Madeline Island. (Wisconsin Historical Society Image ID: 24827) Harriet Wheeler, pictured about forty years after receiving this letter. (Wisconsin Historical Society: Image ID 36771)
Harriet Wheeler, pictured about forty years after receiving this letter. (Wisconsin Historical Society: Image ID 36771) Many Ojibwe leaders, including Hole in the Day, blamed the rotten pork and moldy flour distributed at Sandy Lake for the disease that broke out. The speech in St. Paul is covered on pages 101-109 of Theresa Schenck’s William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and Times of an Ojibwe Leader, my favorite book about this time period. (Photo from Whitney’s Gallery of St. Paul: Wisconsin Historical Society Image ID 27525)
Many Ojibwe leaders, including Hole in the Day, blamed the rotten pork and moldy flour distributed at Sandy Lake for the disease that broke out. The speech in St. Paul is covered on pages 101-109 of Theresa Schenck’s William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and Times of an Ojibwe Leader, my favorite book about this time period. (Photo from Whitney’s Gallery of St. Paul: Wisconsin Historical Society Image ID 27525) Mary Warren (1835-1925), was a teenager at the time of the Sandy Lake Tragedy. She is pictured here over seventy years later. Mary, the sister of William Warren, had been living with the Wheelers but stayed with Hall during their trip east. (Photo found on
Mary Warren (1835-1925), was a teenager at the time of the Sandy Lake Tragedy. She is pictured here over seventy years later. Mary, the sister of William Warren, had been living with the Wheelers but stayed with Hall during their trip east. (Photo found on 







