Indian Agency’s Instructions for the 1854 Treaty
September 26, 2020
Collected and edited by Amorin Mello
Indian Agency’s Instructions to
Henry C. Gilbert and David B. Herriman
for the 1854 Treaty at La Pointe
from Office of Indian Affairs federal archives
Department of the Interior
Office Indian Affairs
August 11, 1854
Gilbert, Henry C.
Indian Agent
Detroit, Michigan
Sir:
The Bill to provide for the Extinguishment of the title of the Chippewas to the lands owned and claimed by them in Wisconsin and Minnesota, which passed the House early in the Sessions, failed in the Senate.
In view however of the importance of extinguishing the Indian title to portions of the Chippewa Country, it is deemed proper to confide to you certain conditional instructions, to the end that if in your judgement it be practicable to conclude a treaty at the period when you assemble the Indians to pay them their annuities this fall, that object may be accomplished.
You will therefore consider yourself in conjunction with Major Herriman as the Officers of the Indian Department designated to make a treaty with the Chippewa Indians of Lake Superior and the Mississippi.
~ Indian Agent Gilbert’s Explanation after the 1854 Treaty
When you arrive at La Pointe, if you are satisfied that you can send a runner over to the Mississippi & have Major Herriman come over immediately, with the principal Chief and three or four of the Headmen of each of the bands who receive pay at the Agency, and who reside on or near the Mississippi, or between that stream & the Lake, you will do so. The design is that the principal Chief and Head Men to the number stated of all the bands, other than those to be paid by you, be present on the Occasion. The latter will of course be represented.
I am informed that that the Mississippi Indians can be brought over in the way I suggest, as soon as you can assemble yours. If you are satisfied of this fact you are authorized to send over the runner, but it is not my wish that any attempt be made, and a failure follow.
If delegates from all the bands can be assembled and negotiations had with them, you are authorized to offer the Chippewas the sum of $500,000 for all the country they now own or claim in the territory of Minnesota, the state of Wisconsin or elsewhere excepting and reserving for the future home of said Indians a quantity of land equal to 743,000 acres which may be selected in one body or in two or three locations, as the Indians may desire, and if the reservations be selected in more than one locality, the quantity of land fixed upon, as the Maximum amount of the reserve must be divided between the different locations of the Indians according to the population of the bands who may elect to inhabit such reservation or reservations. If the Indians could all be placed on one reserve, so that an Agent could always have a perfect Oversight over them it would be much better for their future interests; but if this cannot be effected, the several sub-reserves should be located in such proximity to each other, as to enable the Agent to exercise a watchful care over the Indians.
The future home or reserves should not be in the avenues by which the white population will approach the ceded country, or embrace any of the mineral lands which are now becoming desirable.
I send herewith a copy of the instructions of the Secretary of War of the date of 4th of June 1847, when a former Commission attempted to treat with these Indians, but failed. According to the Estimates of this Office, the Chippewas own about 10,743,000 Acres of land, the greater part of which is of no value to them, and never will be. Some portions of it will be valuable to the White population.
Nevertheless, the condition of Affairs with the Chippewas is such that it is the duty of the Government to Offer them an Opportunity to dispose of their tenure to their Country, and in lieu thereof, to give them a small tract as a permanent home, with such means of support & neutral & moral improvement, as may be of great advantage to them.
I transmit herewith a copy of the bill alluded to and also a copy of a recent treaty with the Ottoe & Missouri Indians, remarking that if a provision is inserted for allowing individual reservations within the general reservations that Eighty Acres to the family, as provided in the bill is deemed ample. These documents may be useful as affording you indications of the views of the Department and of such provisions as it may be desirable to have incorporated in a treaty.
In view of the fact that it is necessary to enter upon this business without permitting those adverse influences, which are always at work to thwart the purposes, and objects of the Government, in its efforts to treat with the Indians, you will not divulge the nature of your instructions, or indeed say any thing about them to any person.

Julius Austrian
~ Madeline Island Museum
When you get to La Point, if you conclude to send for Maj. Herriman, and the principal Men of his bands, you can do so, leaving the impression on those who may be privy to it, that their presence is necessary, in order that a better understanding may exist as to a proper disposition of the present annuities between the Lake bands and those on the Mississippi.
Mr. Austrian who resides at La Point, and who was here last winter, tendered his services to the Office in collecting Indians etc. etc. at any time, and he is recommended to me as a faithful man. He would perhaps be a faithful man to whom to confide the message to Major Herriman.
I have caused a remittance, to be made to you, by requisition of this date for the sum of $1900 as follows:
Provisions for Indians $1500
Presents for 100 $300
Contingencies $100
$1900
which will be applicable to this object, but to be used only in case negotiations are had with the Chippewas. Except so far as the provisions & expenses of a runner may be necessary.
As far as these amounts are expended, to be accounted for under the proper heads of account.

George Washington Manypenny
~ Commons.Wikimedia.org
Very Respect’y Your Ob’t Servant
Geo. W. Manypenny
Commissioner
N.B. I learn that a boat leaves the Sault of St Marie on the 21st instant for Lapoint. If so you should avail yourself of the opportunity to go forward. The enclosed communication to Maj Herriman, you will forward to him by the runner, if you determine to send one, and be satisfied that the expedition will be successful before you send it states the whole matter to Major H. From the instructions to the Commissioners of June 4th 1847, and the Ottoe & Missouri treaty, you will form an idea of the necessary stipulations for the payment of the purchase money, the amount of it that should be invested etc. and the necessary provisions for Stock, Agricultural Implements etc. etc. in place of money. A map showing the country of the Chippewas is also herewith.
Geo. W. Manypenny
Commissioner
Department of the Interior
Office Indian Affairs
August 12th, 1854
Gilbert, H. C.
Indian Agent
Detroit, Michigan
Sir:
Referring to my letter of instruction to you of the 11th instant, I have to remark that should you succeed in having the proposed negotiations with the Chippewas, and a treaty be made, you will provide to pay the $500,000 as follows:
One hundred thousand dollars to be invested at five percent interest, which interest shall be expended annually under the President’s direction for purposes of Education, and the moral improvement of the Indians. The residue to be paid say in twenty annual installments of twenty thousand dollars each without interest, or these deferred payments may be extended over twenty five or thirty years, all of them however to be subject to the President’s discretion, as in Article 4 of the Ottoe & Missouri treaty.
If necessary to accomplish the object, although $500,000 is deemed the value of the Chippewa tenure to the land, you may go as high as $600,000 payments as above.
Should a treaty be made, it is submitted whether the new locations reserved & to the Indians, may not be of such a character as to render some of the smiths, farmers etc. stipulated for under former treaties of no use, and if so, that provisions be inserted cancelling such of these provisions, under former treaties, as can be dispensed with, and providing that a sum equal to the amount, now paid annually for such, may be appropriated for the unexpired term of former treaty stipulations to be expended by the President, for the use of the Indians, as other funds are provided to be expended.
Very Respectfully
Your Ob’t Servant
Geo. W. Manypenny
Commissioner
Department of the Interior
Office Indian Affairs
August 14, 1854
Gilbert, H. C.
Indian Agent
Detroit, Michigan
Sir:
~ Indian Agent Gilbert’s Explanation after the 1854 Treaty
Referring to my letters of instruction of the 11th & 12th instant, both of which were prepared in great haste, I am inclined to the opinion that a state of things may exist that you might feel embarrassed at the suggestions that if the land reserved by the Indians was located in more than one tract the several sub-reserves should be in such close proximity as to enable the agent to have a constant oversight over all the Indians. It may however occur that there may be partialities and predilections among the different bands for different and widely separated districts, and that these partialities cannot be overcome. I am clearly of the opinion that all the land reserved should be in one body and every reasonable effort should be employed to impress the Indians with this view; and if it fail the fewest sub-reserves that can be got along with should be allowed and if possible they should be in the same region of Country; but if the Indians have the predilections alluded to, and they cannot be changed in their views, you will accede to their wishes to a reasonable extent in this particular. And if it should so happen that they select locations widely distant from each other so that it would be more for their interests that one portion might be under one Agent and another under another, it would be well perhaps to adjust all matters between the bands thus located, naming all of them by bands which select a reservation. Setting apart according to the population their portion of such reserved land, and providing to pay them by the same rule, their proportion of the purchase money at their reserve, and so with the bands on each of the reserves. And indeed a clause might be inserted, adjusting and dividing by population to the Indians of each reserve the annuities to become due under former treaties, whether of money or in kind so that no difficulties could hereafter arise provided one part should be in one agency and others in another.
Several members of the Indian Committee of the Senate having expressed a wish that a clause or article of the following import should be inserted in all treaties hereafter made. You will please put it in the treaty which I hope you may be able to enter into with the Chippewas. It is thus:
“The United States agree that an examination shall be made, and all sums that may be found equitably due to the Indians, for arrearages of annuity or other thing, under the provisions of former treaties, shall be paid as the chiefs may direct.”
And; It is agreed between the United States and the said Chippewa Indians, that should it at any time hereafter be considered necessary, and for the benefit of said Indians, it shall be discretionary with the President by & with the advise and consent of the Senate to change the annuities herein provided for or any part thereof into a fund establishing farms among and for them.
Very Respectfully
Your Ob’t Servant
Geo. W. Manypenny
Commissioner
Early Life among the Indians: Chapter II
March 21, 2018
By Amorin Mello

Early life among the Indians
by Benjamin Green Armstrong
continued from Chapter I.
CHAPTER II
In Washington.—Told to Go Home.—Senator Briggs, of New York.—The Interviews with President Fillmore.—Reversal of the Removal Order.—The Trip Home.—Treaty of 1854 and the Reservations.—The Mile Square.—The Blinding. »
After a fey days more in New York City I had raised the necessary funds to redeem the trinkets pledged with the ‘bus driver and to pay my hotel bills, etc., and on the 22d day of June, 1852, we had the good fortune to arrive in Washington.

“Washington Delegation, June 22, 1852“
Engraved from an unknown photograph by Marr and Richards Co. for Benjamin Armstrong’s Early Life Among the Indians. Chief Buffalo, his speaker Oshogay, Vincent Roy, Jr., two other La Pointe Band members, and Armstrong are assumed to be in this engraving.
I took my party to the Metropolitan Hotel and engaged a room on the first floor near the office for the Indians, as they said they did not like to get up to high in a white man’s house. As they required but a couple mattresses for their lodgings they were soon made comfortable. I requested the steward to serve their meals in their room, as I did not wish to take them into the dining room among distinguished people, and their meals were thus served.

Undated postcard of the Metropolitan Hotel, formerly known as Brown’s India Queen Hotel.
~ StreetsOfWashington.com
The morning following our arrival I set out in search of the Interior Department of the Government to find the Commissioner of Indian Affairs, to request an interview with him, which he declined to grant and said :
“I want you to take your Indians away on the next train west, as they have come here without permission, and I do not want to see you or hear of your Indians again.”
I undertook to make explanations, but he would not listen to me and ordered me from his office. I went to the sidewalk completely discouraged, for my present means was insufficient to take them home. I paced up and down the sidewalk pondering over what was best to do, when a gentleman came along and of him I inquired the way to the office of the Secretary of the Interior. He passed right along saying,

Secretary of the Interior
Alexander Hugh Holmes Stuart
~ Department of the Interior
“This way, sir; this way, sir;” and I followed him.
He entered a side door just back of the Indian Commissioner’s office and up a short flight of stairs, and going in behind a railing, divested himself of hat and cane, and said :
“What can I do for you sir.”
I told him who I was, what my party consisted of, where we came from and the object of our visit, as briefly as possible. He replied that I must go and see the Commissioner of Indian Affairs just down stairs. I told him I had been there and the treatment I had received at his hands, then he said :
“Did you have permission to come, and why did you not go to your agent in the west for permission?”
I then attempted to explain that we had been to the agent, but could get no satisfaction; but he stopped me in the middle of my explanation, saying :
“I can do nothing for you. You must go to the Indian Commissioner,”
and turning, began a conversation with his clerk who was there when we went in.
I walked out more discouraged than ever and could not imagine what next I could do. I wandered around the city and to the Capitol, thinking I might find some one I had seen before, but in this I failed and returned to the hotel, where, in the office I found Buffalo surrounded by a crowd who were trying to make him understand them and among them was the steward of the house. On my entering the office and Buffalo recognizing me, the assemblage, seeing I knew him, turned their attention to me, asking who he was, etc., to all of which questions I answered as briefly as possible, by stating that he was the head chief of of the Chippewas of the Northwest. The steward then asked:
“Why don’t you take him into the dining room with you? Certainly such a distinguished man as he, the head of the Chippewa people, should have at least that privilege.”

United States Representative George Briggs
~ Library of Congress
I did so and as we passed into the dining room we were shown to a table in one corner of the room which was unoccupied. We had only been seated a few moments when a couple of gentlemen who had been occupying seats in another part of the dining room came over and sat at our table and said that if there were no objections they would like to talk with us. They asked about the party, where from, the object of the visit, etc. I answered them briefly, supposing them to be reporters and I did not care to give them too much information. One of these gentlemen asked what room we had, saying that himself and one or two others would like to call on us right after dinner. I directed them where to come and said I would be there to meet them.
About 2 o’clock they came, and then for the first time I knew who those gentlemen were. One was Senator Briggs, of New York, and the others were members of President Filmore’s cabinet, and after I had told them more fully what had taken me there, and the difficulties I had met with, and they had consulted a little while aside. Senator Briggs said :
“We will undertake to get you and your people an interview with the President, and will notify you here when a meeting can be arranged. ”
During the afternoon I was notified that an interview had been arranged for the next afternoon at 3 o’clock. During the evening Senator Briggs and other friends called, and the whole matter was talked over and preparations made for the interview the following day, which were continued the next day until the hour set for the interview.

United States President
Millard Fillmore.
~ Library of Congress
When we were assembled Buffalo’s first request was that all be seated, as he had the pipe of peace to present, and hoped that all who were present would partake of smoke from the peace pipe. The pipe, a new one brought for the purpose, was filled and lighted by Buffalo and passed to the President who took two or three draughts from it, and smiling said, “Who is the next?” at which Buffalo pointed out Senator Briggs and desired he should be the next. The Senator smoked and the pipe was passed to me and others, including the Commissioner of Indian Affairs, Secretary of the Interior and several others whose names I did not learn or cannot recall. From them, to Buffalo, then to O-sho-ga, and from him to the four braves in turn, which completed that part of the ceremony. The pipe was then taken from the stem and handed to me for safe keeping, never to be used again on any occasion. I have the pipe still in my possession and the instructions of Buffalo have been faithfully kept. The old chief now rose from his seat, the balance following his example and marched in single file to the President and the general hand-shaking that was began with the President was continued by the Indians with all those present. This over Buffalo said his under chief, O-sha-ga, would state the object of our visit and he hoped the great father would give them some guarantee that would quiet the excitement in his country and keep his young men peaceable. After I had this speech thoroughly interpreted, O-sha-ga began and spoke for nearly an hour. He began with the treaty of 1837 and showed plainly what the Indians understood the treaty to be. He next took up the treaty of 1842 and said he did not understand that in either treaty they had ceded away the land and he further understood in both cases that the Indians were never to be asked to remove from the lands included in those treaties, provided they were peaceable and behaved themselves and this they had done. When the order to move came Chief Buffalo sent runners out in all directions to seek for reasons and causes for the order, but all those men returned without finding a single reason among all the Superior and Mississippi Indians why the great father had become displeased. When O-sha-ga had finished his speech I presented the petition I had brought and quickly discovered that the President did recognize some names upon it, which gave me new courage. When the reading and examination of it had been concluded the meeting was adjourned, the President directing the Indian Commissioner to say to the landlord at the hotel that our hotel bills would be paid by the government. He also directed that we were to have the freedom of the city for a week.

Read Biographical Sketch of Vincent Roy, Jr. manuscript for a different perspective on their meeting the President.
The second day following this Senator Briggs informed me that the President desired another interview that day, in accordance with which request we went to the White House soon after dinner and meeting the President, he told the, delegation in a brief speech that he would countermand the removal order and that the annuity payments would be made at La Pointe as before and hoped that in the future there would be no further cause for complaint. At this he handed to Buffalo a written instrument which he said would explain to his people when interpreted the promises he had made as to the removal order and payment of annuities at La Pointe and hoped when he had returned home he would call his chiefs together and have all the statements therein contained explained fully to them as the words of their great father at Washington.
The reader can imagine the great load that was then removed from my shoulders for it was a pleasing termination of the long and tedious struggle I had made in behalf of the untutored but trustworthy savage.
On June 28th, 1852, we started on our return trip, going by cars to La Crosse, Wis., thence by steamboat to St. Paul, thence by Indian trail across the country to Lake Superior. On our way from St. Paul we frequently met bands of Indians of the Chippewa tribe to whom we explained our mission and its results, which caused great rejoicing, and before leaving these bands Buffalo would tell their chief to send a delegation, at the expiration of two moons, to meet him in grand council at La Pointe, for there was many things he wanted to say to them about what he had seen and the nice manner in which he had been received and treated by the great father.
At the time appointed by Buffalo for the grand council at La Pointe, the delegates assembled and the message given Buffalo by President Filmore was interpreted, which gave the Indians great satisfaction. Before the grand council adjourned word was received that their annuities would be given to them at La Pointe about the middle of October, thus giving them time to get together to receive them. A number of messengers was immediately sent out to all parts of the territory to notify them and by the time the goods arrived, which was about October 15th, the remainder of the Indians had congregated at La Pointe. On that date the Indians were enrolled and the annuities paid and the most perfect satisfaction was apparent among all concerned. The jubilee that was held to express their gratitude to the delegation that had secured a countermanding order in the removal matter was almost extravagantly profuse. The letter of the great father was explained to them all during the progress of the annuity payments and Chief Buffalo explained to the convention what he had seen; how the pipe of peace had been smoked in the great father’s wigwam and as that pipe was the only emblem and reminder of their duties yet to come in keeping peace with his white children, he requested that the pipe be retained by me. He then went on and said that there was yet one more treaty to be made with the great father and he hoped in making it they would be more careful and wise than they had heretofore been and reserve a part of their land for themselves and their children. It was here that he told his people that he had selected and adopted, me as his son and that I would hereafter look to treaty matters and see that in the next treaty they did not sell them selves out and become homeless ; that as he was getting old and must soon leave his entire cares to others, he hoped they would listen to me as his confidence in his adopted son was great and that when treaties were presented for them to sign they would listen to me and follow my advice, assuring them that in doing so they would not again be deceived.

Map of Lake Superior Chippewa territories ceded in 1836, 1837, 1842, and 1854.
~ Great Lakes Indian Fish & Wildlife Commission
After this gathering of the Indians there was not much of interest in the Indian country that I can recall until the next annual payment in 1853. This payment was made at La Pointe and the Indians had been notified that commissioners would be appointed to make another treaty with them for the remainder of their territory. This was the territory lying in Minnesota west of Lake Superior; also east and west of the Mississippi river north to the territory belonging to the Boisfort and Pillager tribe, who are a part of the Chippewa nation, but through some arrangement between themselves, were detached from the main or more numerous body. It was at this payment that the Chippewa Indians proper desired to have one dollar each taken from their annuities to recompense me for the trouble and expense I had been to on the trip to Washington in their behalf, but I refused to accept it by reason of their very impecunious condition.
It was sometime in August, 1854, before the commissioners arrived at LaPointe to make the treaty and pay the annuities of that year. Messengers were despatched to notify all Indians of the fact that the great father had sent for them to come to La Pointe to get their money and clothing and to meet the government commissioners who wished to make another treaty with them for the territory lying west of Lake Superior and they were further instructed to have the Indians council among themselves before starting that those who came could be able to tell the wishes of any that might remain away in regards to a further treaty and disposition of their lands. Representatives came from all parts of the Chippewa country and showed a willingness to treat away the balance of their country. Henry C. Gilbert, the Indian agent at La Pointe, formerly of Ohio, and David B. Herriman, the agent for the Chippewas of the Mississippi country, were the commissioners appointed by the government to consumate this treaty.
While we were waiting the arrival of the interior Indians I had frequent talks with the commissioners and learned what their instructions were and about what they intended to offer for the lands which information I would communicate to Chief Buffalo and other head men in our immediate vicinity, and ample time was had to perfect our plans before the others should arrive, and when they did put in an appearance we were ready to submit to them our views for approval or rejection. Knowing as I did the Indians’ unwillingness to give up and forsake their old burying grounds I would not agree to any proposition that would take away the remainder of their lands without a reserve sufficient to afford them homes for themselves and posterity, and as fast as they arrived I counselled with them upon this subject and to ascertain where they preferred these reserves to be located. The scheme being a new one to them it required time and much talk to get the matter before them in its proper light. Finally it was agreed by all before the meeting of the council that no one would sign a treaty that did not give them reservations at different points of the country that would suit their convenience, that should afterwards be considered their bona-fide home. Maps were drawn of the different tracts that had been selected by the various chiefs for their reserve and permanent home. The reservations were as follows :
One at L’Anse Bay, one at Ontonagon, one at Lac Flambeau, one at Court O’Rilles, one at Bad River, one at Red Cliff or Buffalo Bay, one at Fond du Lac, Minn., and one at Grand Portage, Minn.

Joseph Stoddard (photo c.1941) worked on the 1854 survey of the Bad River Reservation exterior boundaries, and shared a different perspective about these surveys.
~ Bad River Tribal Historic Preservation Office
The boundaries were to be as near as possible by metes and bounds or waterways and courses. This was all agreed to by the Lake Superior Indians before the Mississippi Chippewas arrived and was to be brought up in the general council after they had come in, but when they arrived they were accompanied by the American Fur Company and most of their employees, and we found it impossible to get them to agree to any of our plans or to come to any terms. A proposition was made by Buffalo when all were gathered in council by themselves that as they could not agree as they were, a division should be drawn, dividing the Mississippi and the Lake Superior Indians from each other altogether and each make their own treaty After several days of counselling the proposition was agreed to, and thus the Lake Superiors were left to make their treaty for the lands mouth of Lake Superior to the Mississippi and the Mississippis to make their treaty for the lands west of the Mississippi. The council lasted several days, as I have stated, which was owing to the opposition of the American Fur Company, who were evidently opposed to having any such division made ; they yielded however, but only when they saw further opposition would not avail and the proposition of Buffalo became an Indian law. Our side was now ready to treat with the commissioners in open council. Buffalo, myself and several chiefs called upon them and briefly stated our case but were informed that they had no instructions to make any such treaty with us and were only instructed to buy such territory as the Lake Superiors and Mississippis then owned. Then we told them of the division the Indians had agreed upon and that we would make our own treaty, and after several days they agreed to set us off the reservations as previously asked for and to guarantee that all lands embraced within those boundaries should belong to the Indians and that they would pay them a nominal sum for the remainder of their possessions on the north shores. It was further agreed that the Lake Superior Indians should have two- thirds of all money appropriated for the Chippewas and the Mississippi contingent the other third. The Lake Superior Indians did not seem, through all these councils, to care so much for future annuities either in money or goods as they did for securing a home for themselves and their posterity that should be a permanent one. They also reserved a tract of land embracing about 100 acres lying across and along the Eastern end of La Pointe or Madeline Island so that they would not be cut off from the fishing privilege.
It was about in the midst of the councils leading up to the treaty of 1854 that Buffalo stated to his chiefs that I had rendered them services in the past that should be rewarded by something more substantial than their thanks and good wishes, and that at different times the Indians had agreed to reward me from their annuity money but I had always refused such offers as it would be taking from their necessities and as they had had no annuity money for the two years prior to 1852 they could not well afford to pay me in this way.
“And now,” continued Buffalo, “I have a proposition to make to you. As he has provided us and our children with homes by getting these reservations set off for us, and as we are about to part with all the lands we possess, I have it in my power, with your consent, to provide him with a future home by giving him a piece of ground which we are about to part with. He has agreed to accept this as it will take nothing from us and makes no difference with the great father whether we reserve a small tract of our territory or not, and if you agree I will proceed with him to the head of the lake and there select the piece of ground I desire him to have, that it may appear on paper when the treaty has been completed.”
The chiefs were unanimous in their acceptance of the proposition and told Buffalo to select a large piece that his children might also have a home in future as has been provided for ours.

Kiskitawag (Giishkitawag: “Cut Ear”) signed earlier treaties as a warrior of the Ontonagon Band and became associated with the La Pointe Band at Odanah.
~C.M. Bell, Smithsonian Digital Collections
This council lasted all night and just at break of day the old chief and myself, with four braves to row the boat, set out for the head of Lake Superior and did not stop anywhere only long enough to make and drink some tea, until we reached the head of St. Louis Bay. We landed our canoe by the side of a flat rock quite a distance from the shore, among grass and rushes. Here we ate our lunch and when completed Buffalo and myself, with another chief, Kish-ki-to-uk, waded ashore and ascended the bank to a small level plateau where we could get a better view of the bay. Here Buffalo turned to me, saying: .
“Are you satisfied with this location? I want to reserve the shore of this bay from the mouth of St. Louis river. How far that way do you you want it to go?” pointing southeast, or along the south shore of the lake.
I told him we had better not try to make it too large for if we did the great father’s officers at Washington might throw it out of the treaty and said:
“I will be satisfied with one mile square, and let it start from the rock which we have christened Buffalo rock, running easterly in the direction of Minnesota Point, taking in a mile square immediately northerly from the head of St. Louis Bay”
As there was no other way of describing it than by metes and bounds we tried to so describe it in the treaty, but Agent Gilbert, whether by mistake or not I am unable to say, described it differently. He described it as follows: “Starting from a rock immediately above and adjoining Minnesota Point, etc.”
We spent an hour or two here in looking over the plateau then went back to our canoe and set out for La Pointe. We traveled night and day until we reached home.
During our absence some of the chiefs had been talking more or less with the commissioners and immediately on our return all the Indians met in a grand council when Buffalo explained to them what he had done on the trip and how and where he had selected the piece of land that I was to have reserved in the treaty for my future home and in payment for the services I had rendered them in the past. The balance of the night was spent in preparing ourselves for the meeting with the treaty makers the next day, and about 10 o’clock next morning we were in attendance before the commissioners all prepared for a big council.
Agent Gilbert started the business by beginning a speech interpreted by the government interpreter, when Buffalo interrupted him by saying that he did not want anything interpreted to them from the English language by any one except his adoped son for there had always been things told to the Indians in the past that proved afterwards to be untrue, whether wrongly interpreted or not, he could not say;
“and as we now feel that my adopted son interprets to us just what you say, and we can get it correctly, we wish to hear your words repeated by him, and when we talk to you our words can be interpreted by your own interpreter, and in this way one interpreter can watch the other and correct each other should there be mistakes. We do not want to be deceived any more as we have in the past. We now understand that we are selling our lands as well as the timber and that the whole, with the exception of what we shall reserve, goes to the great father forever.”
Commissioner of Indian affairs. Col. Manypenny, then said to Buffalo:
“What you have said meets my own views exactly and I will now appoint your adopted son your interpreter and John Johnson, of Sault Ste. Marie, shall be the interpreter on the part of the government,” then turning to the commissioners said, “how does that suit you, gentlemen.”
They at once gave their consent and the council proceeded.
Buffalo informed the commissioners of what he had done in regard to selecting a tract of land for me and insisted that it become a part of the treaty and that it should be patented to me directly by the government without any restrictions. Many other questions were debated at this session but no definite agreements were reached and the council was adjourned in the middle of the afternoon. Chief Buffalo asking for the adjournment that he might talk over some matters further with his people, and that night the subject of providing homes for their half-breed relations who lived in different parts of the country was brought up and discussed and all were in favor of making such a provision in the treaty. I proposed to them that as we had made provisions for ourselves and children it would be only fair that an arrangement should be made in the treaty whereby the government should provide for our mixed blood relations by giving to each person the head of a family or to each single person twenty-one years of age a piece of land containing at least eighty acres which would provide homes for those now living and in the future there would be ample room on the reservations for their children, where all could live happily together. We also asked that all teachers and traders in the ceded territory who at that time were located there by license and doing business by authority of law, should each be entitled to 160 acres of land at $1.25 per acre. This was all reduced to writing and when the council met next morning we were prepared to submit all our plans and requests to the commissioners save one, which we required more time to consider. Most of this day was consumed in speech-making by the chiefs and commissioners and in the last speech of the day, which was made by Mr. Gilbert, he said:
“We have talked a great deal and evidently understand one another. You have told us what you want, and now we want time to consider your requests, while you want time as you say to consider another matter, and so we will adjourn until tomorrow and we, with your father. Col. Manypenny, will carefully examine and consider your propositions and when we meet to-morrow we will be prepared to answer you with an approval or rejection.”

Julius Austrian purchased the village of La Pointe and other interests from the American Fur Company in 1853. He entered his Town Plan of La Pointe on August 29th of 1854. He was the highest paid claimant of the 1854 Treaty at La Pointe. His family hosted the 1855 Annuity Payments at La Pointe.
~ Photograph of Austrian from the Madeline Island Museum
That evening the chiefs considered the other matter, which was to provide for the payment of the debts of the Indians owing the American Fur Company and other traders and agreed that the entire debt could not be more than $90,000 and that that amount should be taken from the Indians in bulk and divided up among their creditors in a pro-rata manner according to the amount due to any person or firm, and that this should wipe out their indebtedness. The American Fur Company had filed claims which, in the aggregate, amounted to two or three times this sum and were at the council heavily armed for the purpose of enforcing their claim by intimidation. This and the next day were spent in speeches pro and con but nothing was effected toward a final settlement.
Col. Manypenny came to my store and we had a long private interview relating to the treaty then under consideration and he thought that the demands of the Indians were reasonable and just and that they would be accepted by the commissioners. He also gave me considerable credit for the manner in which I had conducted the matter for Indians, considering the terrible opposition I had to contend with. He said he had claims in his possession which had been filed by the traders that amounted to a large sum but did not state the amount. As he saw the Indians had every confidence in me and their demands were reasonable he could see no reason why the treaty could not be speedily brought to a close. He then asked if I kept a set of books. I told him I only kept a day book or blotter showing the amount each Indian owed me. I got the books and told him to take them along with him and that he or his interpreter might question any Indian whose name appeared thereon as being indebted to me and I would accept whatever that Indian said he owed me whether it be one dollar or ten cents. He said he would be pleased to take the books along and I wrapped them up and went with him to his office, where I left them. He said he was certain that some traders were making claims for far more than was due them. Messrs. Gilbert and Herriman and their chief clerk, Mr. Smith, were present when Mr. Manypenny related the talk he had with me at the store. He considered the requests of the Indians fair and just, he said, and he hoped there would be no further delays in concluding the treaty and if it was drawn up and signed with the stipulations and agreements that were now understood should be incorporated in it, he would strongly recommend its ratification by the President and senate.

Naagaanab of Fond Du Lac
~ Minnesota Historical Society
The day following the council was opened by a speech from Chief Na-gon-ab in which he cited considerable history.
“My friends,” he said, “I have been chosen by our chief, Buffalo, to speak to you. Our wishes are now on paper before you. Before this it was not so. We have been many times deceived. We had no one to look out for us. The great father’s officers made marks on paper with black liquor and quill. The Indian can not do this. We depend upon our memory. We have nothing else to look to. We talk often together and keep your words clear in our minds. When you talk we all listen, then we talk it over many times. In this way it is always fresh with us. This is the way we must keep our record. In 1837 we were asked to sell our timber and minerals. In 1842 we were asked to do the same. Our white brothers told us the great father did not want the land. We should keep it to hunt on. Bye and bye we were told to go away; to go and leave our friends that were buried yesterday. Then we asked each other what it meant. Does the great father tell the truth? Does he keep his promises? We cannot help ourselves! We try to do as we agree in treaty. We ask you what this means? You do not tell from memory! You go to your black marks and say this is what those men put down; this is what they said when they made the treaty. The men we talk with don’t come back; they do not come and you tell us they did not tell us so! We ask you where they are? You say you do not know or that they are dead and gone. This is what they told you; this is what they done. Now we have a friend who can make black marks on paper When the council is over he will tell us what we have done. We know now what we are doing! If we get what we ask our chiefs will touch the pen, but if not we will not touch it. I am told by our chief to tell you this: We will not touch the pen unless our friend says the paper is all right.”
Na-gon-ab was answered by Commissioner Gilbert, saying:
“You have submitted through your friend and interpreter the terms and conditions upon which you will cede away your lands. We have not had time to give them all consideration and want a little more time as we did not know last night what your last proposition would be. Your father. Col. Manypenny, has ordered some beef cattle killed and a supply of provisions will be issued to you right away. You can now return to your lodges and get a good dinner and talk matters over among yourselves the remainder of the day and I hope you will come back tomorrow feeling good natured and happy, for your father, Col. Manypenny, will have something to say to you and will have a paper which your friend can read and explain to you.”
When the council met next day in front of the commissioners’ office to hear what Col. Manypenny had to say a general good feeling prevailed and a hand-shaking all round preceded the council, which Col. Manypenny opened by saying:
“My friends and children: I am glad to see you all this morning looking good natured and happy and as if you could sit here and listen to what I have to say. We have a paper here for your friend to examine to see if it meets your approval. Myself and the commissioners which your great father has sent here have duly considered all your requests and have concluded to accept them. As the season is passing away and we are all anxious to go to our families and you to your homes, I hope when you read this treaty you will find it as you expect to and according to the understandings we have had during the council. Now your friend may examine the paper and while he is doing so we will take a recess until afternoon.”
Chief Buffalo, turning to me, said:
“My son, we, the chiefs of all the country, have placed this matter entirely in your hands. Go and examine the paper and if it suits you it will suit us.”
Then turning to the chiefs, he asked,
“what do you all say to that?”
The ho-ho that followed showed the entire circle were satisfied.
I went carefully through the treaty as it had been prepared and with a few exceptions found it was right. I called the attention of the commissioners to certain parts of the stipulations that were incorrect and they directed the clerk to make the changes.
The following day the Indians told the commissioners that as their friend had made objections to the treaty as it was they requested that I might again examine it before proceeding further with the council. On this examination I found that changes had been made but on sheets of paper not attached to the body of the instrument, and as these sheets contained some of the most important items in the treaty, I again objected and told the commissioners that I would not allow the Indians to sign it in that shape and not until the whole treaty was re-written and the detached portions appeared in their proper places. I walked out and told the Indians that the treaty was not yet ready to sign and they gave up all further endeavors until next day. I met the commissioners alone in their office that afternoon and explained the objectionable points in the treaty and told them the Indians were already to sign as soon as those objections were removed. They were soon at work putting the instrument in shape.

“One version of the boundaries for Chief Buffalo’s reservation is shown at the base of Minnesota Point in a detail from an 1857 map preserved in the National Archives in Washington, D.C. Other maps show a larger and more irregularly shaped versions of the reservation boundary, though centered on the same area.”
~ DuluthStories.net
The next day when the Indians assembled they were told by the commissioners that all was ready and the treaty was laid upon a table and I found it just as the Indians had wanted it to be, except the description of the mile square. The part relating to the mile square that was to have been reserved for me read as follows:
“Chief Buffalo, being desirous of providing for some of his relatives who had rendered them important services, it is agreed that he may select one mile square of the ceded territory heretofore described.”
“Now,” said the commissioner,
“we want Buffalo to designate the person or persons to whom he wishes the patents to issue.”
Buffalo then said:
“I want them to be made out in the name of my adopted son.”
This closed all ceremony and the treaty was duly signed on the 30th day of September, 1854. This done the commissioners took a farewell shake of the hand with all the chiefs, hoping to meet them again at the annuity payment the coming year. They then boarded the steamer North Star for home. In the course of a few days the Indians also disappeared, some to their interior homes and some to their winter hunting grounds and a general quiet prevailed on the island.

Portrait of the Steamer North Star from American Steam Vessels, by Samuel Ward Stanton, page 40.
~ Wikimedia.org
About the second week in October, 1854, I went from La Pointe to Ontonagon in an open boat for the purpose of purchasing my winter supplies as it had got too late to depend on getting them from further below. While there a company was formed for the purpose of going into the newly ceded territory to make claims upon lands that would be subject to entry as soon as the late treaty should be ratified. The company consisted of Samuel McWaid, William Whitesides, W. W. Kingsbury, John Johnson, Oliver Melzer, John McFarland, Daniel S. Cash, W. W. Spaulding, all of Ontonagon, and myself. The two last named gentlemen, Daniel S. Cash and W. W. Spaulding, agreeing to furnish the company with supplies and all necessaries, including money, to enter the lands for an equal interest and it was so stipulated that we were to share equally in all that we, or either of us, might obtain. As soon as the supplies could be purchased and put aboard the schooner Algonquin we started for the head of the lake, stopping at La Pointe long enough for me to get my family aboard and my business matters arranged for the winter. I left my store at La Pointe in charge of Alex. Nevaux, and we all sailed for the head of Lake Superior, the site of which is now the city of Duluth. Reaching there about the first week in December—the bay of Superior being closed by ice—we were compelled to make our landing at Minnesota Point and take our goods from there to the main land on the north’ shore in open boats, landing about one and-one half miles east of Minnesota Point at a place where I desired to make a preemption for myself and to establish a trading post for the winter. Here I erected a building large enough for all of us to live in, as we expected to make this our headquarters for the winter, and also a building for a trading post. The other members of the company made claims in other places, but I did no more land looking that winter.

Detail of Superior City townsite at the head of Lake Superior from the 1854 U.S. General Land Office survey by Stuntz and Barber.
About January 20th, 1855, I left my place at the head of the lake to go back to La Pointe and took with me what furs I had collected up to that time, as I had a good place at La Pointe to dry and keep them. I took four men along to help me through and two dog trains. As we were passing down Superior Bay and when just in front of the village of West Superior a man came to us on the ice carrying a small bundle on his back and asked me if I had any objections to his going through in my company. He said the snow was deep and the weather cold and it was bad for one man to travel alone. I told him I had no objections provided he would take his turn with the other men in breaking the road for the dogs. We all went on together and camped that night at a place well known as Flag River. We made preparations for a cold night as the thermometer must have been twenty-five or thirty degrees below zero and the snow fully two feet deep. As there were enough of us we cut and carried up a large quantity of wood, both green and dry, and shoveled the snow away to the ground with our snow shoes and built a large fire. We then cut evergreen boughs and made a wind break or bough camp and concluded we could put in a very comfortable night. We then cooked and ate our supper and all seemed happy. I unrolled a bale of bear skins and spread them out on the ground for my bed, filled my pipe and lay down to rest while the five men with me were talking and smoking around the camp fire. I was very tired and presume I was not long in falling asleep. How long I slept I cannot tell, but was awakened by something dropping into my face, which felt like a powdered substance. I sprang to my feet for I found something had got into my eyes and was smarting them badly. I rushed for the snow bank that was melting from the heat and applied handful after handful to my eyes and face. I found the application was peeling the skin off my face and the pain soon became intense. I woke up the crew and they saw by the firelight the terrible condition I was in. In an hour’s time my eyeballs were so swollen that I could not close the lids and the pain did not abate. I could do nothing more than bathe my eyes until morning, which I did with tea-grounds. It seemed an age before morning came and when it did come I could not realize it, for I was totally blind. The party started with me at early dawn for La Pointe. The man who joined us the day before went no further, but returned to Superior, which was a great surprise to the men of our party, who frequently during the day would say:
“There is something about this matter that is not right,”
and I never could learn afterward of his having communicated the fact of my accident to any one or to assign any reason or excuse for turning back, which caused us to suspect that he had a hand in the blinding, but as I could get no proof to establish that suspicion, I could do nothing in the matter. This man was found dead in his cabin a few months afterwards.
At La Pointe I got such treatment as could be procured from the Indians which allayed the inflamation but did not restore the sight. I remained at La Pointe about ten days, and then returned home with dog train to my family, where I remained the balance of the winter, when not at Superior for treatment. When the ice moved from the lake in the spring I abandoned everything there and returned to La Pointe and was blind or nearly so until the winter of 1861.
Returning a little time to the north shore I wish to relate an incident of the death of one of our Ontonagon company. Two or three days after I had reached home from La Pointe, finding my eyes constantly growing worse I had the company take me to Superior where I could get treatment. Dr. Marcellus, son of Prof. Marcellus, of an eye infirmary in Philadelphia, who had just then married a beautiful young wife, and come west to seek his fortune, was engaged to treat me. I was taken to the boarding house of Henry Wolcott, where I engaged rooms for the winter as I expected to remain there until spring. I related to the doctor what had befallen me and he began treatment. At times I felt much better but no permanent relief seemed near. About the middle February my family required my presence at home, as there was some business to be attended to which they did not understand. My wife sent a note to me by Mr. Melzer, stating that it was necessary for me to return, and as the weather that day was very pleasant, she hoped that I would come that afternoon. Mr. Melzer delivered me the note, which I requested him to read. It was then 11 a. m. and I told him we would start right after dinner, and requested him to tell the doctor that I wished to see him right away, and then return and get his dinner, as it would be ready at noon, to which he replied:
“If I am not here do not wait for me, but I will be here at the time you are ready for home.”
Mr. Melzer did return shortly after we had finished our dinner and I requested him to eat, as I would not be ready to start for half an hour, but he insisted he was not hungry. We had no conveyance and at 1 p. m. we set out for home. We went down a few steps to the ice, as Mr. Wolcott’s house stood close to the shore of the bay, and went straight across Superior Bay to Minnesota Point, and across the point six or eight rods and struck the ice on Lake Superior. A plain, hard beaten road led from here direct to my home. After we had proceeded about 150 yards, following this hard beaten road, Melzer at once stopped and requested me to go ahead, as I could follow the beaten road without assistance, the snow being deep on either side.
“Now,” he says go ahead, for I must go back after a drink.”
I followed the road quite well, and when near the house my folks came out to meet me, their first inquiry being:
“Where is Melzer?”
I told them the circumstances of his turning back for a drink of water. Reaching the bank on which my house stood, some of my folks, looking back over the road I had come, discovered a dark object apparently floundering on the ice. Two or three of our men started for the spot and there found the dead body of poor Melzer. We immediately notified parties in Superior of the circumstances and ordered a post-mortem examination of the body. The doctors found that his stomach was entirely empty and mostly gone from the effects of whisky and was no thicker than tissue paper and that his heart had burst into three pieces. We gave him a decent burial at Superior and peace to his ashes, His last act of kindness was in my behalf.
To be continued in Chapter III…
Indian Agency’s Explanation of the 1854 Treaty
December 13, 2017
By Amorin Mello
Treaty Commissioner Henry C. Gilbert’s
Explanation of the Treaty Concluded in 1854
with the Assistance of David B. Herriman
Transactions of the Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters:
Volume 79, No. 1, Appendix 5
Office Michigan Indian Agency
Detroit October 17th, 1854
Sir

Mackinac Indian Agent
Henry Clark Gilbert
~ Branch County Photographs
I transmit herewith a treaty concluded at LaPointe on the 30th Ultimo between Mr. Herriman and myself as Commissioners on the part of the United States and the Chippewas of Lake Superior and the Mississippi.
On receiving your letters of August 10th, 12th, and 14th, relative to this treaty, I immediately dispatched a special messenger from this place by way of Chicago, Galena and St. Paul to Mr. Herriman at the Crow wing Chippewa Agency transmitting to him your letter requesting him to meet me at LaPointe with the Chiefs and Headmen of his Agency at as early a day as possible. I adopted this course in preference to sending a messenger from La Pointe on my arrival there for the purpose of saving time and I was thus enabled to secure the attendance of Mr Herriman and the Mississippi Chiefs some 10 or 12 days earlier than I could otherwise have done.
I left for LaPointe on the 26th of August last and arrived there the 1st day of September – Mr Herriman meeting me there the 14th of the same Month.
By this time a large number of Indians had assembled – including not only those entitled to payment but all those from the Interior who live about Lakes de Flambeau and Lake Courteilles. The Chiefs who were notified to attend brought with them in every instance their entire bands. We made a careful estimate of the number present and found there were about 4,000. They all had to be fed and taken care of, thus adding greatly to the expenses attending the negotiations.

Charles William Wulff Borup and Charles Henry Oakes married into the La Pointe mixed blood Beaulieu family; built the American Fur Company’s new La Pointe outfit during the 1830’s; sold La Pointe to Julius Austrian during 1853; and started the first bank in Minnesota during 1854 at St. Paul.
~ 1854 banknote from HeritageAuctions.com
A great number of traders and claim agents were also present as well as some of the persons from St. Paul’s who I had reason to believe attended for the purpose of preventing if possible the consummation of the treaty. The utmost precautions were taken by me to prevent a knowledge of the fact that negotiations were to take place from being public. The Messenger sent by me to Mr Herriman was not only trust worthy but was himself totally ignorant of the purport of the dispatches to Major Herriman. Information however of the fact was communicated from some source and the persons present in consequence greatly embarrassed our proceedings.
After Major Herriman’s arrival we soon found that the Mississippi Indians could not be induced to sell their land on any terms. Much jealousy and ill feeling existed between them and the Lake Superior Indians and they could not even be prevailed upon to meet each other in council. They were all however anxious that a division should be made of the payments to become due under former existing treaties and a specific apportionment made between the Mississippi and the Lake Superior Indians and places of payment designated.
Taking advantage of this feeling we proposed to them a division of the country between them and the establishment of a boundary line, on one side of which the country should belong exclusively to the Lake Superior and on the other side to the Mississippi Indians. We had but little difficulty in inducing them to agree to this proposition and after much negotiation the line designated in the treaty was agreed upon.
We then obtained from the Lake Indians a cession of their portion of the Country on the terms stated in the treaty. The district ceded embraces all the mineral region bordering on Lake Superior and Pigeon river & is supposed to be by far the most valuable portion of their country. But a small portion of the amount agreed to be paid in annuities is payable in coin. The manner of payment is such as in our judgement would most tend to promote the permanent welfare and hasten the civilization of the Indians.
We found the points most strenuously insisted upon by them were first the privilege of remaining in the country where they reside and next the appropriation of land for their future homes. Without yielding these points, it was idle for us to talk about a treaty. We therefore agreed to the selection of lands for them in territory heretofore ceded.
The tract for the Ance and Vieux Desert bands is a the head of Ke, wa, we naw Bay Michigan and is at present occupied by them. I estimate the quantity at about 60,000 acres.

Detail of La Pointe Indian Reservation survey boundaries including Gichi-ziibiiwishenhnyan from a letter dated March 30th, 1855, written by the Commissioner John Wilson of the General Land Office to General Surveyor Warner Lewis.
~ National Archives Microfilm Publications; Microcopy No. 27; Roll 16; Volume 16.
These reservations are located in Wisconsin, the principal of which is for the LaPointe Band on Bad river – A large number of Indians now reside there and I presume it will ultimately become the home of most of the Chippewas residing in that state. It is a tract of land well adapted for Agricultural purposes and includes the present Missionary Station under the care of the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions. About one third of the land however lying on the Lake Superior is swamp and valueless, except as it gives them access to the Lake for fishing purposes.
The other Wisconsin reservations lie on Lac de Flambeau and Lac Courteirelle in the Interior and the whole amount of land reserved in that state I estimate at about 200,000 acres exclusive of the Swamp land included in the LaPointe reservation. in the ceded Country there are two tracts set apart for the Indians – one on St Louis river of 100,000 acres for the Fond DuLac bands and one embracing the point bounded by the Lake and Pigeon river and containing about 120,000 acres.
There are two or three other small reservations to be hereafter selected under the direction of the President. The whole quantity of land embrace within all the tracts set apart we estimate at about 486,000 acres – No portion of the reserved lands are occupied by whites except the Missionary establishment on Bad river.
The provision going to each Half Breed family 80 acres of land was most strenuously insisted upon by the Indians. There are about 200 such families on my pay roll and allowing as many more to the Interior Indians which is a very liberal estimate, the amount of land required will be about 32,000 acres.
A principal source of embarrassment was the provision setting aside a portion of the consideration to be paid as the Chiefs might direct &c. In other words to pay their debts with. We had much difficulty in reducing the amount insisted upon to the sum stated in the treaty. I have no doubt that there are many just claims upon these Indians. The regular payment of their annuities was so long withheld that they were forced to depend to a great extent upon their traders. There claims that were all disposed to acknowledge and insisted upon providing for their payment and without the insertion of the provision referred to, we could not have concluded the treaty.
I regret very much that we could not have purchased the whole country and made the treaty in every particular within the limit of your instructions. But this was absolutely impossible and we were forced to the alternative of abandoning the attempt to treaty or of making the concessions detailed in the treaty.

Bureau of Indian Affairs Director
George W. Manypenny
~ Commons.Wikimedia.org
There are many points respecting which I should like much to make explanations, and for that purpose and in order to make a satisfactory settlement of the accounts for treaty purposes and in order to make a satisfactory settlement of the accounts for treaty expenses I respectfully request the privilege of attending at Washington at such time after making my other annuity payments as you may think proper.
Very Respectfully
Your Obt. Servt.
Henry C. Gilbert
Commissioner
Hon. Geo. W. Manypenny
Com. Ind. Affs.
Washington D.C.
1854 Treaty of La Pointe Appropriations
November 29, 2017
By Amorin Mello

House Documents, Volume 112
By United States House of Representatives
33d Congress,
2nd Session.
Ex. Doc. No. 61.
TREATY WITH CHIPPEWA INDIANS.
————————
MESSAGE
FROM
THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES,

United States President
Franklin Pierce
circa 1855
~ Commons.Wikimedia.com
TRANSMITTING
Estimates of appropriations for carrying into effect the treaty with the Chippewa Indians &c.
————————
February 8, 1855.—Laid upon the table and ordered to be printed.
————————
To the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States:
I communicate to Congress the following letter from the Secretary of the Interior, with its enclosure, on the subject of a treaty between the United States and the Chippewa Indians of Lake Superior, and recommend that the appropriations therein asked for may be made.
FRANLIN PEIRCE.
Washington, February 7, 1855.
Department Of The Interior,
Washington, February 6,1855.

Secretary of the Interior
Robert McClelland
circa 1916
~ Commons.Wikipedia.com
SIR: I have the honor to transmit to you, herewith, a copy of a communication from the Commissioner of Indian Affairs, dated the 5th instant, calling my attention to the subject of a treaty made at La Pointe, Wisconsin, by Henry C. Gilbert and Daniel B. Herriman, commissioners on the part of the United States, and the Chippewa Indians of Lake Superior; and, to enable this department to carry the treaty into effect, recommend that Congress be requested to make the appropriations specified in the letter of the Commissioner, and which will be immediately required for that purpose.
I am, sir, very respectfully, your obedient servant,
R. McCLELLAND,
Secretary.
To the President.
Department Of The Interior,
Office Indian Affairs, February 5, 1855.

Mackinac Indian Agent
Henry Clark Gilbert
~ Branch County Photographs
Sir: Having received the official information on the 24th ultimo of the approval and ratification, by the President and Senate, of the articles of agreement and convention made and entered into at La Pointe, in the State of Wisconsin, by Henry C. Gilbert and Daniel B. Herriman, commissioners on the part of the United States, and the Chippewa Indians of Lake Superior and Mississippi, I have the honor now to call your attention to the appropriations that will be required immediately to enable the department to carry the treaty into effect, viz:
For fulfilling treaties with the Chippewas of Lake Superior.
- For expenses (in part) of selecting reservations, and surveying and marking the boundaries thereof, per 2d, 3d, and 12th articles of the treaty of September 30, 1854 …….. $3,000
- For the payment of the first of twenty instalments in coin, goods, &c, agricultural implements, &c, and education, &c, per 4th article of the treaty of September 30, 1854 …….. 19,000
- For the purchase of clothing and other articles to be given to the young men at the next annuity payment, as per 4th article of the treaty of September 30, 1854 …….. 4,800
- For the purchase of agricultural implements and other articles, as presents for the mixed bloods, per 4th article of the treaty of September 30, 1854 …….. 6,000
- For the payment of such debts as may be directed by the chiefs in open council, and found to be just and correct by the Secretary of the Interior, per 4th article of the treaty of September 30, 1854 …….. 90,000
- For the payment of such debts of the Bois Forte bands as may be directed by their chiefs, and found lo be just and correct by the Secretary of the Interior, per 12th article of the treaty of September 30, 1844 …….. 10,000
- For the payment of the first of five instalments in blankets, cloth, &c, to the Bois Forte band, per 12th article of the treaty of September 30, 1854 …….. 2,000
- For the first of twenty instalments for the pay of six smiths and assistants, per 5th and 2d articles of the treaty of September 30, 1854 …….. 5,040
- For the first of twenty instalments for the support of six smith shops, per 5th and 2d articles of the treaty of September 30, 1854 …….. 1,320
It will be observed that the treaty of September 30, 1854, recognized the Chippewas of Lake Superior as a branch of the nation, and that the pecuniary and beneficiary stipulations therein are for their exclusive use.
By the fifth article of the treaty the Lake Superior Chippewas are to have six blacksmiths and assistants, and they relinquish, by the same article, all other employés to which they might otherwise have been entitled under former treaties.
The Chippewas of the Mississippi are, by the eighth article of the treaty, entitled to one-third of the benefits of treaties prior to 1847; and, by consequence, retain an interest of one-third in the stipulations for smith shops, &c., and farmers, &c, per second article of the treaty of July 29, 1837; and in the farmers, and carpenters, and smiths, &c., mentioned in the fourth article of the treaty of October 4, 1842.
On an examination of the condition of existing appropriations to fulfil the stipulations just mentioned, it is found that the balances in the treasury are sufficient to sustain these employés and otherwise meet the requirements of the stipulations referred to, so far as the Chippewas of the Mississippi are interested, during the next fiscal year.
In case appropriations are made by Congress, in pursuance of the foregoing estimates, it will be perceived that the following items of the Indian appropriation bill now before Congress might, with propriety, be stricken out, viz:
House bill 555, reported, with amendments, January 16, 1855:
- Page 4, lines 68, 69, 70, and 71, “three thousand dollars,” ($3,000.)
- Page 4, lines 72, 73, 74, 75, and 76, “one thousand dollars,” ($1,000.)
- Page 5, lines 89, 90, 91, 92, and 93, “two thousand dollars,” ($2,000.)
- Page 5, lines 94, 95, and 96, “one thousand dollars,” ($1,000.) Page 5, lines 97, 98, and 99, “one thousand two hundred dollars,” ($1,200.)

Director of of the Bureau of Indian Affairs
George Washington Manypenny
circa 1886
~ Commons.Wikimedia.org
As it is not deemed necessary, I do not therefore submit, at present an estimate for appropriations to pay employés for the Bois Forte band, as per twelfth article of the treaty of September 30, 1854, or to liquidate a balance, should any be found due to these Indians by the investigation, which it is provided by the ninth article of the same treaty shall be made.
Should the foregoing estimates and suggestions be approved by you, I respectfully recommend that they be laid before Congress as early as practicable.
Very respectfully, your obedient servant,
GEO. W. MANYPENNY,
Commissioner.
Hon. R. McCLELLAND,
Secretary of the Interior.
Wheeler Papers: 1854 La Pointe before the Treaty
August 7, 2017
By Amorin Mello
Selected letters from the
Wheeler Family Papers,
Box 3, Folders 11-12; La Pointe County.
Crow-wing, Min. Ter.
Jan. 9th 1854
Brother Wheeler,

Reverend Leonard Hemenway Wheeler ~ In Unnamed Wisconsin by Silas Chapman, 1895, cover image.
Though not indebted to you just now on the score of correspondence, I will venture to intrude upon you a few lines more. I will begin by saying we are all tolerably well. But we are somewhat uncomfortable in some respects. Our families are more subject to colds this winter than usual. This probably may be attributed in part at least to our cold and open houses. We were unable last fall to do any thing more than fix ourselves temporarily, and the frosts of winter find a great many large holes to creep in at. Some days it is almost impossible for us to keep warm enough to be comfortable.
Our prospects for accomplishing much for the Indians here I do not think look more promising than they did last fall. There are but few Indians here. These get drunk every time they can get whiskey, of which there is an abundance nearby. Among the white people here, none are disposed to attend meetings much except Mr. [Welton?]. He and his wife are discontented and unhappy here, and will probably get away as soon as they can. We hear not a word from the Indian Department. Why they are minding us in this manner I cannot tell. But I should like it much better, if they would tell us at once to be gone. I have got enough of trying to do anything for Indians in connection with the Government. We can put no dependence upon any thing they will do. I have tried the experiment till I am satisfied. I think much more could be done with a boarding school in the neighborhood of Lapointe than here And my opinion is, that since things have turned out as they have here, we had better get out of it as soon as we can. With such an agent as we now have, nothing will prosper here. He is enough to poison everything, and will do more moral evil in such a community, as this, than a half a dozen missionaries can do good. My opinion is, that if they knew at Washington how things are and have been managed here, there would be a change. But I do not feel certain of this. For I sometimes am tempted to adopt the opinion that they do not care much there how things go here. But should there be a change, I have little hope that is would would make things materially better. The moral and social improvement of the Indians, I fear, has little to do with the appointment of agents and superintendents. I do not think I ought to remain here very long and keep my family here, as things are now going. If we were not involved with the Government with regard to the school matter, I would advise the Committee to quit here as soon as we can find a place to go to. My health is not very good. The scenes, and labors and attacks of sickness which I have passed through during the past two years have made almost a wreck of my constitution. It might rally under some circumstances. But I do not think it will while I stay here, so excluded from society, and so harassed with cares and perplexities as I have been and as I am likely to be in future, should we go on and try to get up a school. My wife is in no better spirits than I am. She has had several quite ill turns this winter. the children all wish to get away from here, and I do not know that I shall have power to keep them here, even if I am to stay.
But what to do I do not know. The Committee say they do not wish to abandon the Ojibwas. I cannot in future favor the removal of the lake Indians. I believe that all the aid they will receive from the Government will never civilize or materially benifit them. I judge from the manner in which things have been managed here. Our best hope is to do what we can to aid them where they are to live peaceably with the whites, and to improve and become citizens. The idea of the Government sending infidels and heathens here to civilize and Christianize the Indians is rediculous.
I always thought it doubtful whether the experiment we are trying would succeed. In that case it was my intention to remove somewhere below here, and try to get a living, either by raising my potatoes or by trying to preach to white people, or by uniting both. but I do not hardly feel strong enough to begin entirely anew in the wilderness to make me a home. I suppose my family would be as happy at Lapointe, as they would any where in the new and scattered settlements for fifty or a hundred miles below here. And if thought I could support myself then, I might think of going back there. There are our old friends for whose improvement we have laborred so many years. I feel almost as much attachment for them as for my won children. And I do not think they ought to be left like sheep upon the mountains without a shepherd. And if the Board think it best to expend money and labor for the Ojibwas, they had better expend it there than here, as things now are at least. I think we were exerting much much more influence there before we left, then we have here or are likely to exert. I have no idea that the lake Indians will ever remove to this place, or to this region.

Reverend Sherman Hall
~ Madeline Island Museum
What do you think of recommending to the Board to day to exert a greater influence on the people in the neighborhood of Lapointe[?/!] I feel reluctant to give up the Indians. And if I could get a living at Lapointe, and could get there, I should be almost disposed to go back and live among those few for whom I have labored so long, if things turn out here as I expect they will. I have not much funds to being life with now, nor much strength to dig with. But still I shall have to dig somewhere. The land is easier tilled in this region than that about the lake. But wood is more scarce. My family do not like Minesota. Perhaps they would, if they should get out of the Indian country. Edwin says he will get out of it in the spring, and Miles says he will not stay in such a lonesome place. I shall soon be alone as to help from my children. My boys must take care of themselves as soon as they arrive at a suitable age, and will leave me to take care of myself. We feel very unsettled. Our affairs here must assume a different aspect, or we cannot remain here many months longer. Is there enough to do at Lapointe; or is there a prospect that there will soon be business to draw people enough then, to make it an object to try to establish the institution of the gospel there? Write me and let me know your views on such subjects as these.
[Unsigned, but appears to be from Sherman Hall]
Crow-wing Feb. 10th 1854
Brother Wheeler:
I received your letter of jan. 16th yesterday, and consequently did not sleep as much as usual last night. We were glad to hear that you are all well and prosperous. We too are well which we consider a great blessing, as sickness in present situation would be attended with great inconvenience. Our house is exceedingly cold and has been uncomfortable during some of the severe cold weather have had during the last months. Yet we hope to get through the winter without suffering severely. In many respects our missionary spirit has been put to a severer test than at any previous time since we have been in the Indian country, during the past year. We feel very unsettled, and of course somewhat uneasy. The future does not look very bright. We cannot get a word from the Indian Department whether we may go on or not. If we cannot get some answer from them before long I shall be taking measures to retire. We have very little to hope, I apprehend, from all the aid the Government will render to words the civilization and moral and intellectual improvement of the Indians. For missionaries or Indians to depend on them, is to depend on a broken staff.
~ Minnesota Historical Society
“The American Fur Company therefore built a ‘New Fort’ a few miles farther north, still upon the west shore of the island, and to this place, the present village, the name La Pointe came to be transferred. Half-way between the ‘Old fort’ and the ‘New fort,’ Mr. Hall erected (probably in 1832) ‘a place for worship and teaching,’ which came to be the centre of Protestant missionary work in Chequamegon Bay.”
~ The Story of Chequamegon Bay
I do not see that our house is so divided against itself, that it is in any great danger of falling at present. My wife never did wish to leave Lapointe and we have ever, both of us, thought that the station ought not to be abandoned, unless the Indians were removed. But this seemed not to be the opinion of the committee or of our associates, if I rightly understood them. I had a hard struggle in my mind whether to retire wholly from the service of the Board among the Indians, or to come here and make a further experiment. I felt reluctant to leave them, till we had tried every experiment which held out any promise of success. When I remove my family here our way ahead looked much more clear than it does now. I had completed an arrangement for the school which had the approval of Gov. Ramsey, and which fell through only in consequence of a little informality on his part, and because a new set of officers just then coming into power must show themselves a little wiser than their predecessors. Had not any associates come through last summer, so as to relieve me of some of my burdens and afford some society and counsel in my perplexities I could not have sustained the burden upon me in the state of my health at that time. A change of officers here too made quite an unfavorable change in our prospects. I have nothing to reproach myself with in deciding to come here, nor in coming when we did, though the result of our coming may not be what we hoped it would be. I never anticipated any great pleasure in being connected with a school connected in any way with the Government, nor did I suppose I should be long connected with it, even if it prospered. I have made the effort and now if it all falls, I shall feel that Providence has not a work for us to do here. The prospects of the Indians look dark, what is before me in the future I do not know. My health is not good, though relief from some of the pressure I had to sustain for a time last fall and the cold season has somewhat [?????] me for the time being. But I cannot endure much excitement, and of course our present unsettled affairs operate unfavorably upon it. I need for a time to be where I can enjoy rest from everything exciting, and when I can have more society that I have here, and to be employed moderately in some regular business.

Antoine Gordon [Gaudin]
~ Noble Lives of a Noble Race by the St. Mary’s Industrial School (Bad River Indian Reservation), 1909, page 207.

Charles Henry Oakes
~ Findagrave.com
As to your account I have not had time to examine it, but will write you something about it by & by. As to any account which Antoine Gaudin has against me, I wish you would have him send it to me in detail before you pay it. I agreed with Mr. Nettleton to settle with him, and paid him the balance due to Antoine as I had the account. I suppose he made the settlement, when he was last at Lapointe. As to the property at Lapointe, I shall immediately write to Mr. Oakes about it. But I suppose in the present state of affairs, it will be perhaps, a long time before it will be settled so as to know who does own it. It is impossible for me to control it, but you had better keep posession of it at present. I cannot send Edwin [??] through to cultivate the land & take care of it. He will be of age in the spring, and if he were to go there I must hire him. He will probably leave us in the spring. Please give my best regards to all. Write me often.
Yours truly
S. Hall
Crow-wing, Min. Ter.
Feb. 21st 1854
Brother Wheeler,

Paul Hudon Beaulieu
~ FamilySearch.org
I wrote you a few days ago, and at the same time I wrote to Mr. Oakes inquiring whether he had got possession of the Lapointe property. I have not yet got a reply from him, but Mr. Beaulieu tells me that he heard the same report which you mentioned in your letter, and that he inquired of Mr. Oakes about it when he saw him on a recent visit to St. Paul, and finds that it is all a humbug. Oakes has nothing to do with it. Mr. Beaulieu said that the sale of last spring has been confirmed, and that Austrian will hold Lapointe. So farewell to all the inhabitants’ claims then, and to anything being done for the prosperity of the peace for the present, unless it gets out of his hands.
I have written to Austrian to try to get something for our property if we can. But I fear there is not much hope. If he goes back to Lapointe in the spring, do the best you can to make him give us something. I feel sorry for the inhabitants there that they are left at his mercy. He may treat them fairly, but it is hardly to be expected.

Clement Hudon Beaulieu
~ TreatiesMatter.org
As to our affairs here, there has been no particular change in their aspects since I wrote a few days ago. There must be a crisis, I think, in a few weeks. We must either go on or break up, I think, in the spring. We are trying to get a decision. I understand our agent has been threatened with removal if he carries on as he has done. I believe there is no hope of reformation in his case, and we may get rid of him. Perhaps God sent us here to have some influence in some such matters, so intimately connected with the welfare of the Indians. I have never thought I [????] can before I was sent in deciding to come here. Some trials and disappointments have grown out of my coming, but I feel conscious of having acted in accordance with my convictions of duty at this time.
If all falls through, I know not what to do in the future. The Home Missionary Society have got more on their hands now than they have funds to pay, if I were disposed to offer myself to labor under them. I may be obliged to build me a shanty somewhere on some little unoccupied piece of land and try to dig out a living. In these matters the Lord will direct by his providence.
You must be on your guard or some body will trip you up and get away your place. There are enough unprincipled fellows who would take all your improvements and send you and all the Indians into the Lake if they could make a dollar by it. I should not enlarge much, without getting a legal claim to the land. Neither would I advise you to carry on more family than is necessary to keep what team you must have, and to supply your family with milk and vegetables. It will be advantage/disadvantage to you in a pecuniary point of view, it will load you with and tend to make you worldly minded, and give your establishment the air of secularity in the eyes of the world. If I were to go back again to my old field, I would make my establishment as small as I could & have enough to live comfortable. I with others have thought that your tendency was rather towards going to largely into farming. I do not say these things because I wish to dictate or meddle with your affairs. Comparing views sometimes leads to new investigations in regard to duty.
May the Lord bless you and yours, and give you success and abundant prosperity in your labours of love and efforts to Save the Souls around you.
Give my best regards to Mrs. W., the children, Miss S and all.
Yours truly,
S. Hall
I forgot to say that we are all well. Henry and his family have enjoyed better health here, then they used to enjoy at Lapointe.
Feb 27
Brother Wheeler.
My delay to answer your note may require an explanation. I have not had time at command to attend to it conveniently at an earlier period. As to your first questions. I suppose there will be no difference of opinion between us as to the correctness of the following remarks.
- The Gospel requires the members of a church to exercise a spirit of love, meekness and forbearance towards an offending brother. They are not to use unnecessary severity in calling him to account for his errors. Ga. 6:1.
- The Object of Church discipline is, not only to [pursue/preserve?] the Church pure in doctrine & morals, that the contrary part may have no evil thing to say of them; but also to bring the offender to a right State of mind, with regard this offense, and gain him back to duty and fidelity.
- If prejudice exist in the mind of the offender towards his brethren for any reason, the spirit of the gospel requires that he be so approached if possible as to allay that prejudice, otherwise we can hardly expect to gain a candid hearing with him.

Charles William Wulff Borup, M.D. ~ Minnesota Historical Society
I consider that these remarks have some bearing on the case before us. If it was our object to gain over Dr. B. to our views of the Sabbath, and bring him to a right State of mind with regard this Sabbath breaking, the manner of approaching him would have, in my view, much to do with the offence. He may be approached in a Kind and [forbearing?] manner, when one of sternness and dictation will only repel him from you. I think we ought, if possible, and do our duty, avoid a personal quarrel with him. To have brought the subject before the Church & made a public affair of it, before [this/then?] and more private means have been tried to get satisfaction, would, I am sure, have resulted in this. I found from my own interviews with him, that there was hope, if the rest of the brethren would pursue a similar course. I felt pretty sure they would obtain satisfaction. IF they had [commenced?] by a public prosecution before the church, it would only have made trouble without doing any good. The peace of our whole community would have been disturbed. I thought one step was gained when I conversed with him, and another when you met him on the subject. I knew also that prejudices existed both in his mind towards us, & in our minds towards him which were likely to affect the settlement of this affair, and which as I thought, would be much allayed by individuals going to him and speaking face to face on this subject in private. He evidently expected they would do so. Mutual conversations and explanations allay these feelings very much. At least it has been so in my experience.
As to your second question. I do not say that it was Mr. Ely’s duty to open the subject to Doc. Borup at the preparatory lecture. If he had done so, it would have been only a private interview; for there [was?] not enough present to transact business. All I meant to affirm respecting that occasion is, that it afforded a good opportunity to do so, if he wishes, and that Dr. B. expected he would have done so, as I afterwards learnt, if he has any objection to make against his coming to the communion.
As to your third question. I have no complaint to make of the church, that I have urged them to the performance of any “duties“ in this case they have refused to perform.
And now permit me to ask in my turn.
What “duties” have they urged me to perform in this case, which I “have been unwilling, or manifested a reluctance to perform?”
Did you intend by anything which wrote to me or said verbally, to request me to commence a public prosecution of Doc. Borup before the Church?
Will you have the goodness to state in writing, the substance of what you said to me in your study as to your opinion and that of others suspecting my delinquency in maintaining church discipline.
A reply to these questions would be gratefully received.
Your brother in Christ
S. Hall
Crow Wing. March 12th 1854
Brother Wheeler:
Your letter of Feb 17th came to hand by our last mail; and though I wrote you but a short time ago, I will say a few words in relation to one or two topics to which you allude. Shortly after I received your former letter I wrote to Mr. Oakes enquiring about the property at Lapointe. In reply, says that himself and some others purchased Mr. Austrian’s rights at Lapointe of Old Hughes on the strength of a power of attorney which he held. Austrian asserts the power of attorney to be fraudulent, and that they cannot hold the property. Oakes writes as if he did not expect to hold it. Some time ago I wrote to Mr. Austrian on the same subject, and said to him that if I could get our old place back, I might go back to Lapointe. He says in reply —

Julius Austrian
~ Madeline Island Museum
“I should feel much gratified to see you back at Lapointe again, and can hold out to you the same inducements and assurances as I have done to all other inhabitants, that is, I shall be at Lapointe early in the spring and will have my land surveyed and laid out into lots, and then I shall be ready to give to every one a deed for the lot he inhabits, at a reasonable price, not paying me a great deal more than cost trouble, and time. But with you, my dear Sir, will be no trouble, as I have always known you a just and upright man, and have provided ways to be kind towards us, therefore take my assurance that I will congratulate myself to see you back again; and it shall not be my fault if you do not come. If you come to Lapointe, at our personal interview, we will arrange the matter no doubt satisfactory.”

“The property” from the James Hughes Affair is outlined in red. This encompassed the Church at La Pointe (New Fort) and the Mission (Middleport) of Madeline Island. 1852 PLSS survey map by General Land Office.
I suppose Austrian will hold the property and probably we shall never realize anything for our improvements. You must do the best you can. Make your appeal to his honor, if he has any. It will avail nothing to reproach him with his dishonesty. I do not know what more I can do to save anything, or for any others whose property is in like circumstances with ours.
You speak discouragingly of my going back to Lapointe. I do not think the Home Miss. Soc. would send a missionary there only for the few he could reach in the English language. If the people want a Methodist, encourage them to get one. It is painful to me to see the place abandoned to irreligion and vices of every Kind, and the labours I have expended there thrown away. I can hardly feel that it was right to give up the station when we did. If I thought I could support myself there by working one half the time and devoting the rest to ministerial labors for the good of those I still love there, I should still be willing to go back, if could get there & had a shelter for my head, unless there is a prospect of being more useful here. But the land at Lapointe is so hard to subdue that I am discouraged about making an attempt to get a living there by farming. I am not much of a fisherman. There is some prospect that we may be allowed to go on here. Mr. Treat has been to Washington, and says he expects soon to get a decision from the Department. We have got our school farm plowed, and the materials are drawn out of the woods for fencing it. If I have no orders to the contrary, I intend to go on & plant a part of it, enough to raise some potatoes. We may yet get our school established. If we can go ahead, I shall remain here, but if not, I think it is not my duty to remain here another year, as I have the past. In other circumstances, I could do more towards supporting myself and do more good probably.
I have felt much concerned for the people of Lapointe and Bad River on account of the small pox. May the Lord stay this calamity from spreading among you. Write us every mail and tell us all. It is now posted here today that the Old Chief [Kibishkinzhugon?] is dead. I hardly credit the report, though I should suppose he might be one of the first victims of the disease.
I can write no more now. We are all very well now. Give my love to all your family and all others.
Tell Robert how the matters stands about the land. It stands him in how to be on good terms with the Jew just now.
Yours truly,
S. Hall
The snow is nearly all off the ground and the weather for two or three weeks has been as mild as April.
Crow Wing M.H. Apr. 1 1854
Dear Br. & Sr. Wheeler.
I have received a letter from you since I wrote to you & am therfore in your debt in that matter. I have also read your letters to Br. & Sr. Welton I suppose you have received my letter of the 13th of Feb. if so, you have some idea of our situation & I need say no more of that now; & will only say that we are all well as usual & have been during the winter. Mrs. P_ is considerably troubled with her old spinal difficulty. She has got over her labors here last summer * fall. Harriet is not well I fear never will be, because the necessary means are not likely to be used, she has more or less pain in her back & side all the time, but she works on as usual & appears just as she did at LaPointe, if she could be freed from work so as to do no more than she could without injury & pursue uninterruptedly & proper medical course I think she might regain pretty good health. (Do not, any of you, send back these remarks it would not be pleasing to her or the family.) We have said what we think it best to say) –
Br. Hall is pretty well but by no means the vigorous man he once was. He has a slight – hacking cough which I suppose neither he nor his family have hardly noticed, but Mrs. P_ says she does not like the sound of it. His side troubles him some especially when he is a good deal confined at writing. Mr. & Mrs. W_ are in usual health. Henry’s family have gone to the bush. They are all quite well. He stays here to assist br. H_ in the revision & keeps one or two of his children with him. They are now in Hebrews, with the Revision. Henry I suppose still intends to return to Lapointe in the spring. –
Now, you ask, in br. Welton’s letter, “are you all going to break up there in the spring.” Not that I know of. It would seem to me like running away rather prematurely. When the question is settled, that we can do nothing here, then I am willing to leave, & it may be so decided, but it is not yet. We have not had a whisper from Govt. yet. Wherefore I cannot say.
It looks now as if we must stay this season if no longer. Dr. Borup writes to br. Hall to keep up good courage, that all will come out right by & by, that he is getting into favor with Gov. Gorman & will do all he can to help us. (Br. Hall’s custom is worth something you know).

Henry C. Gilbert
~ Branch County Photographs
By advise of the Agent, we got out (last month) tamarack rails enough to fence the school farm (which was broke last summer) of some 80 acres & it will be put up immediately. Our great father turned out the money to pay for the job. These things look some like our staying awhile I tell br H_ I think we had better go as far as we can, without incurring expense to the Board (except for our support) & thus show our readiness to do what we can. if we should quit here I do not know what will be done with us. Br Hall would expect to have the service of the Board I suppose. Should they wish us to return to Bad River we should not say nay. We were much pleased with what we have heard of your last fall’s payment & I am as much gratified with the report of Mr. H. C. Gilbert which I have read in the Annual Report of the Com. of Indian Affairs. He recommends that the Lake Superior Indians be included in his Agency, that they be allowed to remain where they are & their farmers, blacksmith & carpenter be restored to them. If they come under his influence you may expect to be aided in your efforts, not thwarted , by his influence. I rejoice with you in your brightening prospects, in your increased school (day & Sabbath) & the increased inclination to industry in those around you. May the lord add his blessing, not only upon the Indians but upon your own souls & your children, then will your prosperity be permanent & real. Do not despise the day of small things, nor overlook especially neglect your own children in any respect. Suffer them not to form idle habits, teach them to be self reliant, to help themselves & especially you, they can as well do it as not & better too, according to their ability & strength, not beyond it, to fear God & keep his commandments & to be kind to one another (Pardon me these words, I every day see the necessity of what I have said.) We sympathize with you in your situation being alone as you are, but remember you have one friend always near who waits to [commence?] with you, tell Him & all with you from Abby clear down to Freddy.
Affectionately yours
C. Pulsifer
Write when you can.
Crow wing Min. Ter.
April 3d 1854
Brother Wheeler

George E. Nettleton and his brother William Nettleton were pioneers, merchants, and land speculators at what is now Duluth and Superior.
~ Image from The Eye of the North-west: First Annual Report of the Statition of Superior, Wisconsin by Frank Abial Flower, 1890, page 75.
Since I wrote you a few days ago, I have received a letter from Mr. G. E. Nettleton, in which he says, that when he was at Lapointe in December last, he was very much hurried and did not make a full settlement with Antoine. He says further, that he showed him my account, and told him I had settled with him, and that he would see the matter right with Antoine. A. replied that all was right. I presume therefore all will be made satisfactory when Mr. N. comes up in the Spring, and that you will have need to make yourself no further trouble about this matter.
I have also received a short note from Mr. Treat in which he says,
“I have not replied to your letters, because I have been daily expecting something decisive from Washington. When I was there, I had the promise of immediate action; but I have not heard a word from them”.
“I go to Washington this Feb, once more. I shall endeavor to close up the whole business before I return. I intend to wait till I get a decision. I shall propose to the Department to give up the school, if they will indemnify us. If I can get only a part of what we lose, I shall probably quit the concern”.
Thus our business with the Government stood on March the 9th, I have lost all confidence in the Indian Department of our Government under this administration, to say nothing of the rest of it. If the way they have treated us is an index to their general management, I do not think they stand very high for moral honesty. The prospects for the Indians throughout all our territories look dark in the extreme. The measures of the Government in relation to them are not such as will benefit and save many of them. They are opening the floodgates of vice and destruction upon them in every quarter. The most solemn guarantees that they shall be let alone in the possession of domains expressly granted them mean nothing.
Our prospects here look dark. For some time past I have been rather anticipating that we should soon get loose and be able to go on. But all is thrown into the dark again. What I am to do in future to support my family, I do not know. If we are ordered to quit here and turn over the property, it would turn [illegible] out of doors.
Mr. Austrian expects us back to Lapointe in the Spring & Mr. Nettleton proposes to us to go to Fond du Lac, (at the Entry). He says there will be a large settlement then next season. A company is chartered to build a railroad through from the Southern boundary of this territory to that place. It is probable that Company [illegible] will make a grant of land for that purpose. If so, it will probably be done in a few years. That will open the lake region effectually. I feel the need of relaxation and rest before I do anything to get established anywhere.
We are still working away at the Testament, it is hard work, and we make lately but slow progress. There is a prospect that the Bible Society will publish it but it is not fully decided. I wish I could be so situated that I could finish the grammar.
But I suppose I am repeating what I have said more than once before. We are generally in good health and spirits. We hope to hear from by next mail.
Yours truly
S. Hall
What do you think about the settlements above Lapointe and above the head of the Lake?
Detroit July 10th 1854
Rev. Dr. Bro.
At your request and in fulfilment of my promise made at LaPointe last fall so after so long a time I write: And besides “to do good & to communicate” as saith the Apostle “forget not, for with such sacrifices God is well pleased.”
We did not close up our Indian payments of last year until the middle of the following January, the labors, exposures and excitements of which proved too much for me and I went home to New York sick & nearly used up about the last of February & continued so for two months. I returned here about a week ago & am now preparing for the fall pay’ts.
The Com’sr. has sent in the usual amounts of Goods for the LaPointe Indians to Mr. Gilbert & I presume means to require him to make the payment at La P. that he did last fall, although we have received nothing from the Dep’t. on the subject.

“George Washington Manypenny (1808-1892) was the Director of the Bureau of Indian Affairs of the United States from 1853 to 1857.”
~ Wikipedia.org
In regard to the Treaty with the Chipp’s of La Sup’r & the Miss’i, the subject is still before Congress and if one is made this fall it has been more than intimated that Com’r Manypenny will make it himself, either at LaP’ or at F. Dodge or perhaps at some place farther west. Of course I do not speak from authority or any of the points mentioned above, for all is rumour & inference beyond the mere arrival here of the Goods to Mr G’s care.
From various sources I learn that you have passed a severe winter and that much sickness has been among the Indians and that many of them have been taken away by the Small Pox.
This is sad and painful intelligence enough and I can but pray God to bless & overrule all to the goods of his creasures and especially to the Missionaries & their families.
Notwithstanding I have not written before be assured that I have often [???] of and prayed for you and yours and while in [Penn.?] you made your case my own so far as to represent it to several of our Christian brethren and the friends of missions there and who being actuated by the benevolent principles of the Gospel, have sent you some substanted relief and they promise to do more.
The Elements of the political world both here and over the waters seem to be in fearful & [?????] commotion and what will come of it all none but the high & holy one can know. The anti Slavery Excitement with us at the North and the Slavery excitement at the South is augmenting fact and we I doubt not will soon be called upon to choose between Slavery & freedom.
If I do not greatly misjudge the blessed cause of our holy religion is or seems to be on the wane. I trust I am mistaken, but the Spirit of averice, pride, sensuality & which every where prevails makes me think otherwise. The blessed Christ will reign [recenth-den?] and his kingdom will yet over all prevail; and so may it be.
Let us present to him daily the homage of a devout & grateful heart for his tender mercies [tousward?] and see to it that by his grace we endure unto the end that we may be saved.
My best regards to Mrs. W. to Miss Spooner to each of the dear children and to all the friends & natives to each of whom I desire to be remembered as opportunity occurs.
The good Lord willing I may see you again this fall. If I do not, nor never see you again in this world, I trust I shall see and meet you in that world of pure delight where saints immortal reign.
May God bless you & yours always & ever
I am your brother
In faith Hope & Charity
Rich. M. Smith
Rev Leonard H. Wheeler
LaPointe
Lake Superior
Miss. House Boston
Augt’ 31, 1854
Rev. L. H. Wheeler,
Lake Superior
Dear Brother
Yours of July 31 I laid before the Com’sr at our last meeting. They have formally authorized the transfer of Mr & Mrs Pulsifer to the Lake, & also that of Henry Blatchford.

Robert Stuart was formerly an American Fur Company agent and Acting Superintendent on Mackinac Island during the first Treaty at La Pointe in 1842.
~ Wikipedia.org
In regard to the “claims” their feeling is that if the Govt’ will give land to your station, they have nothing to say as to the quantity. But if they are to pay the usual govt’ price, the question requires a little caution. We are clear that we may authorize you to enter & [???] take up so much land as shall be necessary for the convenience of the [mission?] families; but we do not see how we can buy land for the Indians. Will you have the [fondness?] to [????] [????] on these points. How much land do you propose to take up in all? How much is necessary for the convenience of the mission families?
Perhaps you & others propose to take up the lands with private funds. With that we have nothing to do, so long as you, Mr P. & H. do not become land speculators; of which, I presume, there is no danger.
As to the La Pointe property, Mr Stuart wrote you some since, as you know already I doubt not, and replied adversely to making any bargain with Austrian. I took up the opinion of the Com’sr after receiving your letter of July 31, & they think it the wise course. I hope Mr Stewart will get this matter in some shape in due time.
I will write to him in reference to the Bad River land, asking him to see it once if the gov’ will do any thing.
Affectionate regards to Mrs W. & Miss Spooner & all.
Fraternally Yours
S. B. Treat
P.S. Your report of July 31 came safely to hand, as you will & have seen from the Herald.
“A real bona fide, unmitigated Irishman”
December 7, 2014
By Leo

“The Usual Irish Way of Doing Things”, by Thomas Nast Published 2 September 1871 in Harper’s Weekly. Nast, who battled Tammany Hall and designed the modern image of Santa Claus, is one of the most famous American political cartoonists. However, he frequently depicted Irish-Americans as drunken, monkey-like monsters (Wikimedia Images).
It has been a while since I’ve posted anything new. My personal life has made it impossible to meet my former quota of three new posts a month. Now, it seems like I’ll be lucky to get one every three months. I haven’t forgotten about this site, however, and there is certainly no shortage of new topics. Unfortunately, most of them require more effort than I am able to give right now. Today, however, I have a short one.
Regular readers will know that the 1855 La Pointe annuity payment to the Lake Superior Chippewa bands is a frequent subject on Chequamegon History. To fully understand the context of this post, I recommend reading some of the earlier posts on that topic. The 1855 payment produced dozens of interesting stories and anecdotes: some funny, some tragic, some heroic, some bizarre, and many complicated. We’ve covered everything from Chief Buffalo’s death, to Hanging Cloud the female warrior, to Chief Blackbird’s great speech, to the random arrival of several politicians, celebrities, and dignitaries on Madeline Island.
Racism is an unavoidable subject in nearly all of these stories. The decisive implementation of American power on the Chequamegon Region in the 1850s cannot be understood without harshly examining the new racial order that it brought.
The earlier racial order (Native, Mix-blood, European) allowed Michel Cadotte Jr., being only of one-eighth European ancestry to be French while Antoine Gendron, of full French ancestry, was seen as fully Ojibwe. The new American order, however, increasingly defined ones race according to the shade of his or her skin.
But there are never any easy narratives in the history of this area, and much can be missed if the story of American domination is only understood as strictly an Indian/White conflict. There are always misfits, and this area was full of them.
I recently found an example from the November 7, 1855 edition of the Western Reserve Chronicle in Warren, Ohio shows just how the suffocating paternalism directed toward the Ojibwe at the 1855 payment hit others as well:
A GENUINE IRISHMAN
A correspondent of the Home Journal relates the following characteristic incident of Irish tactic. He says:
Does the wide world contain another paradox that will compare with a real bona fide, unmitigated Irishman? Imagination and sensuality, poetry and cupidity, generosity and avarice, heroism and cowardice–and so on, to the end of the list; all colors, shades and degrees of character congregated together, and each in most intimate association with its intensest antithesis–a very Joseph’s coat, and yet, most marvelous of marvels! a perfect harmony pervading the whole.
Among the reminiscences of a month’s sojourn at La Pointe, Lake Superior, during the annual Indian payment of the last summer, I find the following truly ‘representative’ anecdote:
One day while Commissioner Monypenny was sitting in council with the chiefs, intelligence was brought to Mr. Gilbert (the Indian agent) that two or three Indians were drunk and fighting, at a certain wigwam. With his usual promptitude, Mr. Gilbert summoned one of his interpreters, and proceeded directly to the lodge, where he seized the parties and locked them in the little wooden jail of the village, having first ascertained from them where they obtained their liquor. He then went immediately to the house they had designated, which was a private dwelling, occupied by an Irishman and his wife, and demanded if they kept liquor to sell to the Indians.

Henry C. Gilbert was the Indian Agent during the Treaty of 1854 and oversaw the 1855 annuity payment along with Commissioner of Indian Affairs George Manypenny (Branch County Photographs).
Both the man and woman, with rational vehemence and volubility–and both at once, of course, utterly denied having ‘a dhrop in the house, more nor a little jug full, which we just kape by us, like, for saysonin’ the vittals, and sickness.’ But, unfortunately for the veracity of the parties, on searching the premises, the interpreter discovered, in a little back wood-shed, two barrels of whiskey, besides the ‘little jug’ which proved to be a two gallon one, and full.
Mr. Gilbert ordered some of his men to roll the barrels out on the green, where in the presence of the whole council, they knocked in head, and the jug broken. But the flow of whisky was as nothing compared with the Irish wife’s temper, meanwhile. I had never conceived it possible for a tongue to possess such leverage; it seemed literally to be ‘hung in the middle and to work both ways.’ However, mother Earth drank the whisky, and the abuse melted into ‘the circumambient air’–though one would not have suspected their volubility, they seemed to be such concrete masses of venom.
In the evening of the same day, as Col. Monypenny was walking out with a friend, he encountered and was accosted by, the Irish whisky vender.
‘The first star of the avenin’ to yees, Misther Commissioner! An’ sure it was a bad thrick ye were putting on a poor mon, this mornin’. Och, murther! to think how ye dissipayted the illegant whisky; but ye’ll not be doin’ less nor payin’ me the first cost of it, will ye?’
‘On the contrary,’ said the commissioner, ‘we are thinking of having you up in the morning, and fining you; and if we catch you selling another drop to the Indians, we shall forcibly remove you from the island.’
Quick as–but I despair of a simile, for surely there is no operation of nature or art that will furnish a parallel to the agility of an Irishman’s wit–his whole tone and manner changed, and dropping his voice to the pitch confidential, he said:
‘Wll, Misther Commissioner, an’ its truth I’m tellin’ ye–its mighty glad I was, intirely, to see the dirty barrels beheaded; sure I’d a done it meself, for the moral of the thing, ef it hadn’t been for the ould woman. Good avenin’ to ye, Misther Commissioner.’
It is hardly necessary to add that no further application was made for the ‘first cost of it.’
Very truly yours.
~ Western Reserve chronicle. (Warren, Ohio) November 07, 1855
(Library of Congress Chronicling America Historic Newspaper Collection)
The sale of alcohol was illegal at La Pointe at that time. However, the law was generally impossible to enforce and liquor flowed freely into and out of the island.
Admittedly I chuckled at the depiction of the Irish wit and the temper of the “Irish wife,” but as a descendant of immigrants who fled the Great Famine in the 1840s, it’s hard to read the condescending stereotypes my ancestors would have been subjected to.
That said, it’s important to note that the two or three Ojibwe people in this story were imprisoned without charges or trial for drinking, while the couple selling the illegal liquor only lost his stock and wasn’t fined. This is something those of us of European descent need to be careful of when trying to draw equivalencies.
So then who was the bona fide, unmitigated Irishman?
Hundreds of thousands of Irish immigrants came to America during the 1840s and ’50s. Inevitably, some of them ended up in this area. However, by 1855 it was only a handful.
Just a few weeks prior to the payment, Alexis Carpentier, a former voyageur from a mixed French-Ojibwe family was charged with taking the Wisconsin State Census for La Pointe County. He found 37 residents of foreign birth. Most of these were French or mix-blooded men, born in Canada, who married into local Ojibwe and mix-blood families.
In only one household, more than one person is listed as being foreign-born. This was the home of Patric Sullivan. State censuses only listed the name of the head of household and do not list country of origin. However, in the 1860 Federal census, we find Patrick and Johanna Sullivan living with their three sons in La Pointe township. Both were born in Ireland.

Page 1 of 1855 Wisconsin State Census for La Pointe County (familysearch.org)

Pages 2 and 3. Patric Sullivan is fourth from the bottom on the right side. enlarge
Patrick Sullivan did not sign the LaPoint Agreement to Stop Whiskey Trade of September 10, 1855. In fact, I haven’t been able to find much information at all about Patrick and Johanna Sullivan in later years. It does appear the family stayed in the area and their children were still living in Ashland at the dawn of the 20th century.
Finally, since this post deals with the 1855 census and issues of race and identity, it’s worth noting another interesting fact. The state census had only two categories for race: “White” and “Colored.” As non-citizens, full-blooded Ojibwe people would not have been counted among the 447 names on the census. However, it seems that Carpentier and his boss, La Pointe town clerk Samuel S. Vaughn, were not sure how to categorize by race.
Carpentier crossed out the designation “Colored” and replaced it with “Half-Breed.” By their count, 329 “Half-Breeds” and 118 Whites (many of them in mixed families) lived in La Pointe County in 1855. Mix-bloods were considered Ojibwe tribal members under the Treaty of 1847. However, they traditionally had their own identity and were thought eligible for U.S. citizenship.
One wonders what conversations were had as the census was completed, but in the final compilation, all 447 names (including several core Red Cliff and Bad River families) were submitted to the state as “White” rather than “Colored.” Despite America’s best efforts to create a racial duality, which would only intensify following the Civil War, this region would continue to defy such categorization for the remainder of the 19th century.
Sources:
Kohl, J. G. Kitchi-Gami: Life among the Lake Superior Ojibway. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 1985. Print.
Miller, Kerby A. Emigrants and Exiles: Ireland and the Irish Exodus to North America. New York: Oxford UP, 1985. Print.
NOTES: Research originally featured on Chequamegon History is featured in the new Changing Currents exhibit opening today at the Chippewa Valley Museum in Eau Claire. I had a chance to preview the exhibit on Friday, and John Vanek and crew have created an incredibly well-done display of Ojibwe treaty and removal politics of the mid 1800s. See their website for more information. The research found in this exhibit, which extends into several topics, is very deep and does not shy away from uncomfortable topics. I highly recommend it.
There may be some exciting guest research featured on Chequamegon History in the coming months dealing with the aftermath of the 1854 Treaty and fraudulent land claims in the Penokee Iron Range. Stay tuned.
Steamboats, Celebrities, Soo Shipping, and Superior Speculation: Joseph R. Williams’ Account of the 1855 Payment
July 30, 2014
By Leo
“They fade, they perish, as the grass of the prairies withers before the devouring element. The officers of our government, in their conference, have been accustomed to talk about the protection their Great Father vouchsafes to them, but it is the protection which the vulture affords the sparrow. Whatever may be the intentions of our professedly paternal government, no alternative seems to remain to the Indian, but submission to its crushing and onward march.”
-Joseph R. Williams, 1855
When Joseph R. Williams stepped out from the steamboat Planet onto the dock at La Pointe in August of 1855 he tried to make sense out of the scene before him. The arrival of the Toledo-based newspaper editor and hundreds of his fellow passengers, including dignitaries, celebrities, and politicians at Madeline Island coincided with the arrival of thousands of members of the Lake Superior Ojibwe bands for the first annuity payment under the Treaty of 1854.
The portrayal of the Chequamegon region in history would never be the same.
Prior to that year, the main story depicted in the written record is the expansion of the indigenous Ojibwe and Ojibwe-French mix-blood populations, their interactions with the nations of France, Britain, and the Dakota Sioux, and ultimately their attempt to defend their lands and sovereignty against an ever-encroaching United States.
After 1855, the Ojibwe and even the first-wave white settlers appear in the written history only as curious relics of a bygone age. They are an afterthought to the story of “progress”: shipping, real estate, mining, logging, and tourism. This second version of history, what I often call “Shipwrecks and Lighthouses” still dominates today. Much of it has been written by outsiders and newcomers, and it is a more sanitary history. It’s heavy on human triumph and light on controversy, but ultimately it conceals the earlier more-interesting history and its legacy.
If we could pick one event to mark this shift, what would it be? Was it the death of Chief Buffalo that summer of 1855? Was it the creation of the reservations? Was it the new Indian policies in Washington? While those events are related, and each is significant in its own right, none explains why the ideology of Manifest Destiny (as expressed by men like Williams) so swiftly and thoroughly took over the written record.
No, if there is one event that gets credit (or I would argue blame) for changing the tone of history in the summer of 1855, it was that the first vessels passed through the new canal at Sault Ste. Marie.
The Soo Locks and Superior
The St. Mary’s Falls Canal, or the Soo Locks as we commonly call them today, had been a dream of Great Lakes industrialists and the State of Michigan for years. In their view, Lake Superior was essentially cut off from the rest of the United States because all its water passes through Sault Ste. Marie, dropping over twenty feet as it drains into Lake Huron.
These falls, or more accurately rapids, were of immense economic, symbolic, and strategic value to the Ojibwe people. The French, British, and American governments also recognized their significance as a gateway to Lake Superior and beyond. However, for the merchants of Detroit, Cleveland, and Buffalo, drawn to Lake Superior by the copper mines of the Upper Peninsula or the rich iron deposits on the North Shore (opened up by the Treaty of 1854), the falls were only an obstacle to be overcome. Traders and speculators in the western part of Lake Superior also stood to gain from increased shipping traffic and eagerly watched the progress on the canal. We can see this in the amount of space Joseph Austrian, brother of La Pointe merchant Julius Austrian, gave the canal in his memoirs.
For the young city of Superior, the opening of the canal was seen as one of the critical steps toward becoming the next St. Louis or Chicago. In 1855, Duluth did not exist. Squatters had made claims on the Minnesota side under the Preemption Act, but the real action was on the Wisconsin side where a faction of Americans led by Col. D. A. Robinson was locked in a full-on real estate speculation battle with Sen. Henry M. Rice of Minnesota. Rice, had many La Pointe traders including Vincent Roy Jr. wrapped up in his scheme, but without the lifeline of the canal, neither faction would have the settlers, goods, or commerce necessary to grow the city beyond its few hundred residents.

Steamer North Star: From American Steam Vessels, page 40 by Samuel Ward Stanton (Wikimedia Images)
The Steamers
When the first steamboats embarked on the lower Great Lakes in the 1810s, few large sailing vessels had ever appeared on Lake Superior. Birchbark canoes and Mackinac boats provided virtually all the shipping traffic. Brought by the copper rush in the Upper Peninsula, a few steamers appeared on Lake Superior in the late 1840s and early 1850s but these were modified from earlier sailing ships or painfully brought overland around the Sault. Once on Lake Superior, these vessels were confined and could no longer go back and forth to Mackinaw, Detroit, or beyond. These steamers did carry passengers, but primarily their job was to go back and forth from the copper mines to the Sault.
The opening of the canal on June 22, 1855, however, brought a new type of steamer all the way to the western end of Lake Superior. The North Star, Illinois, and Planet were massive, brightly-painted, beauties with grand dining halls with live music. They could luxuriously carry hundreds of passengers from Cleveland to Superior and back in a little over a week, a trip that had previously taken three weeks.
Decrease travel time also meant that news could travel back and forth much more quickly. Chequamegon Bay residents could get newspaper articles about unfolding war in the Crimea and the bloody fallout from the Kansas-Nebraska Act. And on June 12, 1855 the first issue of the weekly Superior Chronicle appeared off the presses of John C. Wise and Washington Ashton of Superior. The paper printed literature, world news, local events and advertisements, but large portions of its pages were devoted to economic opportunities and descriptions of the Superior area. Conspicuously absent from its pages is much mention at all of the politics of the local Ojibwe bands or any indication whatsoever that Ojibwe and mix-blooded families made up the largest percentage of the area’s population. In this way, the Chronicle, being backed by Henry Rice, was as much about promoting Superior to the outside world as it was about bringing news in.
Advertisements began to appear in the eastern papers…

New-York daily tribune. August 04, 1855 (Image provided by Library of Congress, Washington, DC Persistent link: http://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn83030213/1855-08-04/ed-1/seq-3/)
…and the press took notice:
THE NEW YORK MIRROR says: “The fashionable watering places are not nearly as full as they were a year ago at this season; one reason for the falling off is, that thousands who have hitherto summered at these resorts have gone to Europe; and another is that the hard times of last autumn and winter have left their pinching reminiscences in many men’s purses.” The editor of the Sandusky Register seems to think that if these “fashionables” would cease to frequent Saratoga, Newport and Niagra, where $100 goes just far enough to make a waiter smile, there would be no cause for complaints of “too poor to spend the season North.”–When the snobs and devotees at the shrine of show and fashion learn that there are such places as Lake Superior, as the Islands in Lake Erie, as St. Catherines in Canada, where to live costs no more than a residence at home, we might suppose no further cause for complaint of poverty would exist. But the fact is, “go where the crowd goes or go not at all” is the motto with the fashionables; and until the places above named become popular resorts they will receive the attention only of those whose good sense leads them to prefer pure air, quiet, the pleasures of boating, bathing, fishing, &c., to the follies of Saratoga or Newport. To those who would enjoy a healthful and truly agreeable resort we can but commend the islands in Lake Erie, with a trip to the Upper Lake of Superior.
Bedford [IN] White River Standard, July 26, 1855

North Star: from American Steam Vessels by Samuel Ward Stanton, 1895 (Google Books).
By the time the August payment rolled around, steamers carrying hundreds of passengers from the highest rungs of American society. Chequamegon Bay had become a tourist destination.
The Tourists

Prof. J. G. Kohl (Wikimedia Images)
Johann Georg Kohl is a familiar name to readers of the Chequamegon History website. Kohl’s Kitchi Gami, originally published in his native Germany, is a standard of Ojibwe cultural history and anthropology. His astute observations and willingness to actually ask questions about unfamiliar cultural practices of the people practicing them, created a work that has stood the test of time much better than those of his contemporaries. The modern reader will find Kohl’s depiction of Ojibwe people as actual intelligent human beings stands in refreshing contrast to most 19th-century works. Kohl also wrote some untranslated articles for German newspapers mentioning his time at La Pointe. One of these, on the subject of the death and conversion of Chief Buffalo, partially appeared on this site back in April.
Johann Kohl was atypical of the steamboat tourists, but he was a steamboat tourist nonetheless:
Prof. Kohl, professor in Dresden University has been rusticating for a few weeks past, in the Lake Superior Country, collecting matter for a forthcoming work, which he intends publishing after his return to Germany. He expressed himself highly pleased with his visit, and remarked that the more familiar he became with the American people and the resources of our country, the better satisfied he was that America had fallen into the hands of those who were perfectly competent to develop her riches and improve the natural sources of wealth and prosperity, which nature has given her.
Grace Greenwood has also been paying her respects to the Lake Superior region, and came down on the North Star with Prof. Kohl.
[Milwaukee] Daily Free Democrat, September 15, 1855

Sara Jane Lippincott, a.k.a. Grace Greenwood (Wikimedia Images).
“Grace Greenwood” was the pseudonym of Sara Jane Lippincott, and a household name in 1855. Though more forgotten to history than some of the other names in this post, the New York native was probably the biggest celebrity to visit La Pointe in the summer of 1855. As an acclaimed poet, she had risen to the highest rungs of American literary society and was a strong advocate of abolitionism and women’s rights. However, she was probably best known as the editor of The Little Pilgrim, a popular children’s magazine. She is mentioned in several accounts of the 1855 payment, but none mention an important detail, considered improper for the time, detail. Sara was very pregnant. Annie Grace Lippincott was born less than two months after her mother left Lake Superior on the North Star.
Although much of her work is digitized and online for the public, the only mention of the trip I’ve found from her pen is this blurb from the front page of the September 1855 edition of The Little Pilgrim:
Our little readers will please forgive whatever delay there may be in the coming of our paper this month, for we are among the wild Indians away up in Lake Superior on the island of La Pointe; and the mails from this far region are so slow and irregular that our articles may not reach Philadelphia till two or three weeks after they should do so (The Little Pilgrim: Google Books).
Dr. Richard F. Morse was one of the chroniclers of the 1855 payment who made sure to mention Lippincott. Morse’s essay, The Chippewas of Lake Superior, published in the third volume of the Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin (1857), is entirely about the payment. It is also the clearest example of the abrupt shift in narrative discussed above. It is full of the suffocating racism of benevolent paternalism. Morse arrogantly portrays himself as an advocate for the Lake Superior bands, but his analysis shows how little he knows of the Ojibwe and their political situation in 1855. Unlike Kohl, he doesn’t seem to care enough to ask and learn.
In fairness, Morse’s account is a valuable document, excerpted in several posts on this website (see People Index). It is also the document that years ago inspired the first steps toward this research by planting the question, “Where did all these fancy people at the 1855 annuity come from?” Chippewas of Lake Superior is too long and too well-known to bother reproducing on this site, but it can be read in it’s entirety on Google Books.

Crockett McElroy (Cyclopedia of Michigan [1890])
After the Civil War, McElroy would go on to find wealth in the Great Lakes shipping industry and be elected as a Republican to several offices in the State of Michigan. In the summer of 1855, however, he was only nineteen years old and looking for work. Crockett’s father, Francis McElroy appears in several later 19th-century censuses as a resident of Bayfield. Apparently, Francis (along with Crockett’s younger brothers) split time between Bayfield and Michigan. Young Crockett did not stay in Bayfield, but his biography in the Cyclopedia of Michigan (1890) suggest his account can be considered that of a semi-local laborer in contrast to the fancier visitors he would have shared a steamboat with:
Crocket McElroy, the subject of this sketch, received his early education at Gait, Ontario; and, when twelve years of age, removed to Detroit. Here he attended one of. the public schools of that city for a short time, and, afterwards, a commercial academy. When thirteen years of age, he began to act as clerk in a wholesale and retail grocery store, remaining three years; he then, for two years, sold small beer. In 1853 he went to Ira, St. Clair County, as clerk, to take charge of a general store; and for the next five years served as clerk and taught school, spending the summer months of 1854-55 in the Lake Superior region (pg. 310).

Lewis Cass (Wikimedia Images)
Another Michigan-based politician, considerably more famous than McElroy, Lewis Cass’ excursion to Lake Superior in 1855 was portrayed as a homecoming of sorts. The 72 year-old Michigan senator had by then occupied several high-level cabinet and congressional positions, and was the Democratic nominee for president in 1848, but those came after he had already entered the American popular imagination. Thirty-five years earlier, as a little known governor of the Michigan Territory (which included Wisconsin and the arrowhead of Minnesota) he led an American expedition to Red Cedar (Cass) Lake near the headwaters of the Mississippi. Thirty-seven years after the Treaty of Paris, and seven years after the death of Tecumseh, it was the first real attempt by the United States to assert dominion over the Lake Superior country. In some ways, 1855 marked the end of that colonization process and brought the Cass Expedition full-circle, the significance of which was not lost on the editors of the Superior Chronicle:
The Predictions of Gen. Cass.: At the opening of the Wabash and Erie Canal, which unites the waters of Lake Erie with those of the Mississippi, the celebration of which took place at Fort Wayne, Indiana, in 1844, Gen. Cass in his address subsequently predicted the union of Lake Michigan from Chicago to the Mississippi; this prediction was fulfilled in 1850. At the same time he said that there were then present those who would witness the settlement of the region at the southwest extremity of Lake Superior, and lay the foundation for a similar union of the waters of that lake with the Mississippi.
On the last trip of the steamer Illinois to this place, Gen. Cass was among the passengers, and witnessed the fulfillment of his prediction in respect to the settlement of this region. May he live to be present at the opening of the channel which will connect this end of the lake with the Mississippi, and witness the consummation of all his prophesies.
Superior Chronicle, August 21, 1855

Charles Sumner in 1855 (Wikimedia Images)
A political opponent of western Democrats like Cass, Charles Sumner has gone down in history as the only man to be nearly beaten to death on the floor of the United States senate. Less than a year before Rep. Preston Brooks of South Carolina would attack him with a cane, sending the country hurtling ever-faster toward civil war, the Massachusetts senator visited La Pointe to watch the annuity payment. By 1855, Sumner already had a reputation as a staunch abolitionist, and he even wrote a letter to the Anti-Slavery Reporter while on board the North Star. Aside from a handful of like-minded native New Englanders like Edmund Ely and Leonard Wheeler, Sumner was not in a part of the country where most voters shared his views (the full-blood and most mix-blood Ojibwe were not considered citizens and therefore ineligible to vote). The Lake Superior country was overwhelmingly Democratic, and the Superior Chronicle praised the “popular sovereignty” views of Stephen Douglas in the midst of the violence following the Kansas-Nebraska Act. Sumner, whose caning resulted from his fierce criticism of popular sovereignty, was among those “radical Bostonians” the Chronicle warned its readers about. However, the newspaper was kind and uncritical when the senator appeared in its city:
Senator Sumner at Superior and La Pointe.: In our last number we neglected to announce the visit of Hon. Charles Sumner, Bishop McClosky, and other distinguished persons to Superior. They came by the North Star, and staying but a few hours, had merely time to hastily view our thriving town. They expressed gratfication at its admirable location and rapidity of its growth.
At La Pointe, the heat stopped to allow the passengers an opportunity to see that pretty village and the large number of Indians and others congregating there to the last great payment at this station of the Lake Superior Chippewas. Here Mr. Sumner was the guest of the reverend Catholic missionary, whose successful endeavors to gratify the numerous visitors at La Pointe we have frequently heard commended.
Superior Chronicle, August 14, 1855

Jesse D. Bright (Wikimedia Images)
Staying a little longer at Superior, another U.S. senator, Jesse Bright the President pro tempore Indiana, also appeared on Lake Superior in the summer of 1855. For Bright, however, this was more than a pleasure excursion. He had a chance to make real money in the real estate boom of the 1850s. Superior, at the head of the lake with ship traffic through the Soo, and military road and potential railroad connection to St. Paul, looked poised to be the next great gateway to the west. He invested and apparently lost big when the Great Lakes real-estate boom busted in the Panic of 1857.
Bright would go on to be a Southern sympathizer and a “Copperhead” during the Civil War and was the only northerner to be expelled from the Senate for supporting the Confederacy. In 1855, he was already a controversial figure in the partisan (Democrat, Whig, Know-Nothing) newspapers:
The Buffalo Commercial, upon the authority of the Cincinnati Gazette, states “that Mr. Bright, of Indiana, President of the Senate, pro tem lately made a Sunday speech, an hour and a half long to the people of a town on Lake Superior, and the passengers of the steamer in which he was travelling. He discoursed most eloquently on the virtues and glories of modern Democracy, whose greatest exemplar, he said, was the administration of Franklin Pierce.” The Know Nothing press, of which the Commercial and the Gazette are leading journals, must be rather hard up for material, when recourse to such misrepresentation as the above becomes necessary…
…The speaker did not allude to politics, and did not speak over ten minutes.
And out of this mole hill the Commercial manufactures a mountain of speculation, headed “Jesse D. Bright–The Presidency.” –Sandusky Mirror.
Fort Wayne [IN] Sentinel, September 5, 1855

Promoters & Proprietors of Old Superior: (Clockwise from upper left) U.S. Senator W[illiam]. A. Richardson, Sen. R[obert] M. T. Hunter, Sen. Jesse Bright, Sen. John C. Breckinridge, Benjamin Brunson, Col. John W. Fourney, Henry M. Rice (Flower, Frank A. Report of the City Statistician [1890] Digitized by Google Books)

John C. Breckinridge (Wikimedia Images)
It may also be uncomfortable for the modern northern reader to see how cozy the politicians of our area were with unabashedly pro-slavery Democrats and future Confederates. The biggest name among these Lake Superior investors and 1855 visitors would be John C. Breckinridge. Breckinridge, coming off a stint as U.S. Representative from Kentucky, would go on to be Vice President of the United States under James Buchanan, and Secretary of War for the Confederacy. However, he is most famous for finishing second to Abraham Lincoln in the pivotal presidential election of 1860. Chequamegon Bay residents will probably find another investment of the future vice-president more interesting even than the Superior scheme:
A PLEASANT SUMMER RESIDENCE–The senior editor of the Chicago Press writes from Lake Superior:
Basswood Island, one of the group of Apostle Island has been entered by Mr. Breckinridge of Kentucky, who, I am told, contemplates the erection of a summer residence upon it. We landed at this Island for wood. There is deep water up to its base, and our steamer lay close alongside the rocky shore as though it had been a pier erected for the purpose. There is deep water, I am told, in the channels between most of the Islands of the group furnished an excellent shelter for vessels in tempestuous weather.
[Milwaukee] Weekly Wisconsin, August 15, 1855
Hon J. C. Breckenridge, of Kentucky, has purchased Basswood Island, one of the group of Apostle Islands, in Lake Superior, and intends erecting a summer residence thereon.
Boston Post, August 23, 1855

Captain John Wilson (Frank Leslie’s Illustrated)
The Whig/Free Soil press’ condemnation of Senator Bright for allegedly forgetting the Sabbath and to keep it holy may remind the Chequamegon History reader of the A.B.C.F.M missionaries’ obsession with that particular commandment in their efforts among the Ojibwe people. However, it seems to be one of those features of 19th-Century America that was fussed about more than it was actually observed.
A good example of this comes from Captain John Wilson, who led the steamer Illinois to La Pointe in the summer of 1855. He seems to have been one of those larger-than-life characters, and he is often mentioned in newspaper accounts from the various Great Lakes ships he commanded. Wilson died off the shore of Milwaukee in the sinking of the Lady Elgin, in 1860 along with over 300 passengers. “The Titanic of the Great Lakes,” as the disaster came to be known, is still the greatest loss of life in the history of the lakes (this article gives a good overview). Other than the North Star, the Lady Elgin, which began its runs to the “Upper Lake” in 1855, was probably the most famous steamer on Lake Superior before its sinking. Captain Wilson was afterwards praised for his character heroism during the ordeal, which was blamed on the captain of the schooner that collided with the Elgin.
Captain Wilson’s charisma shines through in the following 1855 Lake Superior account, but I’ll let the reader be the judge of his character:
A MAN FOR ALL OCCASIONS–TWO AMUSEMENTS–Capt Wilson, of the steamer Illinois, on the Upper Lakes is proverbially a man for all occasions and is equally at home in a horse-race or a dance. During a recent excursion of his beautiful boat to Lake Superior, he happened to arrive at a place on Sunday, where several tribes of Indians were soon to receive their annuity from the General Government and where a large number were already present. As soon as the breakfast table was cleared Capt. W. commenced arrangements for religious services in the ladies’ cabin, agreeably to the request of a preacher on board. Chairs and sofa were placed across the hall and the piano, with a large bible on it, represented a pulpit. The large bell of the boat was tolled, and in a short time quite a respectable congregation occupied the seats. As soon as service had fairly begun, the Captain came upon the forward deck where a number of gentlemen were enjoying their pipes and meerschaum, and thus addressed them.
Gentlemen–I come to let you know that meetin‘ is now going on in the aft cabin, where all of you in need of prayers and who wish to hear a good sermon had better retire. I would also state that in accordance with the desire of several passengers , I intend to get up an Indian foot race on shore for a barrel of flour.–You can make your own selection of the two amusements.”
The foot race did come off, and it was fortunate that all the lady passengers were at “meetin,” as one of the Indians who started with nothing on him but a calico shirt came in minus that! He won the flour, however. Good for you! —Spirit of the Times
[Milwaukee] Weekly Wisconsin, October 3, 1855

Joseph R. Williams (Wikimedia Images)
Finally, we get back to Joseph R. Williams. The reason so many stories like Captain Wilson’s made it into the papers that summer was that each of the steamboats seemed to be carrying one or more Midwestern newspaper editors. Williams, the editor of the Toledo Blade, arrived on the Planet in time to witness the La Pointe payment.
Williams would go on to become the first president of what would become Michigan State University and serve in multiple positions in the state government in Michigan. His letters and notes from Lake Superior turned into multiple articles that made their way back up to the Superior Chronicle. In a later post, I may transcribe his record of C. C. Trowbridge’s account of the 1820 Cass Expedition or his description of Superior, but in the name of brevity, I’ll limit this post to his a article on the payment itself:
From La Pointe–Indian Payment, etc.
The following interesting incidents of the recent meeting of Chippeways at La Pointe are taken from the letters of Mr. Williams, editor of the Toledo Blade. Mr. W. was among those who visited Lake Superior on the last excursion of the steamer Planet. In another portion of this week’s paper will be made an account of General Cass’ expedition to the Northwest, from the pen of the same gentleman. We commend it and the following extracts, to the perusal of our readers.
This is one of the old American Fur Company’s stations, a village such as formerly existed at Detroit and Mackinac. Indian huts with bark roofs, the long low warehouse, the half dressed and painted Indians, here and there a Frenchman speaking his mother tongue, his whole air indicating his lineage plainly that he was the descendant of an old voyager, revive the reflection of those days so graphically described by Washington Irving in his Astoria. La Pointe is upon an island, and the harbor gracefully curves around us from the north.
Here we find Colonel Manypenny, Commissioner of Indian Affairs; H. C. Gilbert, Indian Agent for Michigan; Hon. D. A. Noble and Hon. H. L. Stevens, late members of Congress, and other gentlemen, who are awaiting the Indian payment to take place the beginning of next month. Grace Greenwood, who came up on the Illinois a few days since is also excursioning here. The store houses are full of the goods provided for the payment, piles of [?] and provisions, [?], plows, spades, [?] carts, mattresses, bedsteads, blankets, clothing, and [?] a well [?] supply of such articles as are calculated to promote the comfort and civilization of the ill-fated remnant of the former lords of these [many] isles scattered around us, and [the] “forests primeval,” on either shore of this vast inland sea.
Colonel Manypenny deserves great credit for the [ind?bility] with which he has endeavoured to carry into wholesale effect the [?] method adopted of paying the Indians their annuities. Formerly, the unfortunate [race] were paid in specie, and close on the tract of the dispenser of the payment came a swarm of cormorant and heartless Indians traders, who, for whisky and trinkets, and inferior arms and implements, including perhaps blankets and some useful articles of dress, obtained the dollars as soon as they were paid. The Indian dances followed by wild drunken orgies, were a perpetual accompaniment. The Indian, besotted by liquor, parted with almost everything of value, and returned to his home and his hunting grounds, poor and in worse condition than he came. Many years since I attended a payment at Grand Rapids, Michigan, and it was a mournful spectacle. One hardly knew whether to pity the weakness of the victims or abhor the heartlessness of the destroyers most. As late as 1833 the last Indian payment was made on the Maumee in the immediate vicinity of Toledo, on the point below Manhattan. One Lloyd was Indian Agent in 1830. It is said that he purloined from each of the thousand dollar boxes paid the Indians one or two hundred dollars, and that during the night whites went around among the wigwams and cut off the portion of the dresses of the Indians in which the specie was tied up. But the picture before us is relieved of features so disgraceful and disgusting. We saw no drunken Indian on shore. Indeed several of the Caucasian lords of these fading tribes, whom we had on board, might have taken a useful lesson in sobriety from the red men. The traders however are here. They mutter curses upon Colonel Manypenny, because he does not wink at their robberies. It is supposed abundance of whisky is concealed on the island, which will be unwrapped and sold, to besot the Indians, as soon at the valuables are distributed among them.
***
On his arrival here, the Indians proposed a dance. As dances end in Bacchanalian revels, the colonel has set his face against them. Enlivened and excited, however, by our band of music, the Indians could resist no longer. A dozen or more emerged from their cabins, bearing before them their war flag, which was a staff with a fringe of long feathers extending its length, and with bells attached to it, and engaged in a war dance. Their bodies were nearly naked and painted. The dance was a pantomimic description of war scenes. The leading brave struck the flagstaff to stop the dance, and made a speech describing how he had, less than thirty days ago, killed and scalped a Sioux, and he held up in his clenched fist, in triumph before us, the almost yet reeking scalp of his victim. His speech was accompanied by vigorous and appropriate [motion]. It was the imprompt and natural movement of body, [hands], and features from this brief specimen, it was easy enough to imagine that the Indian is often eloquent. This small band of dancers were splendid physical specimens of men, and the dance was real exultation over a late actual achievement. The Chippeways–and they are all Chippeways in these regions–maintain a traditional hostility to the Sioux, and are rarely at peace. It was only a few months since a band of Chippeways pioneered down into the village of St. Paul, and killed a Sioux woman trading in a store. Before the witnesses had recovered from the terror excited, the band had fled as rapidly as they appeared. The Sioux remain on the lands beyond, and the Chippeways this side of the Mississippi.
After the war dance was finished, they danced a beggar’s dance, the purport of which was that they wanted three beeves of Colonel Manypenny. At its close, the brave presented a pipe to Captain Ward, who smoked it in a token of amity. He then forced through the surrounding crowd, and sought Colonel M., who stood at a distance. The Colonel rejected the proffered pipe. His acceptance would have been a sanction of the dances he disapproved, and a concession of the three beeves. The Chief returned to the ring, and made a brief vehement speech, evidently a concentration of indignant scorn. Mrs. A., of Monroe, Michigan, an educated lady of Indian blood, informed me that it was full of defiance, bitterness and mortification.
******
In speaking of the Indians assembled at the payment in my last, I said they were a motley crew, and indeed they are. The braves, engaged in the dances described, were fine specimens of manhood. Their erect forms, developed chests, and symmetry, and general health, as developed in every muscle and feature, illustrate the perfection to which physical man is brought in savage life. But in sad contrast, we see around us pitiable specimens of humanity, crouching, lazy, filthy, besotted beings, who possess all the vices of both the white and the red races, and none of the virtues of either.
Canoes are marshalled along the beach, which have wafted here the tenants of both shores of Superior. Indians have dotted their clusters of wigwams over the vicinity, and seem to have brought along all their aged and infirm as well as infants.
I think one Indian woman here is the oldest human being I ever saw. The deep furrows, the folds of skin which have lost almost the appearance of vitality, so withered and dead as to resemble gutta percha, eye sight lost, hearing gone, no sense left except touch, which was indicated by the avidity with which she seized small pieces of money thrown into her lap, all these proofs convinced me that she was older by ten or fifteen years than any person I ever saw. A son and daughter were near her, apparently kind and affectionate, and proud to protect her, who themselves, were verging upon old age, an illustrative example of these [?ate] savages, to unnatural whites of whom melancholy tales of ingratitude are told. Even her children could not tell her age. All they could say was that she was “the oldest Indian.” Old Buffalo, the Chief, who was ninety years old, looked like a young man compared with her.
Nothing more surprised our party than the great proportion of their children, of all sizes, and I may add, shades of color, for the infusion of French blood from a long series of successive intermarriages, is found in every tribe. Infants fastened on boards, with the children and youth under sixteen, outnumber the adults. The children are all plump, all have rounded and full muscles, all good chests, thus showing that their life, vicious as it is, is more favorable to health and development, in consequence of their freedom of motion, perpetual exercise in the open air. Their gregariousness, flocking together where impulse carried them, as self reliant as their parents who seemed to allow them perfect freedom, even though strangers were so numerous among them, bore a pleasing, and to us instructive contrast to the entire and melancholy helplessness to which white children, especially in cities, are doomed.
Many of the Indians wore a feather or feathers in their cap, indicating the number of Sioux they had scalped. One displayed six feathers. He told us that he had in battle killed two, and taken the scalps of four others, killed by unknown hands of his band. The last victim he had slain but a month ago. One erect youth, of not more than eighteen, with a fresh and handsome face, bore proudly a single feather as a token of his early prowess. One man, in answer to the question, whether he had ever taken a scalp, replied gravely, without a smile, that he had not, and was of no more account that a woman in his tribe. An illustration of their generosity and savage ferocity is afforded by a sub-Chief who had an interview with Mr. Gilbert, the Indian Agent, a few days since. He presented Mr. G. an elegant cloak, made entirely of beaver skins, in expectation of nothing but a large medal in return. He was intent in speech, and animated and pleasant in address. No trace of savage ferocity lingered in his face. Yet it was stated that this man had actually killed and eaten his own child.
Sometimes their earnings if economically used would afford them a comfortable subsistence. The whites, even in their ordinary trade have practiced habitually heartless extortion. When Gov. Cass’s expedition visited this country in 1820, the Indians were in the habit of paying the traders a beaver skin, worth sixteen dollars, for a gill of powder; the same for a shirt; the same for thirty balls; and three beaver skins for a single blanket. I inquired of the Chief, Old Buffalo, what was the highest price he had ever paid for tobacco. He replied that they formerly made purchases of the Hudson Bay Company, tobacco was coiled up in ropes of about three quarters of an inch in diameter, and that he had paid ten beaver skins for a fathom, or at least ten dollars for a foot in length. But when the poor creatures became maniacs or idiots from drink, no possession was so prized that they would not part with it for a single cup of fire water. That the trader availed himself of the imbecility he created, is acknowledged. A large share of the boundless wealth of Mr. Astor was based on acquisitions, through his instruments and agents of this questionable and indeed diabolical character. Well might Burns exclaim in sorrow,
“Man’s inhumanity to man.
Makes countless thousands mourn.”
for whether among men and families of the same blood, or between civilized and savage men, either in peace or in the antagonism of war, the whole world and all time has teemed with sickening, heart-rending examples of its melancholy truth.
By chance we have been able to witness what can not be seen, a few years hence on this side of the “Father of waters,” or indeed on the continent. Here in our magnificent floating palace and the crowd of intellectual and cultivated people on board, surrounded by the refinements of life, we have the highest triumphs of civilization, side by side and in contrast with the rudest manifestations of primitive savage life.–An interesting episode in human affairs, though prompting [a] thousand sad reflections. The doom of entire extirpation of the red man seems surely and gradually to approach. The perpetual warfare among tribes on the extreme frontier annually declinates their most vigorous braves, and consequently it is manifest that among this tribe at least there were far more women than men between the ages of twenty and forty. Many perish from ignorance of the laws of nature, and many from excessive exposure and famine. Rapacity of the whites, and whiskey, finish the merciless work. They fade, they perish, as the grass of the prairies withers before the devouring element. The officers of our government, in their conference, have been accustomed to talk about the protection their Great Father vouchsafes to them, but it is the protection which the vulture affords the sparrow. Whatever may be the intentions of our professedly paternal government, no alternative seems to remain to the Indian, but submission to its crushing and onward march.

Dr. Bethune Duffield (Detroit–biographical sketches by Walter Buell [1886] Google Books)
1855 as a Turning Point: A plea to today’s Chequamegon Bay residents
Williams’ quote about the vulture and the sparrow, excerpted at the very top of this post, is about as succinct a statement about Manifest Destiny as I have ever read. If it weren’t surrounded by so many grossly-ignorant and disgusting statements about Ojibwe people, one might almost take it as sympathy for the Ojibwe cause. Still, the statement holds the key to our understanding of the story of 1855.
In the grand scheme of our region’s history, the payment was less significant than the treaty itself or the tragic removal politics of the early 1850s. Sure, it was the first payment under the final treaty and it featured the visit of Indian Affairs Commissioner George Manypenny to La Pointe, but ultimately it was largely like the rest of the 30-plus annuity payments that took place in our area in the middle of the 19th century. The death of Chief Buffalo in September 1855, and visit of Manypenny who shifted American Indian policy from removal to assimilation, represented both real and symbolic breaks with the past, but ultimately the great shift of 1855 is only one of tone.
Ultimately, however, this shift is only superficial and the reality of life for most Chequamegon residents didn’t change overnight in 1855. The careers of men like Blackbird, Vincent Roy Jr., Julius Austrian, Naaganab, and others show the artificiality of such a line. To them, the tourists on the Planet and North Star were probably just a distraction or curiosity.
Williams was wrong. The Ojibwe did not perish before the “devouring element,” and neither did that earlier history. Somehow, though, since then those of us who live in this area have allowed outsiders to write the story. Maybe it’s comfortable for those, like myself, of European ancestry to focus on shipwrecks and lighthouses rather than colonialism and dispossession, but in doing so we deny ourselves the most significant events of our area’s history and an understanding of its legacy on today.
By all means, learn the names of Grace Greenwood, John Breckinridge, and the Lady Elgin, but understand the fleeting impact of those names on our area’s history. Then, read up on Blackbird, Jechiikwii’o, Leonard Wheeler, Benjamin Armstrong and other players in 1855 politics who really did leave a lasting legacy.
Off my soapbox for now…
The bulk of this article comes from newspaper articles found on two digital archives. Access Newspaper Archive is available to Wisconsin library card holders through badgerlink.net. The Library of Congress Chronicling America site is free at http://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/. Other sources are linked within the post.
Chief Buffalo’s Death and Conversion: A new perspective
April 18, 2014
By Leo Filipczak
Chief Buffalo died at La Pointe on September 7, 1855 amid the festivities and controversy surrounding that year’s annuity payment. Just before his death, he converted to the Catholic faith, and thus was buried inside the fence of the Catholic cemetery rather than outside with the Ojibwe people who kept traditional religious practices.
His death was noted by multiple written sources at the time, but none seemed to really dive into the motives and symbolism behind his conversion. This invited speculation from later scholars, and I’ve heard and proposed a number of hypotheses about why Buffalo became Catholic.
Now, a newly uncovered document, from a familiar source, reveals new information. And while it may diminish the symbolic impact of Buffalo’s conversion, it gives further insight into an important man whose legend sometimes overshadows his life.
Buffalo’s Obituary
The most well-known account of Buffalo’s death is from an obituary that appeared in newspapers across the country. It was also recorded in the essay, The Chippewas of Lake Superior, by Dr. Richard F. Morse, who was an eyewitness to the 1855 payment.
While it’s not entirely clear if it was Morse himself who wrote the obituary, he seems to be a likely candidate. Much like the rest of Chippewas of Lake Superior, the obituary is riddled with the inaccuracies and betrays an unfamiliarity with La Pointe society:


From Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin, Volume 3 (Digitized by Google Books)
It isn’t hard to understand how this obituary could invite several interpretations, especially when combined with other sources of the era and the biases of 20th and 21st-century investigators (myself included) who are always looking for a symbolic or political explanation.
Here, we will evaluate these interpretations.
Was Buffalo sending a message to the Ojibwe about the future?
The obituary states, “No tongue like Buffalo’s could control and direct the different bands.” An easy interpretation might suggest that he was trying to send a message that assimilation to white culture was the way of the future, and that all the Ojibwe should follow his lead. We do see suggestions in the writings of Henry Schoolcraft and William Warren that might support this conclusion.
The problem with this interpretation is that no Ojibwe leader, not even Buffalo, had that level of influence. Even if he wanted to, which would have been completely contrary to Ojibwe tolerance of religious pluralism, he could not have pulled a Henry VIII and converted his whole nation.
In fact, by 1855, Buffalo’s influence was at an all-time low. Recent scholarship has countered the image crafted by Benjamin Armstrong and others, of a chief whose trip to Washington and leadership through the Treaty of 1854 made him more powerful in his final years. Consider this 1852 depiction in Wagner and Scherzer’s Reisen in Nordamerika:
…Here we have the hereditary Chippewa chief, whose generations (totem) are carved in the ancient birch bark,** giving us profuse thanks for just a modest silver coin and a piece of dry cloth. What time can bring to a ruler!
So, did Buffalo decide in the last days of his life that Christianity was superior to traditional ways?
The reason why the obituary and other contemporary sources don’t go into the reasons for Buffalo’s conversion was because they hold the implicit assumption that Christianity is the one true religion. Few 19th-century American readers would be asking why someone would convert. It was a given. 160 years later, we don’t make this assumption anymore, but it should be explored whether or not this was purely a religious decision on Buffalo’s part.
I have a difficult time believing this. Buffalo had nearly 100 years to convert to Christianity if he’d wanted to. The traditional Ojibwe, in general, were extremely resistant to conversion, and there are several sources depicting Buffalo as a leader in the Midewiwin. This continuation of the above quote from Wagner and Scherzer shows Buffalo’s relationship to those who felt the Ojibwe needed Christianity.
Strangely, we later learned that the majestic Old Buffalo was violently opposed for years to the education and spiritual progress of the Indians. Probably, it’s because he suspected a better instructed generation would no longer obey. Presently, he tacitly accepts the existence of the school and even visits sometimes, where like ourselves, he has the opportunity to see the gains made in this school with its stubborn, fastidious look of an old German high council.
Accounts like this suggest a political rather than a spiritual motive.
So, did Buffalo’s convert for political rather than spiritual reasons?
Some have tied Buffalo’s conversion to a split in the La Pointe Band after the Treaty of 1854, and it’s important to remember all the heated factional divisions that rose up during the 1855 payment. Until recently, my personal interpretation would have been that Buffalo’s conversion represented a final break with Blackbird and the other Bad River chiefs. Perhaps Buffalo felt alienated from most of the traditional Ojibwe after he found himself in the minority over the issue of debt payments. His final speech was short, and reveals disappointment and exasperation on the part of the aged leader.
By the time of his death, most of his remaining followers, including the mix-blooded Ojibwe of La Pointe, and several of his children were Catholic, while most Ojibwe remained traditional. Perhaps there was additional jealousy over clauses in the treaty that gave Buffalo a separate reservation at Red Cliff and an additional plot of land. We see hints of this division in the obituary when an unidentified Ojibwe man blames the government for Buffalo’s death. This all could be seen as a separation forming between a Catholic Red Cliff and a traditional Bad River.
This interpretation would be perfect if it wasn’t grossly oversimplified. The division didn’t just happen in 1854. The La Pointe Band had always really been several bands. Those, like Buffalo’s, that were most connected to the mix-bloods and traders stayed on the Island more, and the others stayed at Bad River more. Still, there were Catholics at Bad River, and traditional Ojibwe on the Island. This dynamic and Buffalo’s place in it, were well-established. He did not have to convert to be with the “Catholic” faction. He had been in it for years.
Some have questioned whether Buffalo really converted at all. From a political point of view, one could say his conversion was really a show for Commissioner Manypenny to counter Blackbird’s pants (read this post if you don’t know what I’m talking about). I see that as overly cynical and out of character for Buffalo. I also don’t think he was ignorant of what conversion meant. He understood the gravity of what he was deciding, and being a ninety-year-old chief, I don’t think he would have felt pressured to please anyone.
So if it wasn’t symbolic, political, or religious zeal, why did Buffalo convert?
The Kohl article
As he documented the 1855 payment, Richard Morse’s ethnocentric values prevented any meaningful understanding of Ojibwe culture. However, there was another white outsider present at La Pointe that summer who did attempt to understand Ojibwe people as fellow human beings. He had come all the way from Germany.
The name of Johann Georg Kohl will be familiar to many readers who know his work Kitchi-Gami: Wanderings Around Lake Superior (1860). Kohl’s desire to truly know and respect the people giving him information left us with what I consider the best anthropological writing ever done on this part of the world.
My biggest complaint with Kohl is that he typically doesn’t identify people by name. Maangozid, Gezhiiyaash, and Zhingwaakoons show up in his work, but he somehow manages to record Blackbird’s speech without naming the Bad River chief. In over 100 pages about life at La Pointe in 1855, Buffalo isn’t mentioned at all.
So, I was pretty excited to find an untranslated 1859 article from Kohl on Google Books in a German-language weekly. The journal, Das Ausland, is a collection of writings that a would describe as ethnographic with a missionary bent.
I was even more excited as I put it through Google Translate and realized it discussed Buffalo’s final summer and conversion. It has to go out to the English-speaking world.
So without further ado, here is the first seven paragraphs of Remarks on the Conversion of the Canadian Indians and some Stories of Conversion by Johann Kohl. I apologize for any errors arising from the electronic translation. I don’t speak German and I can only hope that someone who does will see this and translate the entire article.

J. G. Kohl (Wikimedia Images)
Das Ausland.
Eine Wochenschrift
fur
Kunde des geistigen und sittlichen Lebens der Völker
[The Foreign Lands: A weekly for scholars of the moral and intellectual lives of foreign nations]
Nr. 2 8 January 1859
Remarks on the Conversion of the Canadian Indians and some Stories of Conversion
By J.G. Kohl
A few years ago, when I was on “La Pointe,” one of the so-called “Apostle Islands” in the western corner of the great Lake Superior, there still lived the old chief of the local Indians, the Chippeway or Ojibbeway people, named “Buffalo,” a man “of nearly a hundred years.” He himself was still a pagan, but many of his children, grandchildren and closest relatives, were already Christians.
I was told that even the aged old Buffalo himself “ébranlé [was shaking]”, and they told me his state of mind was fluctuating. “He thinks highly of the Christian religion,” they told me, “It’s not right to him that he and his family be of a different faith. He is afraid that he will be separated in death. He knows he will not be near them, and that not only his body should be brought to another cemetery, but also he believes his spirit shall go into another paradise away from his children.”
But Buffalo was the main representative of his people, the living embodiment, so to speak, of the old traditions and stories of his tribe, which once ranged over not only the whole group of the Apostle Islands, but also far and wide across the hunting grounds of the mainland of northern Wisconsin. His ancestors and his family, “the Totem of the Loons” (from the diver)* make claim to be the most distinguished chiefly family of the Ojibbeways. Indeed, they believe that from them and their village a far-reaching dominion once reached across all the tribes of the Ojibbeway Nation. In a word, a kind of monarchy existed with them at the center.
(*The Loon, or Diver, is a well-known large North American bird).
Old Buffalo, or Le Boeuf, as the French call him, or Pishiki, his Indian name, was like the last reflection of the long-vanished glory. He was stuck too deep in the old superstition. He was too intertwined with the Medä Order, the Wabanos, and the Jossakids, or priesthood, of his people. A conversion to Christianity would have destroyed his influence in a still mostly-pagan tribe. It would have been the equivalent of voluntarily stepping down from the throne he previously had. Therefore, in spite of his “doubting” state of mind, he could not decide to accept the act of baptism.
One evening, I visited old Buffalo in his bark lodge, and found in him grayed and stooped by the years, but nevertheless still quite a sprightly old man. Who knows what kind of fate he had as an old Indian chief on Lake Superior, passing his whole life near the Sioux, trading with the North West Company, with the British and later with the Americans. With the Wabanos and Jossakids (priests and sorcerers) he conjured for his people, and communed with the sky, but here people would call him an “old sinner.”
But still, due to his advanced age I harbored a certain amount of respect for him myself. He took me in, so kindly, and never forgot even afterwards, promising to remember my visit, as if it had been an honor for him. He told me much of the old glory of his tribe, of the origin of his people, and of his religion from the East. I gave him tobacco, and he, much more generously,gave me a beautiful fife. I later learned from the newspapers that my old host, being ill, and soon after my departure from the island, he departed from this earth. I was seized by a genuine sorrow and grieved for him. Those papers, however, reported a certain cause for consolation, in that Buffalo had said on his deathbed, he desired to be buried in a Christian way. He had therefore received Christianity and the Lord’s Supper, shortly before his death, from the Catholic missionaries, both with the last rites of the Church, and with a church funeral and burial in the Catholic cemetery, where in addition to those already resting, his family would be buried.
The story and the end of the old Buffalo are not unique. Rather, it was something rather common for the ancient pagan to proceed only on his death-bed to Christianity, and it starts not with the elderly adults on their deathbeds, but with their Indian families beginning with their young children. The parents are then won over by the children. For the children, while they are young and largely without religion, the betrayal of the old gods and laws is not so great. Therefore, the parents give allow it more easily. You yourself are probably already convinced that there is something fairly good behind Christianity, and that their children “could do quite well.” They desire for their children to attain the blessing of the great Christian God and therefore often lead them to the missionaries, although they themselves may not decide to give up their own ingrained heathen beliefs. The Christians, therefore, also prefer to first contact the youth, and know well that if they have this first, the parents will follow sooner or later because they will not long endure the idea that they are separated from their children in the faith. Because they believe that baptism is “good medicine” for the children, they bring them very often to the missionaries when they are sick…

Das Ausland: Wochenschrift für Länder- u. Völkerkunde, Volumes 31-32. Only about a quarter of the article is translated above. The remaining pages largely consist of Kohl’s observations on the successes and failures of missionary efforts based on real anecdotes.
Conclusion
According to Johann Kohl, who knew Buffalo, the chief’s conversion wasn’t based on politics or any kind of belief that Ojibwe culture and religion was inferior. Buffalo converted because he wanted to be united with his family in death. This may make the conversion less significant from a historical perspective, but it helps us understand the man himself. For that reason, this is the most important document yet about the end of the great chief’s long life.
Sources:
Armstrong, Benj G., and Thomas P. Wentworth. Early Life among the Indians: Reminiscences from the Life of Benj. G. Armstrong : Treaties of 1835, 1837, 1842 and 1854 : Habits and Customs of the Red Men of the Forest : Incidents, Biographical Sketches, Battles, &c. Ashland, WI: Press of A.W. Bowron, 1892. Print.
Kohl, J. G. Kitchi-Gami: Wanderings round Lake Superior. London: Chapman and Hall, 1860. Print.
Loew, Patty. Indian Nations of Wisconsin: Histories of Endurance and Renewal. Madison: Wisconsin Historical Society, 2001. Print.
McElroy, Crocket. “An Indian Payment.” Americana v.5. American Historical Company, American Historical Society, National Americana Society Publishing Society of New York, 1910 (Digitized by Google Books) pages 298-302.
Morse, Richard F. “The Chippewas of Lake Superior.” Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin. Ed. Lyman C. Draper. Vol. 3. Madison: State Historical Society of Wisconsin, 1857. 338-69. Print.
Paap, Howard D. Red Cliff, Wisconsin: A History of an Ojibwe Community. St. Cloud, MN: North Star, 2013. Print.
Satz, Ronald N. Chippewa Treaty Rights: The Reserved Rights of Wisconsin’s Chippewa Indians in Historical Perspective. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters, 1991. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and times of an Ojibwe Leader. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2007. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe, and Seth Eastman. Historical and Statistical Information Respecting the History, Condition, and Prospects of the Indian Tribes of the United States: Collected and Prepared under the Direction of the Bureau of Indian Affairs per Act of Congress of March 3rd, 1847. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo, 1851. Print.
Wagner, Moritz, and Karl Von Scherzer. Reisen in Nordamerika in Den Jahren 1852 Und 1853. Leipzig: Arnold, 1854. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Blackbird’s Speech at the 1855 Payment
January 20, 2014
“We sold our land for our graves–that we might have a home, where the bones of our fathers are buried. We were not willing to sell the ashes of our relatives which are so dear to us. This was the reason why we sold our lands. It was not to pay debts over and over again, but to benefit the living, those of us who yet remain upon earth, our young men & women & children.”
~Makade-binesi (Blackbird)

Scene at Indian Payment–Odanah, Wis. This image is from a later payment than the one described below (Whitney & Zimmerman c.1870)
Most of us have heard Chief Joseph’s “Fight No More Forever” speech and Chief Seattle’s largely-fictional plea for the environment, but very few will know that a outstanding example of Native American oratory took place right here in the Chequamegon Region in the summer of 1855.
It was exactly eleven months after the Lake Superior Ojibwe bands gave up the Arrowhead region of Minnesota, in their final treaty with the United States, in exchange for permanent reservations. Already, the American government was trying to back out of a key provision of the agreement. It concerned a clause in Article Four of the 1854 Treaty of La Pointe that reads:
The United States will also pay the further sum of ninety thousand dollars, as the chiefs in open council may direct, to enable them to meet their present just engagements.
The inclusion of clauses to pay off trade debts was nothing new in Ojibwe treaties. In 1837, $70,000 went to pay off debts, and in 1842 another $75,000 went to the traders. Personal debts would often be paid out of annuity funds by the government directly to the creditors and certain Ojibwe families would never see their money. However, from the beginning there were accusations that these debts were inflated or illegitimate, and that it was the traders rather than the Ojibwe themselves, who profited from the sale of the lands. Therefore, in 1854, when $90,000 in claims were inserted in the treaty, the chiefs demanded that they be the ones to address the claims of the creditors.
However, less than a year later, at the first post-1854 payment, the government was pressured to back off of the language in the treaty. George Manypenny, the Commissioner of Indian Affairs, came to La Pointe to oversee the payment where he was asked by Indian Agent Henry Gilbert to let the Agency oversee the disbursement of the $90,000. Most white inhabitants, and many of the white tourists in town to view the spectacle that was the 1855 payment, supported the agent’s plan, as did most of the mix-blooded Ojibwe (most of whom were employed in the trading business in one way or another) and a substantial minority of the full-bloods.
However, the clear majority of the Lake Superior chiefs insisted they keep the right to handle their own debt claims. As we saw in this post, the Odanah-based missionary Leonard Wheeler also felt the Government needed to honor its treaties to the letter. This larger faction of Ojibwe rallied around one chief. He was from the La Pointe Band and was entrusted to speak for Ojibwe with one voice. From this description, you might assume it was Chief Buffalo. However, Buffalo, in the final days of his life, found himself in the minority on this issue. The speaker for the majority was the Bad River chief Blackbird, and he may have delivered one of the greatest speeches ever given in the Chequamegon Bay region.
Unfortunately, the Ojibwe version of the speech has not survived, and it’s English version, originally translated by Paul Bealieu, exists in pieces recorded by multiple observers. None of these accounts captures all the nuances of the speech, so it is necessary to read all of them and then analyze the different passages to see its true brilliance.
The first reference to Blackbird’s speech I remember seeing appeared in the eyewitness account of Dr. Richard F. Morse of Detroit who visited La Pointe that summer specifically to see the payment. His article, The Chippewas of Lake Superior appeared in the third volume of the Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin. As you’ll read, it doesn’t speak very highly of Blackbird or the speech, celebrating instead the oratory of Naaganab, the Fond du Lac chief who was part of the minority faction and something of a celebrity among the visiting whites in 1855:




From Morse’s clear bias against Ojibwe culture, I thought there may have been more to this story, but my suspicions weren’t confirmed until I transcribed another account of the payment for Chequamegon History. An Indian Payment written by another eyewitness, Crocket McElroy, paints a different picture of Blackbird and quotes part of his speech:

Paul H. Beaulieu translated the speeches at the 1855 annuity payment (Minnesota Historical Society Collections).
In August 1855 about three thousand Chippewa Indians gathered at the village of Lapointe, on Lapointe Island, Lake Superior, for an Indian Payment and also to hold a council with the commissioner of Indian affairs, who at that time was George W. Monypenny of Ohio. The Indians selected for their orator a chief named Blackbird, and the choice was a good one, as Blackbird held his own well in a long discussion with the commissioner. Blackbird was not one of the haughty style of Indians, but modest in his bearing, with a good command of language and a clear head. In his speeches he showed much ingenuity and ably pleaded the cause of his people. He spoke in Chippewa stopping frequently to give the interpreter time to translate what he said into English. In beginning his address he spoke substantially as follows:
“My great white father, we are pleased to meet you and have a talk with you We are friends and we want to remain friends. We expect to do what you want us to do, and we hope that you will deal kindly with us. We wish to remind you that we are the source from which you have derived all your riches. Our furs, our timber, our lands, everything that we have goes to you; even the gold out of which that chain was forged (pointing to a heavy watch chain that the commissioner carried) came from us, and now we hope that you will not use that chain to bind us.”
These conflicting accounts of the largely-unremembered Bad River chief’s speech made me curious, and after I found the Blackbird-Wheeler-Manypenny letters written after the payment, I knew I needed to learn more about the speech. Luckily, digging further into the Wheeler Papers uncovered the following. To my knowledge, this is the first time it has been transcribed or published in any form.
[Italics, line breaks, and quotation marks added by transcriber to clearly differentiate when Wheeler is quoting a speaker. Blackbird’s words are in blue.]
O-da-nah Jan 18, 1856.
L. H. Wheeler to Richard M. Smith
Dear Sir,
The following is the substance of my notes taken at the Indian council at La Pointe a copy of which you requested. Council held in front of Mr. Austrian’s store house Aug 30. 1855.
Short speech first from Kenistino of Lac du Flambeau.
My father, I have a little to say to you & to the Indians. There is no difference between myself and the other chiefs in regard to the subject upon which we wish to speak. Our chiefs and young men & old men & even the women & children are all of the same mind. Blackbird our chief will speak for us & express our sentiments.
The Commissioner, Col Manypenny replied as follows.
My children I suppose you have come to reply to what I said to you day before yesterday. Is this what you have come for?
“Ah;” or yes, was the reply.
I am happy to see you, but would suggest whether you had not better come tomorrow. It is now late in the day and is unpleasant & you have a great deal to say and will not have time to finish, but if you will come tomorrow we shall have time to hear all you have to say. Don’t you think this will be the best way?
“Ah!” yes was the response.
Think well about what you want to say and come prepared to speak freely & fully about all you wish to say. I would like not only to hear the chiefs and old men speak, but the young men talk, and even the women, if they wish to come, let them come and listen too. I want the women to understand all that is said and done. I understand that some of the Indians were drunk last night with the fire-water. I hope we shall hear nothing more of it. If any body gives you liquor let me know it and I will deal with him as he deserves. I hope we shall have a good time tomorrow and be able to explain all about your affairs.
Aug 31. Commissioner opened the council by saying that he wanted all to keep order.
Let the whites and others sit down on the ground and we will have a pleasant time. If you have anything to say I hope you will speak to the point.
Black Bird. To the Indians.
My brother chiefs, head men & young men & children. I have listened well to all the men & women & others who have spoken in our councils and shall now tell it to my father. I shall have but one mouth to speak your will.
Nose [noose (no-say) “my father”]. My father. We present you our salutations in your heart. We salute you in the name of our great father the President, whose representative you are. We want the Great Spirit now to bless us. The Day is clear, and we hope our thoughts will be clear too. My intention is to tell you what the owner of life has done for us. He has provided for the life of us all. When the Lord made us he provided for us here upon earth he invested it (ie, he made provision for our wants) in the running streams, in the woods & lakes which abound with fish and in the wild animals. We regard you as if men like a spirit, perhaps it is because of your education, because you are so much wiser than we, but if we can trace our tradition right the Great Spirit has not made the white man to cheat us. There is a difference of opinion as it regards different colors among, as to which shall have the preeminence, but the Great Spirit made us to be happy before you discovered us.
I will now tell you about how it was with us before our payments, and before we sold any land. Our furs that we took we sold to our traders. We were then paid 4 martin skins for a dollar. 4 bears skins also & 4 beaver skins for $1.00 too. Can you wonder that we are poor? I say this to show you what our condition was before we had any payments. I[t] was by our treaties that we learned the use of money. I see you White men that sit here how you are dressed. I see your watch chains & seals and your rich clothing. Now I will tell you how it is with our traders. When they first came among us they were very poor, but by & by they became very fat & rich, and wear rich clothing and had their watches & gold chains such as I see you wear. But they got their things out of us. They were made rich at our expense. My father, you told us to bring our women here too. Here they are, and now behold them in their poverty, and pity their condition (at this juncture in the speech several old women stood dressed in their worn out blankets and tattered garments as if designed to appeal to his humanity[)].
My father, I am now coming to the point. We are here to protect our own interests. Our land which we got from our forefathers is ours & we must get what we can for it. Our traders step between us & our father to controll our interests, and we have been imposed upon. Mr. Gilbert was the one I shook hands with last year when he was sent here to treat for our lands. He was the one who was sent to uphold us in our poverty. We are thankful to see you both here to attend to our interests, and that we are permitted to express to you our wants. Last year you came here to treat for our lands we are now speaking about. We sold them because we were poor. We thank our father for bringing clothing to pay for them. We sold our land for our graves–that we might have a home, where the bones of our fathers are buried. We were not willing to sell the ashes of our relatives which are so dear to us. This was the reason why we sold our lands. It was not to pay debts over and over again, but to benefit the living, those of us who yet remain upon earth, our young men & women & children.
You said you wanted to see them. They have been sent for and are now here. Behold them in their poverty & see how poor they look.
They are poor because so much of our money is taken to pay old debts. We want the 90,000 dollars to be paid as we direct. We know that it is just and right that it should be so. We want to have the money paid in our own hands, and we will see that our just debts are paid. We want the 90,000 to feed our poor women, and after paying our just debts we want the remainder to buy what we want. This is the will of all present. The chiefs, & young men & old men & the women & children.
Let what I have now said, my father, enter your head & heart; and let it enter the head of our great father the President, that it may be as we have now said. We own no more land. We must hereafter provide for ourselves. We want to profit by all the provisions of the treaty we have now made. We want the whole annuity paid to us as stipulated in the treaty. I am now done. After you have spoken, perhaps there are others who would like to speak.
This is the first time my father that I have appeared dressed in a coat & pants & I must confess I feel a little awkward.
The Commissioner replied as follows
We have all heard & noted down what you have said. If any others wish to speak they had better speak first and I will reply to all at once.
The Grand Portage Indian [Adikoons] then spoke as follows.
My father, I have a few words to say, and I wish to speak what I think. We have long coveted the privilege of seeing our Great Father. Why not now embrace the opportunity to speak freely while he is here? This man will speak my mind. He is old enough to speak and is a man endowed with good sense. He will speak our minds without reserve.
When we look around us, we think of our God who is the maker of us all. You have come here with the laws of that God we have talked about, and you profess to be a Christian and acknowledge the authority of God. The word of God ought to be obeyed not only by the Indians, but by all. When we see you, we think you must respect that word of God, who gives life to all. Your advice is like the law of God. Those who listen to his law are like God–firm as a rock, (not fickle and vacilating). When the word of the Great Spirit ends. When there is an end to life, we are all pleased with the advice you have given us, and intend to act in accord with it. If we are one here, and keep the word of the Great Spirit we shall be one here after. In what Blackbird said he expressed the mind of a majority of the chiefs now present. We wish the stipulations of the treaty to be carried out to the very letter.
I wish to say our word about our reserves. Will these reserves made for each of our bands, be our homes forever?
When we took credits of our trader last winter, and took no furs to pay him, and wish to get hold of this 90,000 dollars, that we may pay him off of that. This is all we came here for. We want the money in our own hands & we will pay our own traders. We do not think it is right to pay what we do not owe. I always know how I stand my acct. and we can pay our own debts. From what I have now said I do not want you to think that we want the money to cheat our creditors, but to do justice to them I owe. I have my trader & know how much I owe him, & if the money is paid into the hands of the Indians we can pay our own debts.
Naganub.
We have 90,000 dollars set apart to pay our traders, for my part I think it is just that the money should go for this object. We all know that the traders help us. We could not well do without them.
Buffalo.
We who live here are ready to pay our just debts. Some have used expressions as though these debts were not just. I have lived here many years and been very poor. There are some here who have been pleased to assist me in my poverty. They have had pity on me. Those we justly owe I don’t think ought to be defrauded. The trader feeds our women & children. We cannot live one winter without him. This is all I have to say.
 [Wheeler does not identify a new speaker here, but marks a a star (right). Kohl (below) attributes the line about the “came out of the water” to Blackbird, but the line about the copper diggings contradicts Blackbird’s earlier statement, in Kohl, about not knowing their value. This, and Wheeler’s marking of Blackbird as the one who spoke after this speech would indicate this is Buffalo still talking].
[Wheeler does not identify a new speaker here, but marks a a star (right). Kohl (below) attributes the line about the “came out of the water” to Blackbird, but the line about the copper diggings contradicts Blackbird’s earlier statement, in Kohl, about not knowing their value. This, and Wheeler’s marking of Blackbird as the one who spoke after this speech would indicate this is Buffalo still talking].
Our rights ought to be protected. When commissioners have come here to treat for our lands, we have always listened well to their words. Not because we did not know ourselves the worth of our lands. We have noticed the ancient copper diggings, and know their worth. We have never refused to listen to the words of our Great Father. He it is true has had the power but we have made him rich. The traders have always wanted pay for what we do not remember to have bought. At Crow [W]ing River when our lands were ceded there, then there was a large sum demanded to pay old debts. We have always paid our traders we have acted fair on our part. At St. Peters also there was a large amount of old debts to be paid–many of them came from places unknown–for what I know they came out of the water. We think many of them came out of the same bag, and are many of them paid over & over again at every treaty.
Black Bird.
I get up no[w] to finish what you have put into my heart. The night would be heavy on my breast should I retain any of the words of them with whom I have councilled & for whom I speak. I speak no[w] of farmers, carpenters, & other employees of Govt. Where is the money gone to for them? We have not had these laborers for several years that has been appropriated. Where is the money that has been set apart to pay them? You will not probably see your Red Children again in after years to council with them. So we protest by the present opportunity to speak to you of our wants & grievances. We regard you as standing in the place of our great father at Washington, and your judgement must be correct. This is all I have to say about our arrearages, we have not two tongues.
As exciting as it was to have the full speech, as I transcribed some of the passages, some of them seemed very familiar. Sure enough, on page 53 of Johann Georg Kohl’s Kitchi-Gami: Life Among the Lake Superior Ojibway, there is another whole version. Kitchi-Gami is one of the standards of Ojibwe cultural history, and I use it for reference fairly often, but it had been so long since I had read the book cover to cover that I forgot that Kohl had been another witness that August day in 1855:





When one considers that Paul Beaulieu, the man giving the official English translation was probably speaking in his third language, after Ojibwe and Metis-French, and that Kohl was a native German speaker who understood English but may have been relying on his own mix-blood translator, it is remarkable how similar these two accounts are. This makes the parts where they differ all the more fascinating. Undoubtedly there are key parts of this speech that we could only understand if we had the original Ojibwe version and a full understanding of the complicated artistry of Ojibwe rhetoric with all its symbolism and metaphor. Even so, there are enough outstanding passages here for me to call it a great speech.
“My father…great Father…We regard you as if men like a spirit, perhaps it is because of your education, because you are so much wiser than we…”
The ritual language of kinship and humility in traditional Ojibwe rhetoric can be off-putting to those who haven’t read many Ojibwe speeches, and can be mistaken as by-product of American arrogance and paternalism toward Native people. However, the language of “My Father” predates the Americans, going all the way back to New France, and does not necessarily indicate any sort weakness or submission on the part of the speaker. Richard White, Michael Witgen, and Howard Paap, much smarter men than I, have dedicated pages to what Paap calls “fur-trade theater,” so I won’t spend too much time on it other than to say that 1855 was indeed a low point in Ojibwe power, but Blackbird is only acting the ritual part of the submissive child here in a long-running play. He is not grovelling.
On the contrary, I think Blackbird is playing Manypenny here a little bit. George Manypenny’s rise to the head of Indian Affairs coincided with the end of American removal policy and the ushering in of the reservation era. In the short term, this was to the political advantage of the Lake Superior Ojibwe. In Manypenny the Ojibwe got a “Father” who would allow them to stay in their homelands, but they also got a zealous believer in the superiority of white culture who wanted to exterminate Indian cultures as quickly as possible.
In a future post about the 1855 treaty negotiations with the Minnesota Ojibwe we will see how Commissioner Manypenny viewed the Ojibwe, including masterful politicians like Flat Mouth and Hole in the Day, as having the intelligence of children. Blackbird shows himself a a savvy politician here by playing into these prejudices as a way to get the Commissioner off his guard. Other parts of the speech lead me to doubt that Blackbird sincerely believed that the Americans were “so much wiser” than he was.
My intention is to tell you what the owner of life has done for us. He has provided for the life of us all. When the Lord made us he provided for us here upon earth he invested it (ie, he made provision for our wants) in the running streams, in the woods & lakes which abound with fish and in the wild animals… There is a Great Spirit from whom all good things here on earth come. He has given them to mankind–to the white as to the red man; for He sees no distinction of colour…but if we can trace our tradition right the Great Spirit has not made the white man to cheat us. There is a difference of opinion as it regards different colors among, as to which shall have the preeminence, but the Great Spirit made us to be happy before you discovered us…
This part varies slightly between Wheeler and Kohl, but in both it is very eloquent and similar in style to many Ojibwe speeches of the time. One item that piqued my interest was the line about the “difference of opinion.” Many Americans at the time understood the expansion of the United States and the dispossession of Native peoples in religious terms. It was Manifest Destiny. The Ojibwe also sought answers for their hardships in prophecy. On pages 117 and 118 of History of the Ojibwe People, William Warren relates the following:
Warren, writing in the late 1840s and early 1850s, contrasts this tradition with the popularity of the prophecies of Tenskwatawa, brother of Tecumseh, in Ojibwe country forty years earlier. Tenskwatawa taught that Indians would inherit North America and drive whites from the continent. Blackbird seems to be suggesting that in 1855 this question of prophecy was not settled among the Lake Superior Ojibwe. Presumably there would have been fertile ground for a charismatic millenarian Native spiritual leader along the lines of Neolin, Tenskwatawa, or Wovoka to gain adherents among the Lake Superior Ojibwe at that time.

Johann Georg Kohl recorded Blackbird’s speech in his well known account of Lake Superior in the Summer of 1855, Kitchi-Gami: Life Among the Lake Superior Ojibway.
Our furs, our timber, our lands, everything that we have goes to you; even the gold out of which that chain was forged…Now I will tell you how it is with our traders. When they first came among us they were very poor, but by & by they became very fat & rich, and wear rich clothing and had their watches & gold chains such as I see you wear. But they got their things out of us. They were made rich at our expense…and now we hope that you will not use that chain to bind us…
The gold chain appears in each of McElroy, Wheeler, and Kohl’s accounts. It acts as a symbol on multiple levels. To Blackbird, the gold represents the immense wealth produced during the fur trade on the backs of Indian trappers. By 1855, with the fur trade on its last legs, some of the traders are very wealthy while the Ojibwe are much poorer than they were when the trade started. The gold also stands in for the value of the ceded territory itself, specifically the lakeshore lands (ceded in 1842), which thirteen years later were producing immense riches from that other shiny metal, copper. Finally, in McElroy’s account, we also see the chain acting as the familiar symbol of bondage.
…We sold our land for our graves–that we might have a home, where the bones of our fathers are buried…Our debts we will pay. But our land we will keep. As we have already given away so much, we will, at least, keep that land you have left us, and which is reserved for us. Answer us, if thou canst, this question. Assure us, if thou canst, that this piece of land reserved for us, will really always be left to us…
This passage of Blackbird’s speech, and a similar statement by the “Grand Portage Indian” (identified by Morse as Adikoons or Little Caribou), indicate that perhaps, the actual disbursement of the $90,000 was a secondary to the need to hold Agent Gilbert and the Government to their word. It was very important to the Ojibwe that words of the Treaty of 1854 be rock-solid, not for a need to pay off debts or to get annuity payments, but because the Government absolutely needed to keep its promise to grant reservations around the ancestral villages. The memory of the Sandy Lake Tragedy, less than five years earlier, cast a long shadow over this decade. Paap argues in Red Cliff, Wisconsin that the singular goal of the treaty, from the Ojibwe perspective, was to end the removal talk forever, a goal that had seemingly been accomplished. To hear the Government trying to weasel out of a provision of the 1854 Treaty must have been very frightening to those who heard Robert Stuart’s promises in 1842. This time, the chiefs had to make sure a promise of a permanent homeland for their people wouldn’t turn out to be another lie.
This is the first time my father that I have appeared dressed in a coat & pants & I must confess I feel a little awkward.
You can argue that a great speech can’t end with the line, “I must confess I feel a little awkward.” However, I will argue that this might be the best line of all. It is another example of the political brilliance of Blackbird. The Bad River chief knew who his allies were, knew who his opponents were, and knew how to take advantage of the Commissioner’s prejudices. Clothing played a role in all of this.
George Manypenny despised Indian cultures. In fact, the whole council had almost derailed a few days before the speeches when the Commissioner refused to smoke the pipe presented to him by the chiefs in open ceremony. He remedied this insult somewhat by smoking it later while indoors, but he let it be known that he had no use for Ojibwe songs, dances, rituals or clothing. This put Blackbird, an unapologetic traditionalist and practitioner of the midewiwin at a distinct disadvantage, when compared with chiefs like Naaganab who were known to wear European clothes and profess to be Christians.
Although he had the majority of the people behind him, Blackbird had very little negotiating power. He had to persuade Manypenny that he was in the right. He had no chance unless he could appear to the Commissioner that he was trying to become “civilized” and was therefore worthy enough to be listened to. However, by wearing European clothes, he ran the risk of alienating the majority of the people in the crowd who preferred traditional ways and dress. Furthermore, the chiefs most likely to oppose him, Naaganab and Jayjigwyong (Little Buffalo) had been dressing like whites (I would argue also largely for political reasons) for years and were much more likely to come across as “civilized” in the Commissioner’s eyes.
How did the chief solve these dilemmas? In the same way he turned Manypenny’s request to see the Ojibwe women to his advantage, he used the clothing to demonstrate that he had gone out of his way to work with the Commissioner’s wishes, while still solidifying the backing of the traditional Ojibwe majority and putting his opponents on the defensive all with one well-timed joke. Although this joke seems to have gone over Wheeler’s head, and likely Manypenny’s as well, Kohl’s mention of the “applauding laughter of the entire assembly,” shows it reached its target audience. So, contrary to first appearances, the crack about the awkward pants is anything but an awkward ending to this speech.
Conclusion
In the 1840s and early 1850s, Blackbird rarely appears in the historical record. Here and there he is mentioned as a second chief to Chief Buffalo or as leading the village at Bad River. Many mentions of him by English-speaking authors are negative. He is referred to as a rascal, scoundrel, or worse, and I’ve yet to find any mention of his father or other family members as being prominent chiefs.
However, in the late 1850s and early 1860s, he was clearly the most important speaker for not just the La Pointe Band, but for the other Lake Superior Bands as well. This was a mystery to me. I temporarily hypothesized his rise was due to the fact that Chequamegon was seen as the center of the nation and that when Buffalo died, Blackbird succeeded to the position by default. However, this view doesn’t really fit what I understood as Ojibwe leadership.
This speech puts that interpretation to rest. Blackbird earned his position by merit and by the will of the people.
He did not, however, win on the question of the $90,000. A Chequamegon History reader recently sent me a document showing it was eventually paid to the creditors directly by the Agent. However, if my argument is correct, the more important issue was that the Government keep its word that the reservations would belong to the Ojibwe forever. The land question wasn’t settled overnight, and it required many leaders over the last 160 years to hold the United States to its word. But today, Blackbird’s descendants still live beside the swamps of Mashkiziibii at least partially because of the determination of their great ogimaa.
Sources:
Kohl, J. G. Kitchi-Gami: Wanderings round Lake Superior. London: Chapman and Hall, 1860. Print.
McClurken, James M., and Charles E. Cleland. Fish in the Lakes, Wild Rice, and Game in Abundance: Testimony on Behalf of Mille Lacs Ojibwe Hunting and Fishing Rights / James M. McClurken, Compiler ; with Charles E. Cleland … [et Al.]. East Lansing, MI: Michigan State UP, 2000. Print.
McElroy, Crocket. “An Indian Payment.” Americana v.5. American Historical Company, American Historical Society, National Americana Society Publishing Society of New York, 1910 (Digitized by Google Books) pages 298-302.
Morse, Richard F. “The Chippewas of Lake Superior.” Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin. Ed. Lyman C. Draper. Vol. 3. Madison: State Historical Society of Wisconsin, 1857. 338-69. Print.
Paap, Howard D. Red Cliff, Wisconsin: A History of an Ojibwe Community. St. Cloud, MN: North Star, 2013. Print.
Satz, Ronald N. Chippewa Treaty Rights: The Reserved Rights of Wisconsin’s Chippewa Indians in Historical Perspective. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters, 1991. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. The Voice of the Crane Echoes Afar: The Sociopolitical Organization of the Lake Superior Ojibwa, 1640-1855. New York: Garland Pub.,1997. Print.
—————— William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and times of an Ojibwe Leader. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2007. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
White, Richard. The Middle Ground: Indians, Empires, and Republics in the Great Lakes Region, 1650-1815. Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1991. Print.
Witgen, Michael J. An Infinity of Nations: How the Native New World Shaped Early North America. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania, 2012. Print.
The Enemy of my Enemy: The 1855 Blackbird-Wheeler Alliance
November 29, 2013
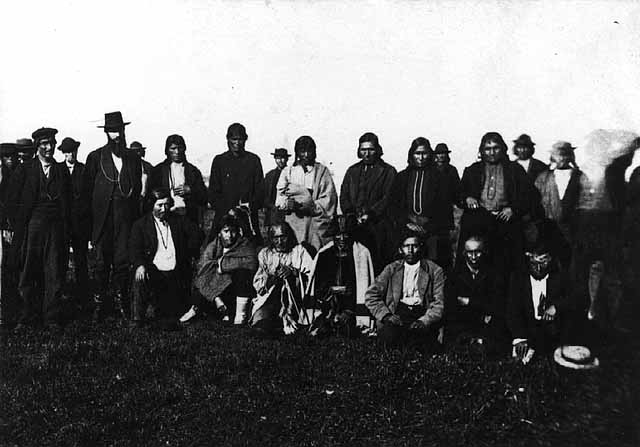

Identified by the Minnesota Historical Society as “Scene at Indian payment, probably at Odanah, Wisconsin. c. 1865.” by Charles Zimmerman. Judging by the faces in the crowd, this is almost certainly the same payment as the more-famous image that decorates the margins of the Chequamegon History site (Zimmerman MNHS Collections)
A staunch defender of Ojibwe sovereignty, and a zealous missionary dedicating his life’s work to the absolute destruction of the traditional Ojibwe way of life, may not seem like natural political allies, but as Shakespeare once wrote, “Misery acquaints a man with strange bedfellows.”
In October of 1855, two men who lived near Odanah, were miserable and looking for help. One was Rev. Leonard Wheeler who had founded the Protestant mission at Bad River ten years earlier. The other was Blackbird, chief of the “Bad River” faction of the La Pointe Ojibwe, that had largely deserted La Pointe in the 1830s and ’40s to get away from the men like Wheeler who pestered them relentlessly to abandon both their religion and their culture.
Their troubles came in the aftermath of the visit to La Pointe by George Manypenny, Commissioner of Indian Affairs, to oversee the 1855 annuity payments. Many readers may be familiar with these events, if they’ve read Richard Morse’s account, Chief Buffalo’s obituary (Buffalo died that September while Manypenny was still on the island), or the eyewitness account by Crockett McElroy that I posted last month. Taking these sources together, some common themes emerge about the state of this area in 1855:
- After 200 years, the Ojibwe-European relationship based on give and take, where the Ojibwe negotiated from a position of power and sovereignty, was gone. American government and society had reached the point where it could by impose its will on the native peoples of Lake Superior. Most of the land was gone and with it the resource base that maintained the traditional lifestyle, Chief Buffalo was dead, and future chiefs would struggle to lead under the paternalistic thumb of the Indian Department.
- With the creation of the reservations, the Catholic and Protestant missionaries saw an opportunity, after decades of failures, to make Ojibwe hunters into Christian farmers.
- The Ojibwe leadership was divided on the question of how to best survive as a people and keep their remaining lands. Some chiefs favored rapid assimilation into American culture while a larger number sought to maintain traditional ways as best as possible.
- The mix-blooded Ojibwe, who for centuries had maintained a unique identity that was neither Native nor European, were now being classified as Indians and losing status in the white-supremacist American culture of the times. And while the mix-bloods maintained certain privileges denied to their full-blooded relatives, their traditional voyageur economy was gone and they saw treaty payments as one of their only opportunities to make money.
- As with the Treaties of 1837 and 1842, and the tragic events surrounding the attempted removals of 1850 and 1851, there was a great deal of corruption and fraud associated with the 1855 payments.
This created a volatile situation with Blackbird and Wheeler in the middle. Before, we go further, though, let’s review a little background on these men.

This 1851 reprint from Lake Superior Journal of Sault Ste. Marie shows how strongly Blackbird resisted the Sandy Lake removal efforts and how he was a cultural leader as well as a political leader. (New Albany Daily Ledger, October 9, 1851. Pg. 2).
Who was Blackbird?
Makadebineshii, Chief Blackbird, is an elusive presence in both the primary and secondary historical record. In the 1840s, he emerges as the practical leader of the largest faction of the La Pointe Band, but outside of Bad River, where the main tribal offices bear his name, he is not a well-known figure in the history of the Chequamegon area at all.
Unlike, Chief Buffalo, Blackbird did not sign many treaties, did not frequently correspond with government officials, and is not remembered favorably by whites. In fact, his portrayal in the primary sources is often negative. So then, why did the majority of the Ojibwe back Blackbird at the 1855 payment? The answer is probably the same reason why many whites disliked him. He was an unwavering defender of Ojibwe sovereignty, he adhered to his traditional culture, and he refused to cooperate with the United States Government when he felt the land and treaty rights of his people were being violated.
One needs to be careful drawing too sharp a contrast between Blackbird and Buffalo, however. The two men worked together at times, and Blackbird’s son James, later identified his father as Buffalo’s pipe carrier. Their central goals were the same, and both labored hard on behalf of their people, but Buffalo was much more willing to work with the Government. For instance, Buffalo’s response in the aftermath of the Sandy Lake Tragedy, when the fate of Ojibwe removal was undecided, was to go to the president for help. Blackbird, meanwhile, was part of the group of Ojibwe chiefs who hoped to escape the Americans by joining Chief Zhingwaakoons at Garden River on the Canadian side of Sault Ste. Marie.
Still, I hesitate to simply portray Blackbird and Buffalo as rivals. If for no other reason, I still haven’t figured out what their exact relationship was. I have not been able to find any reference to Blackbird’s father, his clan, or really anything about him prior to the 1840s. For a while, I was working under the hypothesis that he was the son of Dagwagaane (Tugwaganay/Goguagani), the old Crane Clan chief (brother of Madeline Cadotte), who usually camped by Bad River, and was often identified as Buffalo’s second chief.
However, that seems unlikely given this testimony from James Blackbird that identifies Oshkinawe, a contemporary of the elder Blackbird, as the heir of Guagain (Dagwagaane):

Statement of James Blackbird: Condition of Indian affairs in Wisconsin: hearings before the Committee on Indian Affairs, United States Senate, [61st congress, 2d session], on Senate resolution, Issue 263. pg 203. (Digitized by Google Books).
It seems Commissioner Manypenny left La Pointe before the issue was entirely settled, because a month later, we find a draft letter from Blackbird to the Commissioner transcribed in Wheeler’s hand:
Mushkesebe River Oct. 1855
Blackbird. Principal chief of the Mushkisibi-river Indians to Hon. G. Manepenny Com. of Indian Affairs Washington City.
Father; Although I have seen you face to face, & had the privilege to talking freely with you, we did not do all that is to be attended to about our affairs. We have not forgotten the words you spoke to us, we still keep them in our minds. We remember you told us not to listen to all the foolish stories that was flying about–that we should listen to what was good, and mind nothing about anything else. While we listened to your advice we kept one ear open and the other shut, & [We?] kept retained all you spoke said in our ears, and. Your words are still ringing in our ears. The night that you left the sound of the paddles in boat that carried you away from us was had hardly gone ceased before the minds of some of the chiefs was were tuned by the traders from the advice you gave, but we did not listen to them. Ja-jig-wy-ong, (Buffalo’s son) son says that he & Naganub asked Mr. Gilbert if they could go to Washington to see about the affairs of the Indians. Now father, we are sure you opened your heart freely to us, and did not keep back anything from us that is for our good. We are sure you had a heart to feel for us & sympathise with us in our trials, and we think that if there is any important business to be attended to you would not have kept it secret & hid it from us, we should have knew it. If I am needed to go to Washington, to represent the interests of our people, I am ready to go. The ground that we took against about our old debts, I am ready to stand shall stand to the last. We are now in Mr. Wheelers house where you told us to go, if we had any thing to say, as Mr. W was our friend & would give us good advice. We have done so. All the chiefs & people for whom I spoke, when you were here, are of the same mind. They all requested before they left that I should go to Washington & be sure & hold on to Mr. Wheeler as one to go with me, because he has always been our steadfast friend and has al helped us in our troubles. There is another thing, my father, which makes us feel heavy hearted. This is about our reservation. Although you gave us definite instructions about it, there are some who are trying to shake our reserve all to pieces. A trader is already here against our will & without any authority from Govt, has put him up a store house & is trading with our people. In open council also at La Pointe when speaking for our people, I said we wanted Mr. W to be our teacher, but now another is come which whom we don’t want, and is putting up a house. We supposed when you spoke to us about a teacher being permitted to live among us, you had reference to the one we now have, one is enough, we do not wish to have any more, especially of the kind of him who has just come. We forbid him to build here & showed him the paper you gave us, but he said that paper permitted him rather than forbid him to come. If the chiefs & young men did not remember what you told them to keep quiet there would already be have been war here. There is always trouble when there two religions come together. Now we are weak and can do nothing and we want you to help us extend your arms to help us. Your arms can extend even to us. We want you to pity & help us in our trouble. Now we wish to know if we are wanted, or are permitted, three or four of us to come to which Washington & see to our interests, and whether our debts will be paid. We would like to have you write us immediately & let us know what your will is, when you will have us come, if at all. One thing further. We do not want any account to be allowed that was not presented to us for us to pass our opin us to pass judgement on, we hear that some such accounts have been smuggled in without our knowledge or consent.
The letter is unsigned, lacks a specific date, and has numerous corrections, which indicate it was a draft of the actual letter sent to Manypenny. This draft is found in the Wheeler Family Papers in the collections of the Wisconsin Historical Society at the Northern Great Lakes Visitor Center. As interesting as it is, Blackbird’s letter raises more questions than answers. Why is the chief so anxious to go to Washington? What are the other chiefs doing? What are these accounts being smuggled in? Who are the people trying to shake the reservation to pieces and what are they doing? Perhaps most interestingly, why does Blackbird, a practitioner of traditional religion, think he will get help from a missionary?
For the answer to that last question, let’s take a look at the situation of Leonard H. Wheeler. When Wheeler, and his wife, Harriet came here in 1841, the La Pointe mission of Sherman Hall was already a decade old. In a previous post, we looked at Hall’s attitudes toward the Ojibwe and how they didn’t earn him many converts. This may have been part of the reason why it was Wheeler, rather than Hall, who in 1845 spread the mission to Odanah where the majority of the La Pointe Band were staying by their gardens and rice beds and not returning to Madeline Island as often as in the past.
When compared with his fellow A.B.C.F.M. missionaries, Sherman Hall, Edmund Ely, and William T. Boutwell, Wheeler comes across as a much more sympathetic figure. He was as unbending in his religion as the other missionaries, and as committed to the destruction of Ojibwe culture, but in the sources, he seems much more willing than Hall, Ely, or Boutwell to relate to Ojibwe people as fellow human beings. He proved this when he stood up to the Government during the Sandy Lake Tragedy (while Hall was trying to avoid having to help feed starving people at La Pointe). This willingness to help the Ojibwe through political difficulties is mentioned in the 1895 book In Unnamed Wisconsin by John N. Davidson, based on the recollections of Harriet Wheeler:

From In Unnamed Wisconsin pg. 170 (Digitized by Google Books).
So, was Wheeler helping Blackbird simply because it was the right thing to do? We would have to conclude yes, if we ended it here. However, Blackbird’s letter to Manypenny was not alone. Wheeler also wrote his own to the Commissioner. Its draft is also in the Wheeler Family Papers, and it betrays some ulterior motives on the part of the Odanah-based missionary:
example not to meddle with other peoples business.
Mushkisibi River Oct. 1855
L.H. Wheeler to Hon. G.W. Manypenny
Dear Sir. In regard to what Blackbird says about going to Washington, his first plan was to borrow money here defray his expenses there, & have me start on. Several of the chiefs spoke to me before soon after you left. I told them about it if it was the general desire. In regard to Black birds Black Bird and several of the chiefs, soon after you left, spoke to me about going to Washington. I told them to let me know what important ends were to be affected by going, & how general was the desire was that I should accompany such a delegation of chiefs. The Indians say it is the wish of the Grand Portage, La Pointe, Ontonagun, L’anse, & Lake du Flambeaux Bands that wish me to go. They say the trader is going to take some of their favorite chiefs there to figure for the 90,000 dollars & they wish to go to head them off and save some of it if possible. A nocturnal council was held soon after you left in the old mission building, by some of the traders with some of the Indians, & an effort was made to get them Indians to sign a paper requesting that Mr. H.M. Rice be paid $5000 for goods sold out of the 90,000 that be the Inland Indians be paid at Chippeway River & that the said H.M. Rice be appointed agent. The Lake du Flambeau Indians would not come into the [meeting?] & divulged the secret to Blackbird. They wish to be present at [Shington?] to head off [sail?] in that direction. I told Blackbird I thought it doubtful whether I could go with him, was for borrowing money & starting immediately down the Lake this fall, but I advised him to write you first & see what you thought about the desirability of his going, & know whether his expenses would be born. Most of the claimants would be dread to see him there, & of course would not encourage his going. I am not at all certain certain that I will be [considered?] for me to go with Blackbird, but if the Dept. think it desirable, I will take it into favorable consideration. Mr. Smith said he should try to be there & thought I had better go if I could. The fact is there is so much fraud and corruption connected with this whole matter that I dread to have anything to do with it. There is hardly a spot in the whole mess upon which you can put your finger without coming in contact with the deadly virus. In regard to the Priest’s coming here, The trader the Indians refer to is Antoine [Gordon?], a half breed. He has erected a small store house here & has brought goods here & acknowledges that he has sold them and defies the Employees. Mssrs. Van Tassel & Stoddard to help [themselves?] if they can. He is a liquer-seller & a gambler. He is now putting up a house of worship, by contract for the Catholic Priest. About what the Indians said about his coming here is true. In order to ascertain the exact truth I went to the Priest myself, with Mr. Stoddard, Govt [S?] man Carpenter. His position is that the Govt have no right to interfere in matters of religion. He says he has a right to come here & put up a church if there are any of his faith here, and they permit him to build on his any of their claims. He says also that Mr. Godfrey got permission of Mr. Gilbert to come here. I replied to him that the Commissioner told me that it was not the custom of the Gov. to encourage but one denomination of Christians in a place. Still not knowing exactly the position of Govt upon the subject, I would like to ask the following questions.
1. When one Missionary Society has already commenced labors a station among a settlement of Indians, and a majority of the Indians people desire to have him for their religious teacher, have missionaries of another denomination a right to come in and commence a missionary establishment in the same settlement?
Have they a right to do it against the will of a majority of the people?
Have they a right to do it in any case without the permission of the Govt?
Has any Indian a right, by sold purchase, lease or otherwise a right to allow a missionary to build on or occupy a part of his claim? Or has the same missionary a right to arrange with several missionaries Indians for to occupy by purchase or otherwise a part of their claims severally? I ask these questions, not simply with reference to the Priest, but with regard to our own rights & privileges in case we wish to commence another station at any other point on the reserve. The coming of the Catholic Priest here is a [mere stroke of policy, concocted?] in secret by such men as Mssrs. Godfrey & Noble to destroy or cripple the protestant mission. The worst men in the country are in favor of the measure. The plan is under the wing of the priest. The plan is to get in here a French half breed influence & then open the door for the worst class of men to come in and com get an influence. Some of the Indians are put up to believe that the paper you gave Blackbird is a forgery put up by the mission & Govt employ as to oppress their mission control the Indians. One of the claimants, for whom Mr. Noble acts as attorney, told me that the same Mr. Noble told him that the plan of the attorneys was to take the business of the old debts entirely out of your hands, and as for me, I was a fiery devil they when they much[?] tell their report was made out, & here what is to become of me remains to be seen. Probably I am to be hung. If so, I hope I shall be summoned to Washington for [which purpose?] that I may be held up in [t???] to all missionaries & they be [warned?] by my […]
The dramatic ending to this letter certainly reveals the intensity of the situation here in the fall of 1855. It also reveals the intensity of Wheeler’s hatred for the Roman Catholic faith, and by extension, the influence of the Catholic mix-blood portion of the La Pointe Band. This makes it difficult to view the Protestant missionary as any kind of impartial advocate for justice. Whatever was going on, he was right in the middle of it.
So, what did happen here?
From Morse, McElroy, and these two letters, it’s clear that Blackbird was doing whatever he could to stop the Government from paying annuity funds directly to the creditors. According to Wheeler, these men were led by U.S. Senator and fur baron Henry Mower Rice. It’s also clear that a significant minority of the Ojibwe, including most of the La Pointe mix-bloods, did not want to see the money go directly to the chiefs for disbursement.
I haven’t uncovered whether the creditors’ claims were accepted, or what Manypenny wrote back to Blackbird and Wheeler, but it is not difficult to guess what the response was. Wheeler, a Massachusetts-born reformist, had been able to influence Indian policy a few years earlier during the Whig administration of Millard Fillmore, and he may have hoped for the same with the Democrats. But this was 1855. Kansas was bleeding, the North was rapidly turning toward “Free Soil” politics, and the Dred Scott case was only a few months away. Franklin Pierce, a Southern-sympathizer had won the presidency in a landslide (losing only Massachusetts and three other states) in part because he was backed by Westerners like George Manypenny and H. M. Rice. To think the Democratic “Indian Ring,” as it was described above, would listen to the pleas coming from Odanah was optimistic to say the least.
“[E]xample not to meddle with other peoples business” is written at the top of Wheeler’s draft. It is his handwriting, but it is much darker than the rest of the ink and appears to have been added long after the fact. It doesn’t say it directly, but it seems pretty clear Wheeler didn’t look back on this incident as a success. I’ll keep looking for proof, but for now I can say with confidence that the request for a Washington delegation was almost certainly rejected outright.
So who are the good guys in this situation?
If we try to fit this story into the grand American narrative of Manifest Destiny and the systematic dispossession of Indian peoples, then we would have to conclude that this is a story of the Ojibwe trying to stand up for their rights against a group of corrupt traders. However, I’ve never had much interest in this modern “Dances With Wolves” version of Indian victimization. Not that it’s always necessarily false, but this narrative oversimplifies complex historical events, and dehumanizes individual Indians as much as the old “hostile savages” framework did. That’s why I like to compare the Chequamegon story more to the Canadian narrative of Louis Riel and company than to the classic American Little Bighorn story. The dispossession and subjugation of Native peoples is still a major theme, but it’s a lot messier. I would argue it’s a lot more accurate and more interesting, though.
So let’s evaluate the individuals involved rather than the whole situation by using the most extreme arguments one could infer from these documents and see if we can find the truth somewhere in the middle:

Henry Mower Rice (Wikimedia Images)
Henry M. Rice
The case against: H. M. Rice was businessman who valued money over all else. Despite his close relationship with the Ho-Chunk people, he pressed for their 1847 removal because of the enormous profits it brought. A few years later, he was the driving force behind the Sandy Lake removal of the Ojibwe. Both of these attempted removals came at the cost of hundreds of lives. There is no doubt that in 1855, Rice was simply trying to squeeze more money out of the Ojibwe.
The case for: H. M. Rice was certainly a businessman, and he deserved to be paid the debts owed him. His apparent actions in 1855 are the equivalent of someone having a lien on a house or car. That money may have justifiably belonged to him. As for his relationship with the Ojibwe, Rice continued to work on their behalf for decades to come, and can be found in 1889 trying to rectify the wrongs done to the Lake Superior bands when the reservations were surveyed.

From In Unnamed Wisconsin pg. 168. It’s not hard to figure out which Minnesota senator is being referred to here in this 1895 work informed by Harriet Wheeler. (Digitized by Google Books).

Antoine Gordon from Noble Lives of a Noble Race (pg. 207) published by the St. Mary’s Industrial School in Odanah.
Antoine Gordon
The case against: Antoine Gaudin (Gordon) was an unscrupulous trader and liquor dealer who worked with H. M. Rice to defraud his Ojibwe relatives during the 1855 annuities. He then tried to steal land and illegally squat on the Bad River Reservation against the expressed wishes of Chief Blackbird and Commissioner Manypenny.
The case for: Antoine Gordon couldn’t have been working against the Ojibwe since he was an Ojibwe man himself. He was a trader and was owed debts in 1855, but most of the criticism leveled against him was simply anti-Catholic libel from Leonard Wheeler. Antoine was a pious Catholic, and many of his descendants became priests. He built the church at Bad River because there were a number of people in Bad River who wanted a church. Men like Gordon, Vincent Roy Jr., and Joseph Gurnoe were not only crucial to the development of Red Cliff (as well as Superior and Gordon, WI) as a community, they were exactly the type of leaders the Ojibwe needed in the post-1854 world.

Portrait of Naw-Gaw-Nab (The Foremost Sitter) n.d by J.E. Whitney of St. Paul (Smithsonian)
Naaganab
The case against: Chiefs like Naaganab and Young Buffalo sold their people out for a quick buck. Rather than try to preserve the Ojibwe way of life, they sucked up to the Government by dressing like whites, adopting Catholicism, and using their favored position for their own personal gain and to bolster the position of their mix-blooded relatives.
The case for: If you frame these events in terms of Indians vs. Traders, you then have to say that Naaganab, Young Buffalo, and by extension Chief Buffalo were “Uncle Toms.” The historical record just doesn’t support this interpretation. The elder Buffalo and Naaganab each lived for nearly a century, and they each strongly defended their people and worked to preserve the Ojibwe land base. They didn’t use the same anti-Government rhetoric that Blackbird used at times, but they were working for the same ends. In fact, years later, Naaganab abandoned his tactic of assimilation as a means to equality, telling Rice in 1889:
“We think the time is past when we should take a hat and put it on our heads just to mimic the white man to adopt his custom without being allowed any of the privileges that belong to him. We wish to stand on a level with the white man in all things. The time is past when my children should stand in fear of the white man and that is almost all that I have to say (Nah-guh-nup pg. 192).”
Leonard H. Wheeler

L. H. Wheeler (WHS Image ID 66594)
The case against: Leonard Wheeler claimed to be helping the Ojibwe, but really he was just looking out for his own agenda. He hated the Catholic Church and was willing to do whatever it took to keep the Catholics out of Bad River including manipulating Blackbird into taking up his cause when the chief was the one in need. Wheeler couldn’t mind his own business. He was the biggest enemy the Ojibwe had in terms of trying to maintain their traditions and culture. He didn’t care about Blackbird. He just wanted the free trip to Washington.
The case for: In contrast to Sherman Hall and some of the other missionaries, Leonard Wheeler was willing to speak up forcefully against injustice. He showed this during the Sandy Lake removal and again during the 1855 payment. He saw the traders trying to defraud the Ojibwe and he stood up against it. He supported Blackbird in the chief’s efforts to protect the territorial integrity of the Bad River reservation. At a risk to his own safety, he chose to do the right thing.
Blackbird
The case against: Blackbird was opportunist trying to seize power after Buffalo’s death by playing to the outdated conservative impulses of his people at a time when they should have been looking to the future rather than the past. This created harmful factional differences that weakened the Ojibwe position. He wanted to go to Washington because it would make him look stronger and he manipulated Wheeler into helping him.
The case for: From the 1840s through the 1860s, the La Pointe Ojibwe had no stronger advocate for their land, culture, and justice than Chief Blackbird. While other chiefs thought they could work with a government that was out to destroy them, Blackbird never wavered, speaking consistently and forcefully for land and treaty rights. The traders, and other enemies of the Ojibwe, feared him and tried to keep their meetings and Washington trip secret from him, but he found out because the majority of the people supported him.

I’ve yet to find a picture of Blackbird, but this 1899 Bad River delegation to Washington included his son James (bottom right) along with Henry and Jack Condecon, George Messenger, and John Medegan–all sons and/or grandsons of signers of the Treaty of 1854 (Photo by De Lancey Gill; Smithsonian Collections).
Final word for now…
An entire book could be written about the 1855 annuity payments, and like so many stories in Chequamegon History, once you start the inquiry, you end up digging up more questions than answers. I can’t offer a neat and tidy explanation for what happened with the debts. I’m inclined to think that if Henry Rice was involved it was probably for his own enrichment at the expense of the Ojibwe, but I have a hard time believing that Buffalo, Jayjigwyong, Naaganab, and most of the La Pointe mix-bloods would be doing the same. Blackbird seems to be the hero in this story, but I wouldn’t be at all surprised if there was a political component to his actions as well. Wheeler deserves some credit for his defense of a position that alienated him from most area whites, but we have to take anything he writes about his Catholic neighbors with a grain of salt.
As for the Blackbird-Wheeler relationship, showcasing these two fascinating letters was my original purpose in writing this post. Was Blackbird manipulating Wheeler, was Wheeler manipulating Blackbird, or was neither manipulating the other? Could it be that the zealous Christian missionary and the stalwart “pagan” chief, were actually friends? What do you think?