1837 Petitions from La Pointe to the President
January 29, 2023
Collected & edited by Amorin Mello
Letters Received by the Office of Indian Affairs:
La Pointe Agency 1831-1839
National Archives Identifier: 164009310
O. I. A. La Pointe J171.
Hon Geo. W. Jones
Ho. of Reps. Jany 9, 1838
Transmits petition dated 31st Augt 1837, from Michel Cadotte & 25 other Chip. Half Breeds, praying that the amt to be paid them, under the late Chip. treaty, be distributed at La Pointe, and submitting the names of D. P. Bushnell, Lyman M. Warren, for the appt of Comsr to make the distribution.
Transmits it, that it may receive such attention as will secure the objects of the petitioners, says as the treaty has not been satisfied it may be necessary to bring the subject of the petition before the Comsr Ind Affrs of the Senate.
Recd 10 Jany 1838
file
[?] File.
House of Representatives Jany 9th 1838
Sir
I hasten to transmit the inclosed petition, with the hope, that the subject alluded to, may receive such attention, as to secure the object of the petitioners. As the Chippewa Treaty has not yet been ratified it may be necessary to bring the subject of the petition before the Committee of Indian Affairs of the Senate.
I am very respectfully
Your obt svt
Geo W. Jones
C. A. Harris Esqr
Comssr of Indian Affairs
War Department
To the President of the United States of America
The humble petition of the undersigned Chippewa Half-Breeds citizens of the United Sates, respectfully Shareth:

Bizhiki (Buffalo), Dagwagaane (Two Lodges Meet), and Jechiikwii’o (Snipe, aka Little Buffalo) signed the 1837 Treaty of St Peters for the La Pointe Band.
That, your petitioners having lately heard that a Treaty had been concluded between the Government of the United Sates and the Chippewa Indians at St Peters, for the cession of certain lands belonging to that tribe:
ARTICLE 3.
“The sum of one hundred thousand dollars shall be paid by the United States, to the half-
breeds of the Chippewa nation, under the direction of the President. It is the wish of the
Indians that their two sub-agents Daniel P. Bushnell, and Miles M. Vineyard, superintend
the distribution of this money among their half-breed relations.”
That, the said Chippewa Indians X, having a just regard to the interest and welfare of their Half Breed brethren, did there and then stipulate; that, a certain sum of money should be paid once for all unto the said Half-Breeds, to satisfy all claim they might have on the lands so ceded to the United States.
That, your petitioners are ignorant of the time and place where such payment is to be made.
That the great majority of the Half-Breeds entitled to a distribution of said sum of money, are either residing at La Pointe on Lake Superior, or being for the most part earning their livelihood from the Traders, are consequently congregated during the summer months at the aforesaid place.
Your petitioners humbly solicit their father the President, to take their case into consideration, and not subject them to a long and costly journey in ordering the payments to be made at any inconvenient distance, but on the contrary they trust that in his wisdom he will see the justice of their demand in requiring he will be pleased to order the same to be distributed at Lapointe agreeable to their request.
Your petitioners would also intimate that, although they are fully aware that the Executive will make a judicious choice in the appointment of the Commissioners who will be selected to carry into effect the Provisions of said Treaty, yet, they would humbly submit to the President, that they have full confidence in the integrity of D. P. Bushnell Esqr. resident Indian Agent for the United States at this place and Lyman M Warren Esquire, Merchant.
Your petitioners entertain the flattering hope, that, their petition will not be made in vain, and as in duty bound will ever pray.
La Pointe, Lake Superior,
Territory of Wisconsin 31st August 1837
Michel Cadotte
Michel Bosquet X his mark
Seraphim Lacombe X his mark
Joseph Cadotte X his mark
Antoine Cadotte X his mark
Chs W Borup for wife & Children
A Morrison for wife & children
Pierre Cotte
Henry Cotte X his mark
Frances Roussan X his mark
James Ermatinger for wife & family
Lyman M Warren for wife & family
Joseph Dufault X his mark
Paul Rivet X his mark for wife & family
Charles Chaboullez wife & family
George D. Cameron
Alixis Corbin
Louis Corbin
Jean Bste Denomme X his mark and family
Ambrose Deragon X his mark and family
Robert Morran X his mark ” “
Jean Bst Couvillon X his mark ” “
Alix Neveu X his mark ” “
Frances Roy X his mark ” “
Alixis Brisbant X his mark ” “
Signed in presence of G. Pauchene
John Livingston
O.I.A. La Pointe W424.
Governor of Wisconsin
Mineral Pt. Feby 19, 1838
Transmits the talk of “Buffalo,” a Chip. Chief, delivered at the La Pointe SubAgt, Dec. 9, 1837, asking that the am. due the half-breeds under the late Treaty, be divided fairly among them, & paid them there, as they will not go to St Peters for it, &c.
Says Buffalo has great influence with his tribe, & is friendly to the whites; his sentiments accord with most of those of the half-breeds & Inds in that part of the country.
File
Recd 13 March 1838
[?] File.
Superintendency of Indian Affairs
for the Territory of Wisconsin
Mineral Point, Feby 19, 1838
Sir,
I have the honor to inclose the talk of “Buffalo,” a principal chief of the Chippewa Indians in the vicinity of La Pointe, delivered on the 9th Dec’r last before Mr Bushnell, sub-agent of the Chippewas at that place. Mr. Bushnell remarks that the speech is given with as strict an adherence to the letter as the language will admit, and has no doubt the sentiments expressed by this Chief accord with those of most of the half-breeds and Indians in that place of the Country. The “Buffalo” is a man of great influence among his tribe, and very friendly to the whites.
Very respectfully,
Your obed’t sevt.
Henry Dodge
Supt Ind Affs
Hon C. A. Harris
Com. of Ind. Affairs
Subagency
Lapointe Dec 10 1837
Speech of the Buffalo principal Chief at Lapointe
Father I told you yesterday I would have something to say to you today. What I say to you now I want you to write down, and send it to the Great American Chief that we saw at St Peters last summer, (Gov. Dodge). Yesterday, I called all the Indians together, and have brought them here to hear what I say; I speak the words of all.
ARTICLE 1.
“The said Chippewa nation cede to the United States all that tract of country included
within the following boundaries:
[…]
thence to and along the dividing ridge between the waters of Lake Superior and those of the Mississippi
[…]“
Father it was not my voice, that sold the country last summer. The land was not mine; it belonged to the Indians beyond the mountains. When our Great Father told us at St Peters that it was only the country beyond the mountains that he wanted I was glad. I have nothing to say about the Treaty, good, or bad, because the country was not mine; but when it comes my time I shall know how to act. If the Americans want my land, I shall know what to say. I did not like to stand in the road of the Indians at St Peters. I listened to our Great Father’s words, & said them in my heart. I have not forgotten them. The Indians acted like children; they tried to cheat each other and got cheated themselves. When it comes my time to sell my land, I do not think I shall give it up as they did.
What I say about the payment I do not say on my own account; for myself I do not care; I have always been poor, & don’t want silver now. But I speak for the poor half breeds.
There are a great many of them; more than would fill your house; some of them are very poor They cannot go to St Peters for their money. Our Great Father told us at St Peters, that you would divide the money, among the half breeds. You must not mind those that are far off, but divide it fairly, and give the poor women and children a good share.
Father the Indians all say they will not go to St Peters for their money. Let them divide it in this parts if they choose, but one must have ones here. You must not think you see all your children here; there are so many of them, that when the money and goods are divided, there will not be more than half a Dollar and a breech cloth for each one. At Red Cedar Lake the English Trader (W. Aitken) told the Indians they would not have more than a breech cloth; this set them to thinking. They immediately held a council & their Indian that had the paper (The Treaty) said he would not keep it, and would send it back.
It will not be my place to come in among the first when the money is paid. If the Indians that own the land call me in I shall come in with pleasure.
ARTICLE 4.
“The sum of seventy thousand dollars shall be applied to the payment, by the United States, of certain claims against the Indians; of which amount twenty eight thousand dollars shall, at their request, be paid to William A. Aitkin, twenty five thousand to Lyman M. Warren, and the balance applied to the liquidation of other just demands against them—which they acknowledge to be the case with regard to that presented by Hercules L. Dousman, for the sum of five thousand dollars; and they request that it be paid.“
We are afraid of one Trader. When at St Peters I saw that they worked out only for themselves. They have deceived us often. Our Great Father told us he would pay our old debts. I thought they should be struck off, but we have to pay them. When I heard our debts would be paid, it done my heart good. I was glad; but when I got back here my joy was gone. When our money comes here, I hope our Traders will keep away, and let us arrange our own business, with the officers that the President sends here.
Father I speak for my people, not for myself. I am an old man. My fire is almost out – there is but little smoke. When I set in my wigwam & smoke my pipe, I think of what has past and what is to come, and it makes my heart shake. When business comes before us we will try and act like chiefs. If any thing is to be done, it had better be done straight. The Indians are not like white people; they act very often like children. We have always been good friends to the whites, and we want to remain so. We do not [even?] go to war with our enemies, the Sioux; I tell my young men to keep quiet.
Father I heard the words of our Great Father (Gov. Dodge) last summer, and was pleased; I have not forgotten what he said. I have his words up in my heart. I want you to tell him to keep good courage for us, we want him to do all he can for us. What I have said you have written down; I [?] you to hand him a copy; we don’t know your ways. If I [?] said any thing [?] dont send it. If you think of any thing I ought to say send it. I have always listened to the white men.
O.I.A. Lapointe, B.458
D. P. Bushnell
Lapointe, March 8, 1838
At the request of some of the petitioners, encloses a petition dated 7 March 1838, addressed to the Prest, signed by 167 Chip. half breeds, praying that the amt stipulated by the late Chip. Treaty to be paid to the half breeds, to satisfy all claims they ma have on the lands ceded by this Treaty, may be distributed at Lapointe.
Hopes their request will be complied with; & thinks their annuity should likewise be paid at Lapointe.
File
Recd 2nd May, 1838
Subagency
Lapointe Mch 6 1838
Sir
I have the honor herewith to enclose a petition addressed to the President of the United States, handed to me with a request by several of the petitioners that I would forward it. The justice of the demand of these poor people is so obvious to any one acquainted with their circumstances, that I cannot omit this occasion to second it, and to express a sincere hope that it will be complied with. Indeed, if the convenience and wishes of the Indians are consulted, and as the sum they receive for their country is so small, these should, I conciev, be principle considerations, their annuity will likewise as paid here; for it is a point more convenient of access for the different bands, that almost any other in their own country, and one moreover, where they have interests been in the habit of assembling in the summer months.
I am sir, with great respect,
your most obt servant,
D. P. Bushnell
O. I. A.
C. A. Harris Esqr.
Comr Ind. Affs
To the President of the United States of America
The humble petition of the undersigned Chippewa Half-Breeds citizens of the United States respectfully shareth
That your petitioners having lately heard, that a Treaty has been concluded between the Government of the United States and the Chippewa Indians at St Peters for the cession of certain lands belonging to that tribe;
That the said Chippewa Indians having a just regard to the interest and wellfare of their Half-Breed brethern, did there and then stipulate, that a certain sum of money should be paid once for all unto the said Half-Breeds, to satisfy all claims, they might have on the lands so ceded to the United States;
That your petitioners are ignorant of the time and place, where such payment is to be made; and
That the great majority of the Half-Breeds entitled to a portion of said sum of money are either residing at Lapointe on Lake Superior, or being for the most part earning their livelihood from the Traders, are consequently congregated during the summer months at the aforesaid place;
Your petitioners therefore humbly solicit their Father the President to take their case into consideration, and not subject them to a long and costly journey on ordering the payment to be made at any convenient distance, but on the contrary, they wish, that in his wisdom he will see the justice of this petition and that he will be pleased to order the same to be distributed at Lapointe agreeably to their request.
Your petitioners entertain the flattering hope, that their petition will not be made in vain and as in duly bound will ever pray.
Half Breeds of Folleavoine Lapointe Lac Court Oreilles and Lac du Flambeau
Georg Warren
Edward Warren
William Warren
Truman A Warren
Mary Warren
Michel Cadott
Joseph Cadotte
Joseph Dufault
Frances Piquette X his mark
Michel Bousquet X his mark
Baptiste Bousquet X his mark
Jos Piquette X his mark
Antoine Cadotte X his mark
Joseph Cadotte X his mark
Seraphim Lacombre X his mark
Angelique Larose X her mark
Benjamin Cadotte X his mark
J Bte Cadotte X his mark
Joseph Danis X his mark
Henry Brisette X his mark
Charles Brisette X his mark
Jehudah Ermatinger
William Ermatinger
Charlotte Ermatinger
Larence Ermatinger
Theodore Borup
Sophia Borup
Elisabeth Borup
Jean Bte Duchene X his mark
Agathe Cadotte X her mark
Mary Cadotte X her mark
Charles Cadotte X his mark
Louis Nolin _ his mark
Frances Baillerge X his mark
Joseph Marchand X his mark
Louis Dubay X his mark
Alexis Corbin X his mark
Augustus Goslin X his mark
George Cameron X his mark
Sophia Dufault X her mark
Augt Cadotte No 2 X his mark
Jos Mace _ his mark
Frances Lamoureau X his mark
Charles Morrison
Charlotte L. Morrison
Mary A Morrison
Margerike Morrison
Jane Morrison
Julie Dufault X her mark
Michel Dufault X his mark
Jean Bte Denomme X his mark
Michel Deragon X his mark
Mary Neveu X her mark
Alexis Neveu X his mark
Michel Neveu X his mark
Josette St Jean X her mark
Baptist St Jean X his mark
Mary Lepessier X her mark
Edward Lepessier X his mark
William Dingley X his mark
Sarah Dingley X her mark
John Hotley X his mark
Jeannette Hotley X her mark
Seraphim Lacombre Jun X his mark
Angelique Lacombre X her mark
Felicia Brisette X her mark
Frances Houle X his mark
Jean Bte Brunelle X his mark
Jos Gauthier X his mark
Edward Connor X his mark
Henry Blanchford X his mark
Louis Corbin X his mark
Augustin Cadotte X his mark
Frances Gauthier X his mark
Jean Bte Gauthier X his mark
Alexis Carpentier X his mark
Jean Bte Houle X his mark
Frances Lamieux X his mark
Baptiste Lemieux X his mark
Pierre Lamieux X his mark
Michel Morringer X his mark
Frances Dejaddon X his mark
John Morrison X his mark
Eustache Roussain X his mark
Benjn Morin X his mark
Adolphe Nolin X his mark
Half-Breeds of Fond du Lac
John Aitken
Roger Aitken
Matilda Aitken
Harriet Aitken
Nancy Scott
Robert Fairbanks
George Fairbanks
Jean B Landrie
Joseph Larose
Paul Bellanges X his mark
Jack Belcour X his mark
Jean Belcour X his mark
Paul Beauvier X his mark
Frances Belleaire
Michel Comptois X his mark
Joseph Charette X his mark
Chl Charette X his mark
Jos Roussain X his mark
Pierre Roy X his mark
Joseph Roy X his mark
Vincent Roy X his mark
Jack Bonga X his mark
Jos Morrison X his mark
Henry Cotte X his mark
Charles Chaboillez
Roderic Chaboillez
Louison Rivet X his mark
Louis Dufault X his mark
Louison Dufault X his mark
Baptiste Dufault X his mark
Joseph Dufault X his mark
Chs Chaloux X his mark
Jos Chaloux X his mark
Augt Bellanger X his mark
Bapt Bellanger X his mark
Joseph Bellanger X his mark
Ignace Robidoux X his mark
Charles Robidoux X his mark
Mary Robidoux X her mark
Simon Janvier X his mark
Frances Janvier X his mark
Baptiste Janvier X his mark
Frances Roussain X his mark
Therese Rouleau X his mark
Joseph Lavierire X his mark
Susan Lapointe X her mark
Mary Lapointe X her mark
Louis Gordon X his mark
Antoine Gordon X his mark
Jean Bte Goslin X his mark
Nancy Goslin X her mark
Michel Petit X his mark
Jack Petit X his mark
Mary Petit X her mark
Josette Cournoyer X her mark
Angelique Cournoyer X her mark
Susan Cournoyer X her mark
Jean Bte Roy X his mark
Frances Roy X his mark
Baptist Roy X his mark
Therese Roy X her mark
Mary Lavierge X her mark
Toussaint Piquette X his mark
Josette Piquette X her mark
Susan Montreille X her mark
Josiah Bissel X his mark
John Cotte X his mark
Isabelle Cotte X her mark
Angelique Brebant X her mark
Mary Brebant X her mark
Margareth Bell X her mark
Julie Brebant X her mark
Josette Lefebre X her mark
Sophia Roussain X her mark
Joseph Roussain X his mark
Angelique Roussain X her mark
Joseph Bellair X his mark
Catharine McDonald X her mark
Nancy McDonald X her mark
Mary Macdonald X her mark
Louise Landrie X his mark
In presence of
Chs W Borup
A Morrison
A. D. Newton
Lapointe 7th March 1838
1827 Deed for Old La Pointe
December 27, 2022
Collected & edited by Amorin Mello
Chief Buffalo and other principal men for the La Pointe Bands of Lake Superior Chippewa began signing treaties with the United States at the 1825 Treaty of Prairie Du Chien; followed by the 1826 Treaty of Fond Du Lac, which reserved Tribal Trust Lands for Chippewa Mixed Bloods along the St. Mary’s River between Lake Superior and Lake Huron:
ARTICLE 4.
The Indian Trade & Intercourse Act of 1790 was the United States of America’s first law regulating tribal land interests:
SEC. 4. And be it enacted and declared, That no sale of lands made by any Indians, or any nation or tribe of Indians the United States, shall be valid to any person or persons, or to any state, whether having the right of pre-emption to such lands or not, unless the same shall be made and duly executed at some public treaty, held under the authority of the United States.
It being deemed important that the half-breeds, scattered through this extensive country, should be stimulated to exertion and improvement by the possession of permanent property and fixed residences, the Chippewa tribe, in consideration of the affection they bear to these persons, and of the interest which they feel in their welfare, grant to each of the persons described in the schedule hereunto annexed, being half-breeds and Chippewas by descent, and it being understood that the schedule includes all of this description who are attached to the Government of the United States, six hundred and forty acres of land, to be located, under the direction of the President of the United States, upon the islands and shore of the St. Mary’s river, wherever good land enough for this purpose can be found; and as soon as such locations are made, the jurisdiction and soil thereof are hereby ceded. It is the intention of the parties, that, where circumstances will permit, the grants be surveyed in the ancient French manner, bounding not less than six arpens, nor more than ten, upon the river, and running back for quantity; and that where this cannot be done, such grants be surveyed in any manner the President may direct. The locations for Oshauguscodaywayqua and her descendents shall be adjoining the lower part of the military reservation, and upon the head of Sugar Island. The persons to whom grants are made shall not have the privilege of conveying the same, without the permission of the President.
The aforementioned Schedule annexed to the 1826 Treaty of Fond du Lac included (among other Chippewa Mixed Blood families at La Pointe) the families of Madeline & Michel Cadotte, Sr. and their American son-in-laws, the brothers Truman A. Warren and Lyman M. Warren:
-
To Michael Cadotte, senior, son of Equawaice, one section.
-
To Equaysay way, wife of Michael Cadotte, senior, and to each of her children living within the United States, one section.
-
To each of the children of Charlotte Warren, widow of the late Truman A. Warren, one section.
-
To Ossinahjeeunoqua, wife of Michael Cadotte, Jr. and each of her children, one section.
-
To each of the children of Ugwudaushee, by the late Truman A. Warren, one section.
-
To William Warren, son of Lyman M. Warren, and Mary Cadotte, one section.

Detail of Michilimackinac County circa 1818 from Michigan as a territory 1805-1837 by C.A. Burkhart, 1926.
~ UW-Milwaukee Libraries
Now, if it seems odd for a Treaty in Minnesota (Fond du Lac) to give families in Wisconsin (La Pointe) lots of land in Michigan (Sault Ste Marie), just remember that these places were relatively ‘close’ to each other in the sociopolitical fabric of Michigan Territory back in 1827. All three places were in Michilimackinac County (seated at Michilimackinac) until 1826, when they were carved off together as part of the newly formed Chippewa County (seated at Sault Ste Marie). Lake Superior remained Unceded Territory until later decades when land cessions were negotiated in the 1836, 1837, 1842, and 1854 Treaties.
Ultimately, the United States removed the aforementioned Schedule from the 1826 Treaty before ratification in 1827.
Several months later, at Michilimackinac, Madeline & Michel Cadotte, Sr. recorded the following Deed to reserve 2,000 acres surrounding the old French Forts of La Pointe to benefit future generations of their family.
Register of Deeds
Michilimackinac County
Book A of Deeds, Pages 221-224
Michel Cadotte and
Magdalen Cadotte
to
Lyman M. Warren
~Deed.
Received for Record
July 26th 1827 at two Six O’Clock A.M.
J.P. King
Reg’r Probate

Bizhiki (Buffalo), Gimiwan (Rain), Kaubuzoway, Wyauweenind, and Bikwaakodowaanzige (Ball of Dye) signed the 1826 Treaty of Fond Du Lac as the Chief and principal men of La Pointe.

“Copy of 1834 map of La Pointe by Lyman M. Warren“ at Wisconsin Historical Society. Original map (not shown here) is in the American Fur Company papers of the New York Historical Society.
Whereas the Chief and principal men of the Chippeway Tribe of indians, residing on and in the parts adjacent to the island called Magdalen in the western part of Lake Superior, heretofore released and confirmed by Deed unto Magdalen Cadotte a Chippeway of the said tribe, and to her brothers and sisters as tenants in common, thereon, all that part of the said Island called Magdalen, lying south and west of a line commencing on the eastern shore of said Island in the outlet of Great Wing river, and running directly thence westerly to the centre of Sandy bay on the western side of said Island;
and whereas the said brothers and sisters of said Magdalen Cadotte being tenants in common of the said premises, thereafterwards, heretofore, released, conveyed and confirmed unto their sister, the said Magdalen Cadotte all their respective rights title, interest and claim in and to said premises,
and whereas the said Magdalen Cadotte is desirous of securing a portion of said premises to her five grand children viz; George Warren, Edward Warren and Nancy Warren children of her daughter Charlotte Warren, by Truman A. Warren late a trader at said island, deceased, and William Warren and Truman A. Warren children of her daughter Mary Warren by Lyman M. Warren now a trader at said Island;
and whereas the said Magdalen Cadotte is desirous to promote the establishment of a mission on said Island, by and under the direction, patronage and government of the American board of commissioners for foreign missions, according to the plan, wages, and principles and purposes of the said Board.

William Whipple Warren was one of the beneficiary grandchildren named in this Deed.
Now therefore, Know all men by these presents that we Michael Cadotte and Magdalen Cadotte, wife of the said Michael, of said Magdalen Island, in Lake Superior, for and in consideration of one dollar to us in hand paid by Lyman M. Warren, the receipt whereof is hereby acknowledged, and for and in consideration of the natural love and affection we bear to our Grandchildren, the said George, Edward, Nancy, William W., and Truman A. Warren, children of our said daughters Charlotte and Mary;
and the further consideration of our great desire to promote the establishment of a mission as aforesaid, under and by the direction, government and patronage of Board aforesaid, have granted, bargained, sold, released, conveyed and confirmed, and by these presents do grant, bargain, sell, release, convey and confirm unto the said Lyman M. Warren his heirs and assigns, out of the aforerecited premises and as part and parcel thereof a certain tract of land on Magdalen Island in Lake Superior, bounded as follows,

Detail of Ojibwemowin placenames on GLIFWC’s webmap.
that is to say, beginning at the most southeasterly corner of the house built and now occupied by said Lyman M. Warren, on the south shore of said Island between this tract and the land of the grantor, thence on the east by a line drawn northerly until it shall intersect at right angles a line drawn westerly from the mouth of Great Wing River to the Centre of Sandy Bay, thence on the north by the last mentioned line westward to a Point in said line, from which a line drawn southward and at right angles therewith would fall on the site of the old fort, so called on the southerly side of said Island; thence on the west by a line drawn from said point and parallel to the eastern boundary of said tract, to the Site of the old fort, so called, thence by the course of the Shore of old Fort Bay to the portage; thence by a line drawn eastwardly to the place of beginning, containing by estimation two thousand acres, be the same more or less, with the appurtenances, hereditaments, and privileges thereto belonging.
To have and to hold the said granted premises to him the said Lyman M. Warren his heirs and assigns: In Trust, Nevertheless, and upon this express condition, that whensoever the said American Board of Commissioners for foreign missions shall establish a mission on said premises, upon the plan, usages, principles and purposes as aforesaid, the said Lyman M. Warren shall forthwith convey unto the american board of commissioners for foreign missions, not less than one quarter nor more than one half of said tract herein conveyed to him, and to be divided by a line drawn from a point in the southern shore of said Island, northerly and parallel with the east line of said tract, and until it intersects the north line thereof.
And as to the residue of the said Estate, the said Lyman M. Warren shall divided the same equally with and amongst the said five children, as tenants in common, and not as joint tenants; and the grantors hereby authorize the said Lyman M. Warren with full powers to fulfil said trust herein created, hereby ratifying and confirming the deed and deeds of said premises he may make for the purpose ~~~
In witness whereof we have hereunto set our respective hands, this twenty fifth day of july A.D. one thousand eight hundred and twenty seven, of Independence the fifty first.
(Signed) Michel Cadotte {Seal}
Magdalen Cadotte X her mark {Seal}
Signed, Sealed and delivered
in presence of us }
Daniel Dingley
Samuel Ashman
Wm. M. Ferry
(on the third page and ninth line from the top the word eastwardly was interlined and from that word the three following lines and part of the fourth to the words “to the place” were erased before the signing & witnessing of this instrument.)
~~~~~~
Territory of Michigan }
County of Michilimackinac }
Be it known that on the twenty sixth day of July A.D. 1827, personally came before me, the subscriber, one of the Justices of the Peace for the County of Michilimackinac, Michel Cadotte and Magdalen Cadotte, wife of the said Michel Cadotte, and the said Magdalen being examined separate and apart from her said husband, each severally acknowledged the foregoing instrument to be their voluntary act and deed for the uses and purposes therein expressed.
(Signed) J. P. King
Just. peace
Cxd
fees Paid $2.25
Photos, Photos, Photos
February 10, 2014
The queue of Chequamegon History posts that need to be written grows much faster than my ability to write them. Lately, I’ve been backed up with mysteries surrounding a number of photographs. Many of these photos are from after 1860, so they are technically outside the scope of this website (though they involve people who were important in the pre-1860 era too.
Photograph posts are some of the hardest to write, so I decided to just run through all of them together with minimal commentary other than that needed to resolve the unanswered questions. I will link all the photos back to their sources where their full descriptions can be found. Here it goes, stream-of-consciousness style:

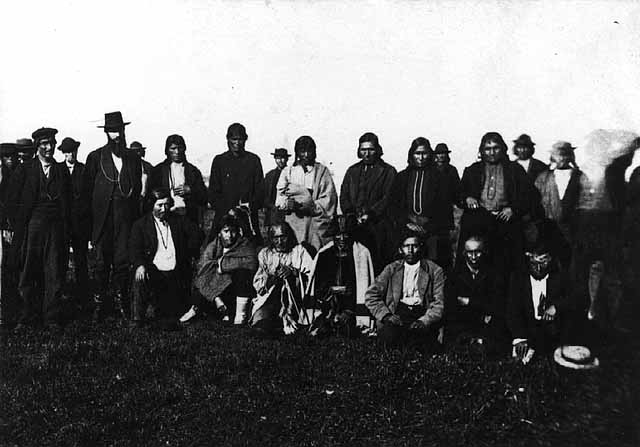
Ojibwa Delegation by C.M. Bell. Washington D.C. 1880 (NMAI Collections)
This whole topic started with a photo of a delegation of Lake Superior Ojibwe chiefs that sits on the windowsill of the Bayfield Public Library. Even though it is clearly after 1860, some of the names in the caption: Oshogay, George Warren, and Vincent Roy Jr. caught my attention. These men, looking past their prime, were all involved in the politics of the 1850s that I had been studying, so I wanted to find out more about the picture.
As I mentioned in the Oshogay post, this photo is also part of the digital collections of the Smithsonian, but the people are identified by different names. According to the Smithsonian, the picture was taken in Washington in 1880 by the photographer C.M. Bell.
I found a second version of this photo as well. If it wasn’t for one of the chiefs in front, you’d think it was the same picture:
While my heart wanted to believe the person, probably in the early 20th century, who labelled the Bayfield photograph, my head told me the photographer probably wouldn’t have known anything about the people of Lake Superior, and therefore could only have gotten the chiefs’ names directly from them. Plus, Bell took individual photos:

Edawigijig (Edawi-giizhig “Both Sides of the Sky”), Bad River chief and signer of the Treaty of 1854 (C.M. Bell, Smithsonian Digital Collections)

Niizhogiizhig: “Second Day,” (C.M. Bell, Smithsonian Digital Collections)

Kiskitawag (Giishkitawag: “Cut Ear”) signed multiple treaties as a warrior of the Ontonagon Band but afterwards was associated with the Bad River Band (C.M. Bell, Smithsonian Digital Collections).
By cross-referencing the individual photos with the names listed with the group photo, you can identify nine of the thirteen men. They are chiefs from Bad River, Lac Courte Oreilles, and Lac du Flambeau.
 According to this, the man identified by the library caption as Vincent Roy Jr., was in fact Ogimaagiizhig (Sky Chief). He does have a resemblance to Roy, so I’ll forgive whoever it was, even if it means having to go back and correct my Vincent Roy post:
According to this, the man identified by the library caption as Vincent Roy Jr., was in fact Ogimaagiizhig (Sky Chief). He does have a resemblance to Roy, so I’ll forgive whoever it was, even if it means having to go back and correct my Vincent Roy post:

Vincent Roy Jr. From C. Verwyst’s Life and Labors of Rt. Rev. Frederic Baraga, First Bishop of Marquette, Mich: To which are Added Short Sketches of the Lives and Labors of Other Indian Missionaries of the Northwest (Digitized by Google Books)

Top: Frank Roy, Vincent Roy, E. Roussin, Old Frank D.o., Bottom: Peter Roy, Jos. Gourneau (Gurnoe), D. Geo. Morrison. The photo is labelled Chippewa Treaty in Washington 1845 by the St. Louis Hist. Lib and Douglas County Museum, but if it is in fact in Washington, it was probably the Bois Forte Treaty of 1866, where these men acted as conductors and interpreters (Digitized by Mary E. Carlson for The Sawmill Community at Roy’s Point).
So now that we know who went on the 1880 trip, it begs the question of why they went. The records I’ve found haven’t been overly clear, but it appears that it involved a bill in the senate for “severalty” of the Ojibwe reservations in Wisconsin. A precursor to the 1888 Allotment Act of Senator Henry Dawes, this legislation was proposed by Senator Thaddeus C. Pound of Wisconsin. It would divide the reservations into parcels for individual families and sell the remaining lands to the government, thereby greatly reducing the size of the reservations and opening the lands up for logging.
Pound spent a lot of time on Indian issues and while he isn’t as well known as Dawes or as Richard Henry Pratt the founder of the Carlisle Indian School, he probably should be. Pound was a friend of Pratt’s and an early advocate of boarding schools as a way to destroy Native cultures as a way to uplift Native peoples.
I’m sure that Pound’s legislation was all written solely with the welfare of the Ojibwe in mind, and it had nothing to do with the fact that he was a wealthy lumber baron from Chippewa Falls who was advocating damming the Chippewa River (and flooding Lac Courte Oreilles decades before it actually happened). All sarcasm aside, if any American Indian Studies students need a thesis topic, or if any L.C.O. band members need a new dartboard cover, I highly recommend targeting Senator Pound.
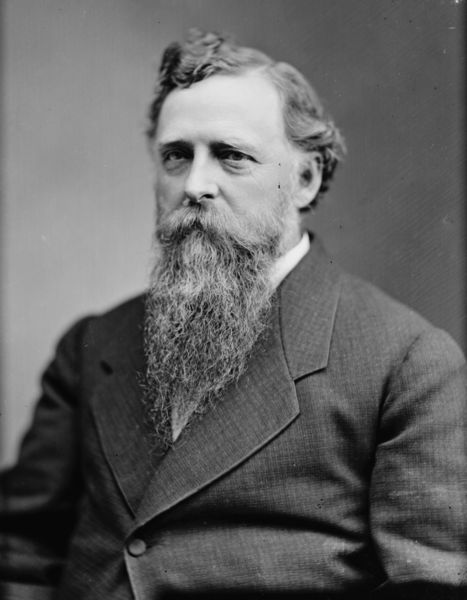

Like many self-proclaimed “Friends of the Indian” in the 1880s, Senator Thaddeus C. Pound of Wisconsin thought the government should be friendly to Indians by taking away more of their land and culture. That he stood to make a boatload of money out of it was just a bonus (Brady & Handy: Wikimedia Commons).
While we know Pound’s motivations, it doesn’t explain why the chiefs came to Washington. According to the Indian Agent at Bayfield they were brought in to support the legislation. We also know they toured Carlisle and visited the Ojibwe students there. There are a number of potential explanations, but without having the chiefs’ side of the story, I hesitate to speculate. However, it does explain the photograph.
Now, let’s look at what a couple of these men looked like two decades earlier:

This stereocard of Giishkitawag was produced in the early 1870s, but the original photo was probably taken in the early 1860s (Denver Public Library).

By the mid 1850s, Akiwenzii (Old Man) was the most prominent chief of the Lac Courte Oreilles Band. This stereocard was made by Whitney and Zimmerman c.1870 from an original possibly by James E. Martin in the late 1850s or early 1860s (Denver Public Library).
Giishkitawag and Akiwenzii are seem to have aged quite a bit between the early 1860s, when these photos were taken, and 1880 but they are still easily recognized. The earlier photos were taken in St. Paul by the photographers Joel E. Whitney and James E. Martin. Their galleries, especially after Whitney partnered with Charles Zimmerman, produced hundreds of these images on cards and stereoviews for an American public anxious to see real images of Indian leaders.
Giishkitawag and Akiwenzii were not the only Lake Superior chiefs to end up on these souvenirs. Aamoons (Little Bee), of Lac du Flambeau appears to have been a popular subject:

Aamoons (Little Bee) was a prominent chief from Lac du Flambeau (Denver Public Library).
As the images were reproduced throughout the 1870s, it appears the studios stopped caring who the photos were actually depicting:
One wonders what the greater insult to Aamoons was: reducing him to being simply “Chippewa Brave” as Whitney and Zimmerman did here, or completely misidentifying him as Na-gun-ub (Naaganab) as a later stereo reproduction as W. M. McLeish does here:

Chief identified as Na-gun-ub (Minnesota Historical Society)
Aamoons and Naaganab don’t even look alike…

Naaganab (Minnesota Historical Society)
…but the Lac du Flambeau and Fond du Lac chiefs were probably photographed in St. Paul around the time they were both part of a delegation to President Lincoln in 1862.

Chippewa Delegation 1862 by Matthew Brady? (Minnesota Historical Society)
Naaganab (seated middle) and Aamoons (back row, second from left) are pretty easy to spot, and if you look closely, you’ll see Giishkitawag, Akiwenzii, and a younger Edawi-giizhig (4th, 5th, and 6th from left, back row) were there too. I can’t find individual photos of the other chiefs, but there is a place we can find their names.
Benjamin Armstrong, who interpreted for the delegation, included a version of the image in his memoir Early Life Among the Indians. He identifies the men who went with him as:
Ah-moose (Little Bee) from Lac Flambeau Reservation, Kish-ke-taw-ug (Cut Ear) from Bad River Reservation, Ba-quas (He Sews) from Lac Courte O’Rielles Reservation, Ah-do-ga-zik (Last Day) from Bad River Reservation, O-be-quot (Firm) from Fond du Lac Reservation, Sing-quak-onse (Little Pine) from La Pointe Reservation, Ja-ge-gwa-yo (Can’t Tell) from La Pointe Reservation, Na-gon-ab (He Sits Ahead) from Fond du Lac Reservation, and O-ma-shin-a-way (Messenger) from Bad River Reservation.
It appears that Armstrong listed the men according to their order in the photograph. He identifies Akiwenzii as “Ba-quas (He Sews),” which until I find otherwise, I’m going to assume the chief had two names (a common occurrence) since the village is the same. Aamoons, Giishkitawag, Edawi-giizhig and Naaganab are all in the photograph in the places corresponding to the order in Armstrong’s list. That means we can identify the other men in the photo.
I don’t know anything about O-be-quot from Fond du Lac (who appears to have been moved in the engraving) or S[h]ing-guak-onse from Red Cliff (who is cut out of the photo entirely) other than the fact that the latter shares a name with a famous 19th-century Sault Ste. Marie chief. Travis Armstrong’s outstanding website, chiefbuffalo.com, has more information on these chiefs and the mission of the delegation.
Seated to the right of Naaganab, in front of Edawi-giizhig is Omizhinawe, the brother of and speaker for Blackbird of Bad River. Finally, the broad-shouldered chief on the bottom left is “Ja-ge-gwa-yo (Can’t Tell)” from Red Cliff. This is Jajigwyong, the son of Chief Buffalo, who signed the treaties as a chief in his own right. Jayjigwyong, sometimes called Little Chief Buffalo, was known for being an early convert to Catholicism and for encouraging his followers to dress in European style. Indeed, we see him and the rest of the chiefs dressed in buttoned coats and bow-ties and wearing their Lincoln medals.
Wait a minute… button coats?… bow-ties?… medals?…. a chief identified as Buffalo…That reminds me of…
This image is generally identified as Chief Buffalo (Wikimedia Commons)
Anyway, with that mystery solved, we can move on to the next one. It concerns a photograph that is well-known to any student of Chequamegon-area history in the mid 19th century (or any Chequamegon History reader who looks at the banners on the side of this page).Noooooo!!!!!!! I’ve been trying to identify the person in The above “Chief Buffalo” photo for years, and the answer was in Armstrong all along! Now I need to revise this post among others. I had already begun to suspect it was Jayjigwyong rather than his father, but my evidence was circumstantial. This leaves me without a doubt. This picture of the younger Chief Buffalo, not his more-famous father.
The photo showing an annuity payment, must have been widely distributed in its day, because it has made it’s way into various formats in archives and historical societies around the world. It has also been reproduced in several secondary works including Ronald Satz’ Chippewa Treaty Rights, Patty Loew’s Indian Nations of Wisconsin, Hamilton Ross’ La Pointe: Village Outpost on Madeline Island, and in numerous other pamphlets, videos, and displays in the Chequamegon Region. However, few seem to agree on the basic facts:
When was it taken?
Where was it taken?
Who was the photographer?
Who are the people in the photograph?
We’ll start with a cropped version that seems to be the most popular in reproductions:

According to Hamilton Ross and the Wisconsin Historical Society: “Annuity Payment at La Pointe: Indians receiving payment. Seated on the right is John W. Bell. Others are, left to right, Asaph Whittlesey, Agent Henry C. Gilbert, and William S. Warren (son of Truman Warren).” 1870. Photographer Charles Zimmerman (more info).
In the next one, we see a wider version of the image turned into a souvenir card much like the ones of the chiefs further up the post:

According to the Minnesota Historical Society “Scene at Indian payment, Wisconsin; man in black hat, lower right, is identified as Richard Bardon, Superior, Wisconsin, then acting Indian school teacher and farmer” c.1871 by Charles Zimmerman (more info).
In this version, we can see more foreground and the backs of the two men sitting in front.

According to the Library of Congress: “Cherokee payments(?). Several men seated around table counting coins; large group of Native Americans stand in background.” Published 1870-1900 (more info).
The image also exists in engraved forms, both slightly modified…

According to Benjamin Armstrong: “Annuity papment [sic] at La Pointe 1852” (From Armstrong’s Early Life Among the Indians)
…and greatly-modified.

Harper’s Weekly August 5, 1871: “Payment of Indian Annuities–Coming up to the Pay Table.” (more info)
It should also be mentioned that another image exists that was clearly taken on the same day. We see many of the same faces in the crowd:
Scene at Indian payment, probably at Odanah, Wisconsin. c.1865 by Charles Zimmerman (more info)
We have a lot of conflicting information here. If we exclude the Library of Congress Cherokee reference, we can be pretty sure that this is an annuity payment at La Pointe or Odanah, which means it was to the Lake Superior Ojibwe. However, we have dates ranging from as early as 1852 up to 1900. These payments took place, interrupted from 1850-1852 by the Sandy Lake Removal, from 1837 to 1874.
Although he would have attended a number of these payments, Benjamin Armstrong’s date of 1852, is too early. A number of secondary sources have connected this photo to dates in the early 1850s, but outside of Armstrong, there is no evidence to support it.
Charles Zimmerman, who is credited as the photographer when someone is credited, became active in St. Paul in the late 1860s, which would point to the 1870-71 dates as more likely. However, if you scroll up the page and look at Giishkitaawag, Akiwenzii, and Aamoons again, you’ll see that these photos, (taken in the early 1860s) are credited to “Whitney & Zimmerman,” even though they predate Zimmerman’s career.
What happened was that Zimmerman partnered with Joel Whitney around 1870, eventually taking over the business, and inherited all Whitney’s negatives (and apparently those of James Martin as well). There must have been an increase in demand for images of Indian peoples in the 1870s, because Zimmerman re-released many of the earlier Whitney images.
So, we’re left with a question. Did Zimmerman take the photograph of the annuity payment around 1870, or did he simply reproduce a Whitney negative from a decade earlier?
I had a hard time finding any primary information that would point to an answer. However, the Summer 1990 edition of the Minnesota History magazine includes an article by Bonnie G. Wilson called Working the Light: Nineteenth Century Professional Photographers in Minnesota. In this article, we find the following:
“…Zimmerman was not a stay-at-home artist. He took some of his era’s finest landscape photos of Minnesota, specializing in stereographs of the Twin Cities area, but also traveling to Odanah, Wisconsin for an Indian annuity payment…”
In the footnotes, Wilson writes:
“The MHS has ten views in the Odanah series, which were used as a basis for engravings in Harper’s Weekly, Aug. 5, 1871. See also Winona Republican, Oct. 12, 1869 p.3;”
Not having access to the Winona Republican, I tried to see how many of the “Odanah series” I could track down. Zimmerman must have sold a lot of stereocards, because this task was surprisingly easy. Not all are labelled as being in Odanah, but the backgrounds are similar enough to suggest they were all taken in the same place. Click on them to view enlarged versions at various digital archives.

Scene at Indian Payment, Odanah Wisconsin (Minnesota Historical Society)

Chippewa Wedding (British Museum)

Domestic Life–Chippewa Indians (British Museum)

Chippewa Wedding (British Museum)
Finally…
So, if Zimmerman took the “Odanah series” in 1869, and the pay table image is part of it, then this is a picture of the 1869 payment. To be absolutely certain, we should try to identify the men in the image.
This task is easier than ever because the New York Public Library has uploaded a high-resolution scan of the Whitney & Zimmerman stereocard version to Wikimedia Commons. For the first time, we can really get a close look at the men and women in this photo.
They say a picture tells a thousand words. I’m thinking I could write ten-thousand and still not say as much as the faces in this picture.
To try to date the photo, I decided to concentrate the six most conspicuous men in the photo:
1) The chief in the fur cap whose face in the shadows.
2) The gray-haired man standing behind him.
3) The man sitting behind the table who is handing over a payment.
4) The man with the long beard, cigar, and top hat.
5) The man with the goatee looking down at the money sitting to the left of the top-hat guy (to the right in our view)
6) The man with glasses sitting at the table nearest the photographer
According to Hamilton Ross, #3 is Asaph Whittlesey, #4 is Agent Henry Gilbert, #5 is William S. Warren (son of Truman), and #6 is John W. Bell. While all four of those men could have been found at annuity payments as various points between 1850 and 1870, this appears to be a total guess by Ross. Three of the four men appear to be of at least partial Native descent and only one (Warren) of those identified by Ross was Ojibwe. Chronologically, it doesn’t add up either. Those four wouldn’t have been at the same table at the same time. Additionally, we can cross-reference two of them with other photos.

Asaph Whittlesey was an interesting looking dude, but he’s not in the Zimmerman photo (Wisconsin Historical Society).

Henry C. Gilbert was the Indian Agent during the Treaty of 1854 and oversaw the 1855 annuity payment, but he was dead by the time the “Zimmerman” photo was taken (Branch County Photographs)
Whittlesey and Gilbert are not in the photograph.
The man who I label as #5 is identified by Ross as William S. Warren. This seems like a reasonable guess, though considering the others, I don’t know that it’s based on any evidence. Warren, who shares a first name with his famous uncle William Whipple Warren, worked as a missionary in this area.
The man I label #6 is called John W. Bell by Ross and Richard Bardon by the Minnesota Historical Society. I highly doubt either of these. I haven’t found photos of either to confirm, but the Ireland-born Bardon and the Montreal-born Bell were both white men. Mr. 6 appears to be Native. I did briefly consider Bell as a suspect for #4, though.
Neither Ross nor the Minnesota Historical Society speculated on #1 or #2.
At this point, I cannot positively identify Mssrs. 1, 2, 3, 5, or 6. I have suspicions about each, but I am not skilled at matching faces, so these are wild guesses at this point:
#1 is too covered in shadows for a clear identification. However, the fact that he is wearing the traditional fur headwrap of an Ojibwe civil chief, along with a warrior’s feather, indicates that he is one of the traditional chiefs, probably from Bad River but possibly from Lac Courte Oreilles or Lac du Flambeau. I can’t see his face well enough to say whether or not he’s in one of the delegation photos from the top of the post.
#2 could be Edawi-giizhig (see above), but I can’t be certain.
#3 is also tricky. When I started to examine this photo, one of the faces I was looking for was that of Joseph Gurnoe of Red Cliff. You can see him in a picture toward the top of the post with the Roy brothers. Gurnoe was very active with the Indian Agency in Bayfield as a clerk, interpreter, and in other positions. Comparing the two photos I can’t say whether or not that’s him. Leave a comment if you think you know.
#5 could be a number of different people.
#6 I don’t have a solid guess on either. His apparent age, and the fact that the Minnesota Historical Society’s guess was a government farmer and schoolteacher, makes me wonder about Henry Blatchford. Blatchford took over the Odanah Mission and farm from Leonard Wheeler in the 1860s. This was after spending decades as Rev. Sherman Hall’s interpreter, and as a teacher and missionary in La Pointe and Odanah area. When this photo was taken, Blatchford had nearly four decades of experience as an interpreter for the Government. I don’t have any proof that it’s him, but he is someone who is easy to imagine having a place at the pay table.
Finally, I’ll backtrack to #4, whose clearly identifiable gray-streaked beard allows us to firmly date the photo. The man is Col. John H. Knight, who came to Bayfield as Indian Agent in 1869.

Col. John H. Knight (Wisconsin Historical Society)
Knight oversaw a couple of annuity payments, but considering the other evidence, I’m confident that the popular image that decorates the sides of the Chequamegon History site was indeed taken at Odanah by Charles Zimmerman at the 1869 annuity payment.
Do you agree? Do you disagree? Have you spotted anything in any of these photos that begs for more investigation? Leave a comment.
As for myself, it’s a relief to finally get all these photo mysteries out of my post backlog. The 1870 date on the Zimmerman photo reminds me that I’m spending too much time in the later 19th century. After all, the subtitle of this website says it’s history before 1860. I think it might be time to go back for a while to the days of the old North West Company or maybe even to Pontiac. Stay tuned, and thanks for reading,
Reconstructing the “Martell” Delegation through Newspapers
November 2, 2013

Symbolic Petition of the Chippewa Chiefs: This pictographic petition was brought to Washington D.C. by a delegation of Ojibwe chiefs and their interpreter J.B. Martell. This one, representing the band of Chief Oshkaabewis, is the most famous, but their were several others copied from birch bark by Seth Eastman and published in the works of Henry Schoolcraft. For more, follow this link.
Henry Schoolcraft. William W. Warren. George Copway. These names are familiar to any scholar of mid-19th-century Ojibwe history. They are three of the most referenced historians of the era, and their works provide a great deal of historical material that is not available in any other written sources. Copway was Ojibwe, Warren was a mix-blood Ojibwe, and Schoolcraft was married to the granddaughter of the great Chequamegon chief Waabojiig, so each is seen, to some extent, as providing an insider’s point of view. This could lead one to conclude that when all three agree on something, it must be accurate. However, there is a danger in over-relying on these early historians in that we forget that they were often active participants in the history they recorded.
This point was made clear to me once again as I tried to sort out my lingering questions about the 1848-49 “Martell” Delegation to Washington. If you are a regular reader, you may remember that this delegation was the subject of the first post on this website. You may also remember from this post, that the group did not have money to get to Washington and had to reach out to the people they encountered along the way.
The goal of the Martell Delegation was to get the United States to cede back title to the lands surrounding the major Lake Superior Ojibwe villages. The Ojibwe had given this land up in the Treaty of 1842 with the guarantee that they could remain on it. However, by 1848 there were rumors of removal of all the bands east of the Mississippi to unceded land in Minnesota. That removal was eventually attempted, in 1850-51, in what is now called the Sandy Lake Tragedy.
The Martell Delegation remains a little-known part of the removal story, although the pictographs remain popular. Those petitions are remembered because they were published in Henry Schoolcrafts’ Historical and statistical information respecting the history, condition, and prospects of the Indian tribes of the United States (1851) along with the most accessible primary account of the delegation:
In the month of January, 1849, a delegation of eleven Chippewas, from Lake Superior, presented themselves at Washington, who, amid other matters not well digested in their minds, asked the government for a retrocession of some portion of the lands which the nation had formerly ceded to the United States, at a treaty concluded at Lapointe, in Lake Superior, in 1842. They were headed by Oshcabawiss, a chief from a part of the forest-country, called by them Monomonecau, on the head-waters of the River Wisconsin. Some minor chiefs accompanied them, together with a Sioux and two boisbrules, or half-breeds, from the Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan. The principal of the latter was a person called Martell, who appeared to be the master-spirit and prime mover of the visit, and of the motions of the entire party. His motives in originating and conducting the party, were questioned in letters and verbal representations from persons on the frontiers. He was freely pronounced an adventurer, and a person who had other objects to fulfil, of higher interest to himself than the advancement of the civilization and industry of the Indians. Yet these were the ostensible objects put forward, though it was known that he had exhibited the Indians in various parts of the Union for gain, and had set out with the purpose of carrying them, for the same object, to England. However this may be, much interest in, and sympathy for them, was excited. Officially, indeed, their object was blocked up. The party were not accredited by their local agent. They brought no letter from the acting Superintendent of Indian Affairs on that frontier. The journey had not been authorized in any manner by the department. It was, in fine, wholly voluntary, and the expenses of it had been defrayed, as already indicated, chiefly from contributions made by citizens on the way, and from the avails of their exhibitions in the towns through which they passed; in which, arrayed in their national costume, they exhibited their peculiar dances, and native implements of war and music. What was wanting, in addition to these sources, had been supplied by borrowing from individuals.
Martell, who acted as their conductor and interpreter, brought private letters from several persons to members of Congress and others, which procured respect. After a visit, protracted through seven or eight weeks, an act was passed by Congress to defray the expenses of the party, including the repayment of the sums borrowed of citizens, and sufficient to carry them back, with every requisite comfort, to their homes in the north-west. While in Washington, the presence of the party at private houses, at levees, and places of public resort, and at the halls of Congress, attracted much interest; and this was not a little heightened by their aptness in the native ceremonies, dancing, and their orderly conduct and easy manners, united to the attraction of their neat and well-preserved costume, which helped forward the object of their mission.
The visit, although it has been stated, from respectable sources, to have had its origin wholly in private motives, in the carrying out of which the natives were made to play the part of mere subordinates, was concluded in a manner which reflects the highest credit on the liberal feelings and sentiments of Congress. The plan of retrocession of territory, on which some of the natives expressed a wish to settle and adopt the modes of civilized life, appeared to want the sanction of the several states in which the lands asked for lie. No action upon it could therefore be well had, until the legislatures of these states could be consulted (pg. 414-416, pictographic plates follow).
I have always had trouble with Schoolcraft’s interpretation of these events. It wasn’t that I had evidence to contradict his argument, but rather that I had a hard time believing that all these chiefs would make so weighty a decision as to go to Washington simply because their interpreter was trying to get rich. The petitions asked for a permanent homeland in the traditional villages east of the Mississippi. This was the major political goal of the Lake Superior Ojibwe leadership at that time and would remain so in all the years leading up to 1854. Furthermore, chiefs continued to ask for, or go “uninvited” on, diplomatic missions to the president in the years that followed.
I explored some of this in the post about the pictograph, but a number of lingering questions remained:
What route did this group take to Washington?
Who was Major John Baptiste Martell?
Did he manipulate the chiefs into working for him, or was he working for them?
Was the Naaganab who went with this group the well-known Fond du Lac chief or the warrior from Lake Chetek with the same name?
Did any chiefs from the La Pointe band go?
Why was Martell criticized so much? Did he steal the money?
What became of Martell after the expedition?
How did the “Martell Expedition” of 1848-49 impact the Ojibwe removal of 1850-51?
Lacking access to the really good archives on this subject, I decided to focus on newspapers, and since this expedition received so much attention and publicity, this was a good choice. Enjoy:


Indiana Palladium. Vevay, IN. Dec. 2, 1848
Capt. Seth Eastman of the U.S. Army took note of the delegation as it traveled down the Mississippi from Fort Snelling to St. Louis. Eastman, a famous painter of American Indians, copied the birch bark petitions for publication in the works of his collaborator Henry Schoolcraft. At least one St. Louis paper also noticed these unique pictographic documents.
 Lafayette Courier. Lafayette, IN. Dec. 8, 1848.
Lafayette Courier. Lafayette, IN. Dec. 8, 1848.
The delegation made its way up the Ohio River to Cincinnati, where Gezhiiyaash’s illness led to a chance encounter with some Ohio Freemasons. I won’t repeat it here, but I covered this unusual story in this post from August.
At Cincinnati, they left the river and headed toward Columbus. Just east of that city, on the way to Pittsburgh, one of the Ojibwe men offered some sound advice to the women of Hartford, Ohio, but he received only ridicule in return.

Madison Weekly Courier. Madison, IN. Jan. 24, 1849

It’s unclear how quickly reports of the delegation came back to the Lake Superior country. William Warren’s letter to his cousin George, written in March after the delegation had already left Washington, still spoke of St. Louis:
William W. Warren (Wikimedia Images)
“…About Martells Chiefs. They were according to last accounts dancing the pipe dance at St. Louis. They have been making monkeys of themselves to fill the pockets of some cute Yankee who has got hold of them. Black bird returned from Cleveland where he caught scarlet fever and clap. He has behaved uncommon well since his return…” (Schenck, pg. 49)
From this letter, we learn that Blackbird, the La Pointe chief, was originally part of the group. In evaluating Warren’s critical tone, we must remember that he was working closely with the very government officials who withheld their permission. Of the La Pointe chiefs, Blackbird was probably the least accepting of American colonial power. However, we see in the obituary of Naaganab, Blackbird’s rival at the 1855 annuity payment, that the Fond du Lac chief was also there.
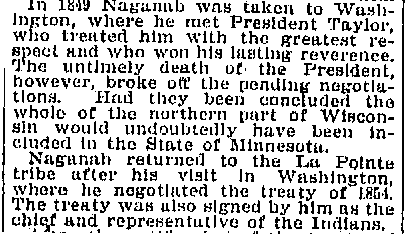
New York World. New York. July 22, 1894
Before finding this obituary, I had thought that the Naaganab who signed the petition was more likely the headman from Lake Chetek. Instead, this information suggests it was the more famous Fond du Lac chief. This matters because in 1848, Naaganab was considered the speaker for his cousin Zhingob, the leading chief at Fond du Lac. Blackbird, according to his son James, was the pipe carrier for Buffalo. While these chiefs had their differences with each other, it seems likely that they were representing their bands in an official capacity. This means that the support for this delegation was not only from “minor chiefs” as Schoolcraft described them, or “Martells Chiefs” as Warren did, from Lac du Flambeau and Michigan. I would argue that the presence of Blackbird and Naaganab suggests widespread support from the Lake Superior bands. I would guess that there was much discussion of the merits of a Washington delegation by Buffalo and others during the summer of 1848, and that the trip being a hasty money-making scheme by Martell seems much less likely.

Madison Daily Banner. Madison, IN. Jan. 3, 1849.
From Pittsburgh, the delegation made it to Philadelphia, and finally Washington. They attracted a lot of attention in the nation’s capital. Some of their adventures and trials: Oshkaabewis and his wife Pammawaygeonenoqua losing an infant child, the group hunting rabbits along the Potomac, and the chiefs taking over Congress, are included this post from March, so they aren’t repeated here.

Adams Sentinel. Gettysburg, PA. Feb. 5, 1849.
According to Ronald Satz, the delegation was received by both Congress and President Polk with “kindly feelings” and the expectation of “good treatment in the future” if they “behaved themselves (Satz 51).” Their petition was added to the Congressional Record, but the reservations were not granted at the time. However, Congress did take up the issue of paying for the debts accrued by the Ojibwe along the way.


George Copway (Wikimedia Commons)
Kah-Ge-Ga-Gah-Bowh (George Copway), a Mississauga Ojibwe and Methodist missionary, was the person “belonging to one of the Canada Bands of Chippewas,” who wrote the anti-Martell letter to Indian Commissioner William Medill. This is most likely the letter Schoolcraft referred to in 1851. In addition to being upset about the drinking, Copway was against reservations in Wisconsin. He wanted the government to create a huge pan-Indian colony at the headwaters of the Missouri River.

William Medill (Wikimedia Commons)

Iowa State Gazette. Burlington, IA. April 4, 1849
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 Weekly Wisconsin. Milwaukee. Feb. 28, 1849.
Weekly Wisconsin. Milwaukee. Feb. 28, 1849.
With $6000 (or did they only get $5000?), a substantial sum for the antebellum Federal Government, the group prepared to head back west with the ability to pay back their creditors.
It appears the chiefs returned to their villages by going back though the Great Lakes to Green Bay and then overland.
The Chippewa Delegation, who have been on a visit to see their “great fathers” in Washington, passed through this place on Saturday last, on their way to their homes near Lake Superior. From the accounts of the newspapers, they have been lionized during their whole journey, and particularly in Washington, where many presents were made them, among the most substantial of which was six boxed of silver ($6,000) to pay their expenses. They were loaded with presents, and we noticed one with a modern style trunk strapped to his back. They all looked well and in good spirits (qtd. in Paap, pg. 205).
Green Bay Gazette. April 4, 1849
So, it hardly seems that the Ojibwe chiefs returned to their villages feeling ripped off by their interpreter. Martell himself returned to the Soo, and found a community about to be ravaged by a epidemic of cholera.

Weekly Wisconsin. Milwaukee. Sep. 5, 1849.
Martell appears in the 1850 census on the record of those deceased in the past year. Whether he was a major in the Mexican War, whether he was in the United States or Canadian military, or whether it was even a real title, remains a mystery. His death record lists his birthplace as Minnesota, which probably connects him to the Martells of Red Lake and Red River, but little else is known about his early years. And while we can’t say for certain whether he led the group purely out of self-interest, or whether he genuinely supported the cause, John Baptiste Martell must be remembered as a key figure in the struggle for a permanent Ojibwe homeland in Wisconsin and Michigan. He didn’t live to see his fortieth birthday, but he made the 1848-49 Washington delegation possible.
So how do we sort all this out?
To refresh, my unanswered questions from the other posts about this delegation were:
1) What route did this group take to Washington?
2) Who was Major John Baptiste Martell?
3) Did he manipulate the chiefs into working for him, or was he working for them?
4) Was the Naaganab who went with this group the well-known Fond du Lac chief or the warrior from Lake Chetek with the same name?
5) Did any chiefs from the La Pointe band go?
6) Why was Martell criticized so much? Did he steal the money?
7) What became of Martell after the expedition?
8) How did the “Martell Expedition” of 1848-49 impact the Ojibwe removal of 1850-51?
We’ll start with the easiest and work our way to the hardest. We know that the primary route to Washington was down the Brule, St. Croix, and Mississippi to St. Louis, and from there up the Ohio. The return trip appears to have been via the Great Lakes.
We still don’t know how Martell became a major, but we do know what became of him after the diplomatic mission. He didn’t survive to see the end of 1849.
The Fond du Lac chief Naaganab, and the La Pointe chief Blackbird, were part of the group. This indicates that a wide swath of the Lake Superior Ojibwe leadership supported the delegation, and casts serious doubt on the notion that it was a few minor chiefs in Michigan manipulated by Martell.
Until further evidence surfaces, there is no reason to support Schoolcraft’s accusations toward Martell. Even though these allegations are seemingly validated by Warren and Copway, we need to remember how these three men fit into the story. Schoolcraft had moved to Washington D.C. by this point and was no longer Ojibwe agent, but he obviously supported the power of the Indian agents and favored the assimilation of his mother-in-law’s people. Copway and Warren also worked closely with the Government, and both supported removal as a way to separate the Ojibwe from the destructive influences of the encroaching white population. These views were completely opposed to what the chiefs were asking for: permanent reservations at the traditional villages. Because of this, we need to consider that Schoolcraft, Warren, and Copway would be negatively biased toward this group and its interpreter.
Finally there’s the question Howard Paap raises in Red Cliff, Wisconsin. How did this delegation impact the political developments of the early 1850s? In one sense the chiefs were clearly pleased with the results of the trip. They made many friends in Congress, in the media, and in several American cities. They came home smiling with gifts and money to spread to their people. However, they didn’t obtain their primary goal: reservations east of the Mississippi, and for this reason, the following statement in Schoolcraft’s account stands out:
The plan of retrocession of territory, on which some of the natives expressed a wish to settle and adopt the modes of civilized life, appeared to want the sanction of the several states in which the lands asked for lie. No action upon it could therefore be well had, until the legislatures of these states could be consulted.
“Kindly feelings” from President Polk didn’t mean much when Zachary Taylor and a new Whig administration were on the way in. Meanwhile, Congress and the media were so wrapped up in the national debate over slavery that they forgot all about the concerns of the Ojibwes of Lake Superior. This allowed a handful of Indian Department officials, corrupt traders, and a crooked, incompetent Minnesota Territorial governor named Alexander Ramsey to force a removal in 1850 that resulted in the deaths of 400 Ojibwe people in the Sandy Lake Tragedy.
It is hard to know how the chiefs felt about their 1848-49 diplomatic mission after Sandy Lake. Certainly their must have been a strong sense that they were betrayed and abandoned by a Government that had indicated it would support them, but the idea of bypassing the agents and territorial officials and going directly to the seat of government remained strong. Another, much more famous, “uninvited” delegation brought Buffalo and Oshogay to Washington in 1852, and ultimately the Federal Government did step in to grant the Ojibwe the reservations. Almost all of the chiefs who made the journey, or were shown in the pictographs, signed the Treaty of 1854 that made them.
Sources:
McClurken, James M., and Charles E. Cleland. Fish in the Lakes, Wild Rice, and Game in Abundance: Testimony on Behalf of Mille Lacs Ojibwe Hunting and Fishing Rights / James M. McClurken, Compiler ; with Charles E. Cleland … [et Al.]. East Lansing, MI: Michigan State UP, 2000. Print.
Paap, Howard D. Red Cliff, Wisconsin: A History of an Ojibwe Community. St. Cloud, MN: North Star, 2013. Print.
Satz, Ronald N. Chippewa Treaty Rights: The Reserved Rights of Wisconsin’s Chippewa Indians in Historical Perspective. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters, 1991. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and times of an Ojibwe Leader. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2007. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe, and Seth Eastman. Historical and Statistical Information Respecting the History, Condition, and Prospects of the Indian Tribes of the United States: Collected and Prepared under the Direction of the Bureau of Indian Affairs per Act of Congress of March 3rd, 1847. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo, 1851. Print.
Oshogay
August 12, 2013
At the most recent count, Chief Buffalo is mentioned in over two-thirds of the posts here on Chequamegon History. That’s the most of anyone listed so far in the People Index. While there are more Buffalo posts on the way, I also want to draw attention to some of the lesser known leaders of the La Pointe Band. So, look for upcoming posts about Dagwagaane (Tagwagane), Mizay, Blackbird, Waabojiig, Andeg-wiiyas, and others. I want to start, however, with Oshogay, the young speaker who traveled to Washington with Buffalo in 1852 only to die the next year before the treaty he was seeking could be negotiated.
I debated whether to do this post, since I don’t know a lot about Oshogay. I don’t know for sure what his name means, so I don’t know how to spell or pronounce it correctly (in the sources you see Oshogay, O-sho-ga, Osh-a-ga, Oshaga, Ozhoge, etc.). In fact, I don’t even know how many people he is. There were at least four men with that name among the Lake Superior Ojibwe between 1800 and 1860, so much like with the Great Chief Buffalo Picture Search, the key to getting Oshogay’s history right is dependent on separating his story from those who share his name.
In the end, I felt that challenge was worth a post in its own right, so here it is.
Getting Started
According to his gravestone, Oshogay was 51 when he died at La Pointe in 1853. That would put his birth around 1802. However, the Ojibwe did not track their birthdays in those days, so that should not be considered absolutely precise. He was considered a young man of the La Pointe Band at the time of his death. In my mind, the easiest way to sort out the information is going to be to lay it out chronologically. Here it goes:
1) Henry Schoolcraft, United States Indian Agent at Sault Ste. Marie, recorded the following on July 19, 1828:
Oshogay (the Osprey), solicited provisions to return home. This young man had been sent down to deliver a speech from his father, Kabamappa, of the river St. Croix, in which he regretted his inability to come in person. The father had first attracted my notice at the treaty of Prairie du Chien, and afterwards received a small medal, by my recommendation, from the Commissioners at Fond du Lac. He appeared to consider himself under obligations to renew the assurance of his friendship, and this, with the hope of receiving some presents, appeared to constitute the object of his son’s mission, who conducted himself with more modesty and timidity before me than prudence afterwards; for, by extending his visit to Drummond Island, where both he and his father were unknown, he got nothing, and forfeited the right to claim anything for himself on his return here.
I sent, however, in his charge, a present of goods of small amount, to be delivered to his father, who has not countenanced his foreign visit.
Oshogay is a “young man.” A birth year of 1802 would make him 26. He is part of Gaa-bimabi’s (Kabamappa’s) village in the upper St. Croix country.
2) In June of 1834, Edmund Ely and W. T. Boutwell, two missionaries, traveled from Fond du Lac (today’s Fond du Lac Reservation near Cloquet) down the St. Croix to Yellow Lake (near today’s Webster, WI) to meet with other missionaries. As they left Gaa-bimabi’s (Kabamappa’s) village near the head of the St. Croix and reached the Namekagon River on June 28th, they were looking for someone to guide them the rest of the way. An old Ojibwe man, who Boutwell had met before at La Pointe, and his son offered to help. The man fed the missionaries fish and hunted for them while they camped a full day at the mouth of the Namekagon since the 29th was a Sunday and they refused to travel on the Sabbath. On Monday the 30th, the reembarked, and Ely recorded in his journal:
The man, whose name is “Ozhoge,” and his son embarked with us about 1/2 past 9 °clk a.m. The old man in the bow and myself steering. We run the rapids safely. At half past one P. M. arrived at the mouth of Yellow River…
Ozhoge is an “old man” in 1834, so he couldn’t have been born in 1802. He is staying on the Namekagon River in the upper St. Croix country between Gaa-bimabi and the Yellow Lake Band. He had recently spent time at La Pointe.
3) Ely’s stay on the St. Croix that summer was brief. He was stationed at Fond du Lac until he eventually wore out his welcome there. In the 1840s, he would be stationed at Pokegama, lower on the St. Croix. During these years, he makes multiple references to a man named Ozhogens (a diminutive of Ozhoge). Ozhogens is always found above Yellow River on the upper St. Croix.
Ozhogens has a name that may imply someone older (possibly a father or other relative) lives nearby with the name Ozhoge. He seems to live in the upper St. Croix country. A birth year of 1802 would put him in his forties, which is plausible.

Ke-che-wask keenk (Gichi-weshki) is Chief Buffalo. Gab-im-ub-be (Gaa-bimabi) was the chief Schoolcraft identified as the father of Oshogay. Ja-che-go-onk was a son of Chief Buffalo.
4) On August 2, 1847, the United States and the Mississippi and Lake Superior Ojibwe concluded a treaty at Fond du Lac. The US Government wanted Ojibwe land along the nation’s border with the Dakota Sioux, so it could remove the Ho-Chunk people from Wisconsin to Minnesota.
Among the signatures, we find O-sho-gaz, a warrior from St. Croix. This would seem to be the Ozhogens we meet in Ely.
Here O-sho-gaz is clearly identified as being from St. Croix. His identification as a warrior would probably indicate that he is a relatively young man. The fact that his signature is squeezed in the middle of the names of members of the La Pointe Band may or may not be significant. The signatures on the 1847 Treaty are not officially grouped by band, but they tend to cluster as such.
5) In 1848 and 1849 George P. Warren operated the fur post at Chippewa Falls and kept a log that has been transcribed and digitized by the University of Wisconsin Eau Claire. He makes several transactions with a man named Oshogay, and at one point seems to have him employed in his business. His age isn’t indicated, but the amount of furs he brings in suggests that he is the head of a small band or large family. There were multiple Ojibwe villages on the Chippewa River at that time, including at Rice Lake and Lake Shatac (Chetek). The United States Government treated with them as satellite villages of the Lac Courte Oreilles Band.
Based on where he lives, this Oshogay might not be the same person as the one described above.
6) In December 1850, the Wisconsin Supreme Court ruled in the case Oshoga vs. The State of Wisconsin, that there were a number of irregularities in the trial that convicted “Oshoga, an Indian of the Chippewa Nation” of murder. The court reversed the decision of the St. Croix County circuit court. I’ve found surprisingly little about this case, though that part of Wisconsin was growing very violent in the 1840s as white lumbermen and liquor salesmen were flooding the country.

Pg 56 of Containing cases decided from the December term, 1850, until the organization of the separate Supreme Court in 1853: Volume 3 of Reports of Cases Argued and Determined in the Supreme Court of the State of Wisconsin: With Tables of the Cases and Principal Matters, and the Rules of the Several Courts in Force Since 1838, Wisconsin. Supreme Court Authors: Wisconsin. Supreme Court, Silas Uriah Pinney (Google Books).
The man killed, Alexander Livingston, was a liquor dealer himself.
Alexander Livingston, a man who in youth had had excellent advantages, became himself a dealer in whisky, at the mouth of Wolf creek, in a drunken melee in his own store was shot and killed by Robido, a half-breed. Robido was arrested but managed to escape justice.
~From Fifty Years in the Northwest by W.H.C Folsom
Several pages later, Folsom writes:
At the mouth of Wolf creek, in the extreme northwestern section of this town, J. R. Brown had a trading house in the ’30s, and Louis Roberts in the ’40s. At this place Alex. Livingston, another trader, was killed by Indians in 1849. Livingston had built him a comfortable home, which he made a stopping place for the weary traveler, whom he fed on wild rice, maple sugar, venison, bear meat, muskrats, wild fowl and flour bread, all decently prepared by his Indian wife. Mr. Livingston was killed by an Indian in 1849.
Folsom makes no mention of Oshoga, and I haven’t found anything else on what happened to him or Robido (Robideaux?).
It’s hard to say if this Oshoga is the Ozhogen’s of Ely’s journals or the Oshogay of Warren’s. Wolf Creek is on the St. Croix, but it’s not far from the Chippewa River country either, and the Oshogay of Warren seems to have covered a lot of ground in the fur trade. Warren’s journal, linked in #4, contains a similar story of a killing and “frontier justice” leading to lynch mobs against the Ojibwe. To escape the violence and overcrowding, many Ojibwe from that part of the country started to relocate to Fond du Lac, Lac Courte Oreilles, or La Pointe/Bad River. La Pointe is also where we find the next mention of Oshogay.
7) From 1851 to 1853, a new voice emerged loudly from the La Pointe Band in the aftermath of the Sandy Lake Tragedy. It was that of Buffalo’s speaker Oshogay (or O-sho-ga), and he spoke out strongly against Indian Agent John Watrous’ handling of the Sandy Lake payments (see this post) and against Watrous’ continued demands for removal of the Lake Superior Ojibwe. There are a number of documents with Oshogay’s name on them, and I won’t mention all of them, but I recommend Theresa Schenck’s William W. Warren and Howard Paap’s Red Cliff, Wisconsin as two places to get started.
Chief Buffalo was known as a great speaker, but he was nearing the end of his life, and it was the younger chief who was speaking on behalf of the band more and more. Oshogay represented Buffalo in St. Paul, co-wrote a number of letters with him, and most famously, did most of the talking when the two chiefs went to Washington D.C. in the spring of 1852 (at least according to Benjamin Armstrong’s memoir). A number of secondary sources suggest that Oshogay was Buffalo’s son or son-in-law, but I’ve yet to see these claims backed up with an original document. However, all the documents that identify by band, say this Oshogay was from La Pointe.
The Wisconsin Historical Society has digitized four petitions drafted in the fall of 1851 and winter of 1852. The petitions are from several chiefs, mostly of the La Pointe and Lac Courte Oreilles/Chippewa River bands, calling for the removal of John Watrous as Indian Agent. The content of the petitions deserves its own post, so for now we’ll only look at the signatures.

November 6, 1851 Letter from 30 chiefs and headmen to Luke Lea, Commissioner of Indian Affairs: Multiple villages are represented here, roughly grouped by band. Kijiueshki (Buffalo), Jejigwaig (Buffalo’s son), Kishhitauag (“Cut Ear” also associated with the Ontonagon Band), Misai (“Lawyerfish”), Oshkinaue (“Youth”), Aitauigizhik (“Each Side of the Sky”), Medueguon, and Makudeuakuat (“Black Cloud”) are all known members of the La Pointe Band. Before the 1850s, Kabemabe (Gaa-bimabi) and Ozhoge were associated with the villages of the Upper St. Croix.

November 8, 1851, Letter from the Chiefs and Headmen of Chippeway River, Lac Coutereille, Puk-wa-none, Long Lake, and Lac Shatac to Alexander Ramsey, Superintendent of Indian Affairs: This letter was written from Sandy Lake two days after the one above it was written from La Pointe. O-sho-gay the warrior from Lac Shatac (Lake Chetek) can’t be the same person as Ozhoge the chief unless he had some kind of airplane or helicopter back in 1851.

Undated (Jan. 1852?) petition to “Our Great Father”: This Oshoga is clearly the one from Lake Chetek (Chippewa River).

Undated (Jan. 1852?) petition: These men are all associated with the La Pointe Band. Osho-gay is their Speaker.
In the early 1850s, we clearly have two different men named Oshogay involved in the politics of the Lake Superior Ojibwe. One is a young warrior from the Chippewa River country, and the other is a rising leader among the La Pointe Band.

Washington Delegation July 22, 1852 This engraving of the 1852 delegation led by Buffalo and Oshogay appeared in Benjamin Armstrong’s Early Life Among the Indians. Look for an upcoming post dedicated to this image.
8) In the winter of 1853-1854, a smallpox epidemic ripped through La Pointe and claimed the lives of a number of its residents including that of Oshogay. It had appeared that Buffalo was grooming him to take over leadership of the La Pointe Band, but his tragic death left a leadership vacuum after the establishment of reservations and the death of Buffalo in 1855.
Oshogay’s death is marked in a number of sources including the gravestone at the top of this post. The following account comes from Richard E. Morse, an observer of the 1855 annuity payments at La Pointe:
The Chippewas, during the past few years, have suffered extensively, and many of them died, with the small pox. Chief O-SHO-GA died of this disease in 1854. The Agent caused a suitable tomb-stone to be erected at his grave, in La Pointe. He was a young chief, of rare promise and merit; he also stood high in the affections of his people.
Later, Morse records a speech by Ja-be-ge-zhick or “Hole in the Sky,” a young Ojibwe man from the Bad River Mission who had converted to Christianity and dressed in “American style.” Jabegezhick speaks out strongly to the American officials against the assembled chiefs:
…I am glad you have seen us, and have seen the folly of our chiefs; it may give you a general idea of their transactions. By the papers you have made out for the chiefs to sign, you can judge of their ability to do business for us. We had but one man among us, capable of doing business for the Chippewa nation; that man was O-SHO-GA, now dead and our nation now mourns. (O-SHO-GA was a young chief of great merit and much promise; he died of small-pox, February 1854). Since his death, we have lost all our faith in the balance of our chiefs…
This O-sho-ga is the young chief, associated with the La Pointe Band, who went to Washington with Buffalo in 1852.
9) In 1878, “Old Oshaga” received three dollars for a lynx bounty in Chippewa County.
Report of the Wisconsin Office of the Secretary of State, 1878; pg. 94 (Google Books)
It seems quite possible that Old Oshaga is the young man that worked with George Warren in the 1840s and the warrior from Lake Chetek who signed the petitions against Agent Watrous in the 1850s.
10) In 1880, a delegation of Bad River, Lac Courte Oreilles, and Lac du Flambeau chiefs visited Washington D.C. I will get into their purpose in a future post, but for now, I will mention that the chiefs were older men who would have been around in the 1840s and ’50s. One of them is named Oshogay. The challenge is figuring out which one.

Ojibwe Delegation c. 1880 by Charles M. Bell. [Identifying information from the Smithsonian] Studio portrait of Anishinaabe Delegation posed in front of a backdrop. Sitting, left to right: Edawigijig; Kis-ki-ta-wag; Wadwaiasoug (on floor); Akewainzee (center); Oshawashkogijig; Nijogijig; Oshoga. Back row (order unknown); Wasigwanabi; Ogimagijig; and four unidentified men (possibly Frank Briggs, top center, and Benjamin Green Armstrong, top right). The men wear European-style suit jackets and pants; one man wears a peace medal, some wear beaded sashes or bags or hold pipes and other props.(Smithsonian Institution National Museum of the American Indian).
- Upper row reading from the left.
- 1. Vincent Conyer- Interpreter 1,2,4,5 ?, includes Wasigwanabi and Ogimagijig
- 2. Vincent Roy Jr.
- 3. Dr. I. L. Mahan, Indian Agent Frank Briggs
- 4. No Name Given
- 5. Geo P. Warren (Born at LaPointe- civil war vet.
- 6. Thad Thayer Benjamin Armstrong
- Lower row
- 1. Messenger Edawigijig
- 2. Na-ga-nab (head chief of all Chippewas) Kis-ki-ta-wag
- 3. Moses White, father of Jim White Waswaisoug
- 4. No Name Given Akewainzee
- 5. Osho’gay- head speaker Oshawashkogijig or Oshoga
- 6. Bay’-qua-as’ (head chief of La Corrd Oreilles, 7 ft. tall) Nijogijig or Oshawashkogijig
- 7. No name given Oshoga or Nijogijig
The Smithsonian lists Oshoga last, so that would mean he is the man sitting in the chair at the far right. However, it doesn’t specify who the man seated on the right on the floor is, so it’s also possible that he’s their Oshoga. If the latter is true, that’s also who the unknown writer of the library caption identified as Osho’gay. Whoever he is in the picture, it seems very possible that this is the same man as “Old Oshaga” from number 9.
11) There is one more document I’d like to include, although it doesn’t mention any of the people we’ve discussed so far, it may be of interest to someone reading this post. It mentions a man named Oshogay who was born before 1860 (albeit not long before).
For decades after 1854, many of the Lake Superior Ojibwe continued to live off of the reservations created in the Treaty of La Pointe. This was especially true in the St. Croix region where no reservation was created at all. In the 1910s, the Government set out to document where various Ojibwe families were living and what tribal rights they had. This process led to the creation of the St. Croix and Mole Lake reservations. In 1915, we find 64-year-old Oshogay and his family living in Randall, Wisconsin which may suggest a connection to the St. Croix Oshogays. As with number 6 above, this creates some ambiguity because he is listed as enrolled at Lac Courte Oreilles, which implies a connection to the Chippewa River Oshogay. For now, I leave this investigation up to someone else, but I’ll leave it here for interest.

United States. Congress. House. Committee on Indian Affairs. Indian Appropriation Bill: Supplemental Hearings Before a Subcommittee. 1919 (Google Books).
This is not any of the Oshogays discussed so far, but it could be a relative of any or all of them.
In the final analysis
These eleven documents mention at least four men named Oshogay living in northern Wisconsin between 1800 and 1860. Edmund Ely met an old man named Oshogay in 1834. He is one. A 64-year old man, a child in the 1850s, was listed on the roster of “St. Croix Indians.” He is another. I believe the warrior from Lake Chetek who traded with George Warren in the 1840s could be one of the chiefs who went to Washington in 1880. He may also be the one who was falsely accused of killing Alexander Livingston. Of these three men, none are the Oshogay who went to Washington with Buffalo in 1852.
That leaves us with the last mystery. Is Ozhogens, the young son of the St. Croix chief Gaa-bimabi, the orator from La Pointe who played such a prominent role in the politics of the early 1850s? I don’t have a smoking gun, but I feel the circumstantial evidence strongly suggests he is. If that’s the case, it explains why those who’ve looked for his early history in the La Pointe Band have come up empty.
However, important questions remain unanswered. What was his connection to Buffalo? If he was from St. Croix, how was he able to gain such a prominent role in the La Pointe Band, and why did he relocate to La Pointe anyway? I have my suspicions for each of these questions, but no solid evidence. If you do, please let me know, and we’ll continue to shed light on this underappreciated Ojibwe leader.
Sources:
Armstrong, Benj G., and Thomas P. Wentworth. Early Life among the Indians: Reminiscences from the Life of Benj. G. Armstrong : Treaties of 1835, 1837, 1842 and 1854 : Habits and Customs of the Red Men of the Forest : Incidents, Biographical Sketches, Battles, &c. Ashland, WI: Press of A.W. Bowron, 1892. Print.
Ely, Edmund Franklin, and Theresa M. Schenck. The Ojibwe Journals of Edmund F. Ely, 1833-1849. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2012. Print.
Folsom, William H. C., and E. E. Edwards. Fifty Years in the Northwest. St. Paul: Pioneer, 1888. Print.
KAPPLER’S INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES. Ed. Charles J. Kappler. Oklahoma State University Library, n.d. Web. 12 August 2013. <http:// digital.library.okstate.edu/Kappler/>.
Nichols, John, and Earl Nyholm. A Concise Dictionary of Minnesota Ojibwe. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota, 1995. Print.
Paap, Howard D. Red Cliff, Wisconsin: A History of an Ojibwe Community. St. Cloud, MN: North Star, 2013. Print.
Redix, Erik M. “The Murder of Joe White: Ojibwe Leadership and Colonialism in Wisconsin.” Diss. University of Minnesota, 2012. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. The Voice of the Crane Echoes Afar: The Sociopolitical Organization of the Lake Superior Ojibwa, 1640-1855. New York: Garland Pub., 1997. Print.
———–William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and times of an Ojibwe Leader. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2007. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe. Personal Memoirs of a Residence of Thirty Years with the Indian Tribes on the American Frontiers: With Brief Notices of Passing Events, Facts, and Opinions, A.D. 1812 to A.D. 1842. Philadelphia, [Pa.: Lippincott, Grambo and, 1851. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
In the Fall of 1850, the Lake Superior Ojibwe (Chippewa) bands were called to receive their annual payments at Sandy Lake on the Mississippi River. The money was compensation for the cession of most of northern Wisconsin, Upper Michigan, and parts of Minnesota in the treaties of 1837 and 1842. Before that, payments had always taken place in summer at La Pointe. That year they were switched to Sandy Lake as part of a government effort to remove the entire nation from Wisconsin and Michigan in blatant disregard of promises made to the Ojibwe just a few years earlier.
There isn’t enough space in this post to detail the entire Sandy Lake Tragedy (I’ll cover more at a later date), but the payments were not made, and 130-150 Ojibwe people, mostly men, died that fall and winter at Sandy Lake. Over 250 more died that December and January, trying to return to their villages without food or money.

George Warren (b.1823) was the son of Truman Warren and Charlotte Cadotte and the cousin of William Warren. (photo source unclear, found on Canku Ota Newsletter)
If you are a regular reader of Chequamegon History, you will recognize the name of William Warren as the writer of History of the Ojibway People. William’s father, Lyman, was an American fur trader at La Pointe. His mother, Mary Cadotte was a member of the influential Ojibwe-French Cadotte family of Madeline Island. William, his siblings, and cousins were prominent in this era as interpreters and guides. They were people who could navigate between the Ojibwe and mix-blood cultures that had been in this area for centuries, and the ever-encroaching Anglo-American culture.
The Warrens have a mixed legacy when it comes to the Sandy Lake Tragedy. They initially supported the removal efforts, and profited from them as government employees, even though removal was completely against the wishes of their Ojibwe relatives. However, one could argue this support for the government came from a misguided sense of humanitarianism. I strongly recommend William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and Times of an Ojibwe Leader by Theresa Schenck if you are interested in Warren family and their motivations. The Wisconsin Historical Society has also digitized several Warren family letters, and that’s what prompted this post. I decided to transcribe and analyze two of these letters–one from before the tragedy and one from after it.
The first letter is from Leonard Wheeler, a missionary at Bad River, to William Warren. Initially, I chose to transcribe this one because I wanted to get familiar with Wheeler’s handwriting. The Historical Society has his papers in Ashland, and I’m planning to do some work with them this summer. This letter has historical value beyond handwriting, however. It shows the uncertainty that was in the air prior to the removal. Wheeler doesn’t know whether he will have to move his mission to Minnesota or not, even though it is only a month before the payments are scheduled.
Sept 6, 1850
Dear Friend,
I have time to write you but a few lines, which I do chiefly to fulfill my promise to Hole in the Day’s son. Will you please tell him I and my family are expecting to go Below and visit our friends this winter and return again in the spring. We heard at Sandy Lake, on our way home, that this chief told [Rev.?] Spates that he was expecting a teacher from St. Peters’ if so, the Band will not need another missionary. I was some what surprised that the man could express a desire to have me come and live among his people, and then afterwards tell Rev Spates he was expecting a teacher this fall from St. Peters’. I thought perhaps there was some where a little misunderstanding. Mr Hall and myself are entirely undecided what we shall do next Spring. We shall wait a little and see what are to be the movements of gov. Mary we shall leave with Mr Hall, to go to school during the winter. We think she will have a better opportunity for improvement there, than any where else in the country. We reached our home in safety, and found our families all well. My wife wishes a kind remembrance and joins me in kind regards to your wife, Charlotte and all the members of your family. If Truman is now with you please remember us to him also. Tomorrow we are expecting to go to La Pointe and take the Steam Boat for the Sault monday. I can scarcely realize that nine years have passed away since in company with yourself and Pa[?] Edward[?] we came into the country.
Mary is now well and will probably write you by the bearer of this.
Very truly yours
L. H. Wheeler
 By the 1850s, Young Hole in the Day was positioning himself to the government as “head chief of all the Chippewas,” but to the people of this area, he was still Gwiiwiizens (Boy), his famous father’s son. (Minnesota Historical Society)
By the 1850s, Young Hole in the Day was positioning himself to the government as “head chief of all the Chippewas,” but to the people of this area, he was still Gwiiwiizens (Boy), his famous father’s son. (Minnesota Historical Society)Samuel Spates was a missionary at Sandy Lake. Sherman Hall started as a missionary at La Pointe and later moved to Crow Wing.
Mary, Charlotte, and Truman Warren are William’s siblings.
The Wheeler letter is interesting for what it reveals about the position of Protestant missionaries in the 1850s Chequamegon region. From the 1820s onward, the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions sent missionaries, mostly Congregationalists and Presbyterians from New England, to the Lake Superior Country. Their names, Wheeler, Hall, Ely, Boutwell, Ayer, etc. are very familiar to historians, because they produced hundreds of pages of letters and diaries that reveal a great deal about this time period.

Leonard H. Wheeler (Wisconsin Historical Society)
Ojibwe people reacted to these missionaries in different ways. A few were openly hostile, while others were friendly and visited prayer, song, and school meetings. Many more just ignored them or regarded them as a simple nuisance. In forty-plus years, the amount of Ojibwe people converted to Protestantism could be counted on one hand, so in that sense the missions were a spectacular failure. However, they did play a role in colonization as a vanguard for Anglo-American culture in the region. Unlike the traders, who generally married into Ojibwe communities and adapted to local ways to some degree, the missionaries made a point of trying to recreate “civilization in the wilderness.” They brought their wives, their books, and their art with them. Because they were not working for the government or the Fur Company, and because they were highly respected in white-American society, there were times when certain missionaries were able to help the Ojibwe advance their politics. The aftermath of the Sandy Lake Tragedy was such a time for Wheeler.
This letter comes before the tragedy, however, and there are two things I want to point out. First, Wheeler and Sherman Hall don’t know the tragedy is coming. They were aware of the removal, and tentatively supported it on the grounds that it might speed up the assimilation and conversion of the Ojibwe, but they are clearly out of the loop on the government’s plans.
Second, it seems to me that Hole in the Day is giving the missionaries the runaround on purpose. While Wheeler and Spates were not powerful themselves, being hostile to them would not help the Ojibwe argument against the removal. However, most Ojibwe did not really want what the missionaries had to offer. Rather than reject them outright and cause a rift, the chief is confusing them. I say this because this would not be the only instance in the records of Ojibwe people giving ambiguous messages to avoid having their children taken.
Anyway, that’s my guess on what’s going on with the school comment, but you can’t be sure from one letter. Young Hole in the Day was a political genius, and I strongly recommend Anton Treuer’s The Assassination of Hole in the Day if you aren’t familiar with him.

I read this as “passed away since in company with yourself and Pa[?] Edward we came into the country.” Who was Wheeler’s companion when a young William guided him to La Pointe? I intend to find out and fix this quote. (from original in the digital collections of the Wisconsin Historical Society)
In 1851, Warren was in failing health and desperately trying to earn money for his family. He accepted the position of government interpreter and conductor of the removal of the Chippewa River bands. He feels removing is still the best course of action for the Ojibwe, but he has serious doubts about the government’s competence. He hears the desires of the chiefs to meet with the president, and sees the need for a full rice harvest before making the journey to La Pointe. Warren decides to stall at Lac Courte Oreilles until all the Ojibwe bands can unite and act as one, and does not proceed to Lake Superior as ordered by Watrous. The agent is getting very nervous.
 Clement and Paul (pictured) Hudon Beaulieu, and Edward Conner, were mix-blooded traders who like the Warrens were capable of navigating Anglo-American culture while maintaining close kin relationships in several Ojibwe communities. Clement Beaulieu and William Warren had been fierce rivals ever since Beaulieu’s faction drove Lyman Warren out of the American Fur Company. (Photo original unknown: uploaded to findadagrave.com by Joan Edmonson)
Clement and Paul (pictured) Hudon Beaulieu, and Edward Conner, were mix-blooded traders who like the Warrens were capable of navigating Anglo-American culture while maintaining close kin relationships in several Ojibwe communities. Clement Beaulieu and William Warren had been fierce rivals ever since Beaulieu’s faction drove Lyman Warren out of the American Fur Company. (Photo original unknown: uploaded to findadagrave.com by Joan Edmonson)For more on Cob-wa-wis (Oshkaabewis) and his Wisconsin River band, see this post.
“Perish” is what I see, but I don’t know who that might be. Is there a “Parrish”, or possibly a “Bineshii” who could have carried Watrous’ letter? I’m on the lookout. (from original in the digital collections of the Wisconsin Historical Society)
Aug 9th 1851
Friend Warren
I am now very anxiously waiting the arrival of yourself and the Indians that are embraced in your division to come out to this place.
Mr. C. H. Beaulieu has arrived from the Lake Du Flambeau with nearly all that quarter and by an express sent on in advance I am informed that P. H. Beaulieu and Edward Conner will be here with Cob-wa-wis and they say the entire Wisconsin band, there had some 32 of the Pillican Lake band come out and some now are in Conner’s Party.
I want you should be here without fail in 10 days from this as I cannot remain longer, I shall leave at the expiration of this time for Crow Wing to make the payment to the St. Croix Bands who have all removed as I learn from letters just received from the St. Croix. I want your assistance very much in making the Crow Wing payment and immediately after the completion of this, (which will not take over two days[)] shall proceed to Sandy Lake to make the payment to the Mississippi and Lake Bands.
The goods are all at Sandy Lake and I shall make the entire payment without delay, and as much dispatch as can be made it; will be quite lots enough for the poor Indians. Perish[?] is the bearer of this and he can tell you all my plans better then I can write them. give My respects to your cousin George and beli[e]ve me
Your friend
J. S. Watrous
W. W. Warren Esq.}
P. S. Inform the Indians that if they are not here by the time they will be struck from the roll. I am daily expecting a company of Infantry to be stationed at this place.
JSW

































