Judge Bell Incidents: King No More
October 16, 2025
Collected & edited by Amorin Mello
This post is the second of a series featuring newspaper items about La Pointe’s infamous Judge John William Bell. Today we explore obituaries of Judge Bell that described his life at La Pointe. Future posts of this series will feature articles about the late Judge Bell written by his son-in-law George Francis Thomas née Gilbert Fayette Thomas a.k.a G.F.T.
… continued from King of the Apostle Islands.
King of the Apostle Islands No More
ASHLAND, Wis., Dec. 31. – Judge Bell, known far and wide as “King of the Apostle Islands,” died yesterday. For nearly half a century he governed what was practically a little monarchy in the wilderness. He was 83 years old, and was the oldest living settler on the historic spot where Marquette founded his mission, two hundred years ago.
KING OF THE ISLANDS.
Judge Bell,
“King of the Apostle Islands,”
Has Given Up His Crown.
The Oldest Living Pioneer
of the Historic Spot
Dies in Apparent Poverty,
Special to the Globe.
ASHLAND, Wis., – “The king of the Apostle islands” is dead. He passed away at an early hour this morning at La Pointe, on Madeline, the largest of the group, where he has lived for forty-four years, the oldest living pioneer of the historic spot where Pere Marquette founded his little Indian mission 200 years ago. Judge Bell was a character in the early history of the Lake Superior region, known far and wide as the “king” of the country known as La Pointe, which was organized in 1846 by Judge Bell. The area of the country was as large as many states of the Union, its borders including nearly all of Wisconsin north of the Chippewa river, the Apostle islands and to an almost
ENDLESS DISTANCE WEST.

Wisconsin Historical Society’s copy of Lyman Warren’s 1834 “Map of La Pointe” from the American Fur Company Papers at New York Historical Society.
The population of whites consisted only of a small handful of French voyagers, traders and trappers, most of whom rendezvous at La Pointe. The country was hardly known by the state, and Bell’s county was practically a young monarchy. He bossed everything and everybody, but in such a way that every Indian and every white was his friend and follower. Judge Bell came here in 1832, from Canada, in the employ of the American Fur company, which at that time was a power here. He had rarely left the island, except in years gone by to make occasional pilgrimages through the settlements. During his eventful life he held every office in the county, and for many years, served as county judge. He was a man of great native ability, possessed of a courage that controlled the rough element which surrounded him in the early days when there was no law except his will. He was honest, fearless,
A NATURAL-BORN RULER
of men, and through his efforts the poor and needy were cared for, and in no instance did he fail to befriend them. For this reason among those who survive him, and who lived in the good old pioneer days, all were his firm friends. His power departed only when the advance guard of civilization reached the great inland sea, through the medium of the iron horse, and opened a new era in the history of the new Wisconsin. For many years he has been old and feeble and has suffered for the comforts of life, having become a charge upon the town. He squandered thousands for the people and died poor but not friendless. He was eighty-three years of age.
ANOTHER PIONEER GONE
DEATH OF “SQUIRE” BELL, “THE KING OF LAPOINTE.”
Sketch of the Life of the Oldest Settler in the Lake Superior Region.
He comes to La Pointe With John Jacob Astor for the American Fur Co.
Judge John W. Bell died Friday morning at seven o’clock at his home at La Pointe, on Madeline Island, aged eighty-four years.

1847 PLSS survey map detailing the mouth of Iron River at what is now Silver City, Michigan along the east entrance to the Porcupine Mountains.
John W. Bell was born in New York City on May 3, 1803, and was consequently eighty-four years and seven months old. He learnt the trade of a cooper, and in this capacity in the year 1835, he came to the Lake superior country for the United States Fur company. He first settled at the mouth of Iron river, in Michigan, about twenty miles west of Ontonagon. Here, at that time, was one of the principal trading and fishing posts of the American Fur company, La Pointe being its headquarters. Remaining at Iron river for a few years, he came to La Pointe about 1840, where he continued to reside till the time of his death.

1845 United States map by John Dower, with the northernmost area of Wisconsin Territory that became La Pointe County.
At the time he came upon this lake its shores were an unbroken wilderness. At the Sault was a United States fort, but from the foot of Lake Superior to the Pacific ocean, no white settlement existed. The American and Northwest Fur companies were lords of this vast empire, and their trading posts and a few mission stations connected with them, held control. A small detachment of United States soldiers formed the distant outposts of Ft. Snelling. The state of Wisconsin had not been organized. No municipal government existed upon this lake. It was many years before Wisconsin was organized.

1845 United States map by J. Calvin Smith, with the original 1845 boundaries of La Pointe County added in red outline.
“beginning at the mouth of Muddy Island river [on the Mississippi River], thence running in a direct line to Yellow Lake, and from thence to Lake Courterille, so to intersect the eastern boundary line at that place, of the county of St Croix, thence to the nearest point on the west fork of Montreal river, thence down said river to Lake Superior.”
Finally the county of La Pointe was formed, embracing all Wisconsin bordering upon the lake and extending to town forty north. “Squire Bell,” as he was always called, became one of the county as well as town officers of the town and county of La Pointe, and for more than thirty years continued to hold office, being at different times chairman of supervisors, register of deeds, justice of the peace, clerk of the circuit court and county judge. This last office he held for many years.
He was a man of genial nature and robust frame. About four years ago, while in Ashland he fell and fractured his thigh, and was never able to walk again. His sufferings from this accident were great and his pleasant face was never seen again in Ashland. He enjoyed the esteem and friendship of his neighbors, so far as is known without exception. He was clear headed and of commanding appearance. His influence among the Indians and the French who for many years were the only inhabitants in the country was very great, and continued to the last. For years his dictum was the last resort for the settlement of the quarrels in this primitive community, and it seems to have been just and satisfactory. He was often called “The King of La Pointe,” and for years no one disputed his supremacy.

Edwin Ellis, M.D.
Dr. Edwin Ellis, of this city, said in speaking of the dead old pioneer:
“Thus one by one the early settlers are passing away, and ere long an entirely new generation will occupy the old haunts. He will rest upon the beautiful isle overlooking Chequamegon bay, where the landscape has been familiar to him for more than a generation. We a little longer linger on the shores of time, waiting the summons to cross the river. While we consign the body of an old friend to the earth we will in all heartfelt sorrow say: ‘Requiescat in Pace.'”
The Lake Superior Monarch
Judge Bell, the ‘king of the Apostle islands,’ who died the other day on Madeline Island at the age of eighty-three, was a conspicuous character in the early history of the Lake Superior region. He was the “king” of the county known as La Pointe, which was organized in 1846 by himself. The county was as large as many states of the Union, its borders including nearly all of Wisconsin north of the Chippewa river, the Apostle islands, and to an almost endless distance west. The white population consisted of a handful of French voyagers, traders and trappers, most of whom made their rendezvous at La Pointe. The country was hardly known by the state, and Bell’s realm was practically a little monarchy. He “bossed” everything and everybody, but in such a way that every Indian and every white was his friend and follower. Judge Bell rarely left the island except to make occasional pilgrimages through the settlements. During his eventful life he held every office in the county, and of late years had served as county judge. He was a man of great native ability, and was possessed of a courage that controlled the rough element that surrounded him in the early days when there was no law except his will. He was an honest, fearless, natural-born ruler of men. Through his efforts the poor and needy were cared for. His power departed only when the advanced guard of civilization reached the great inland sea. For many years he had been feeble, and of late had become a charge upon the town. He spent thousands upon the people.
To be continued in Fooled the Austrian Brothers…
“A real bona fide, unmitigated Irishman”
December 7, 2014
By Leo

“The Usual Irish Way of Doing Things”, by Thomas Nast Published 2 September 1871 in Harper’s Weekly. Nast, who battled Tammany Hall and designed the modern image of Santa Claus, is one of the most famous American political cartoonists. However, he frequently depicted Irish-Americans as drunken, monkey-like monsters (Wikimedia Images).
It has been a while since I’ve posted anything new. My personal life has made it impossible to meet my former quota of three new posts a month. Now, it seems like I’ll be lucky to get one every three months. I haven’t forgotten about this site, however, and there is certainly no shortage of new topics. Unfortunately, most of them require more effort than I am able to give right now. Today, however, I have a short one.
Regular readers will know that the 1855 La Pointe annuity payment to the Lake Superior Chippewa bands is a frequent subject on Chequamegon History. To fully understand the context of this post, I recommend reading some of the earlier posts on that topic. The 1855 payment produced dozens of interesting stories and anecdotes: some funny, some tragic, some heroic, some bizarre, and many complicated. We’ve covered everything from Chief Buffalo’s death, to Hanging Cloud the female warrior, to Chief Blackbird’s great speech, to the random arrival of several politicians, celebrities, and dignitaries on Madeline Island.
Racism is an unavoidable subject in nearly all of these stories. The decisive implementation of American power on the Chequamegon Region in the 1850s cannot be understood without harshly examining the new racial order that it brought.
The earlier racial order (Native, Mix-blood, European) allowed Michel Cadotte Jr., being only of one-eighth European ancestry to be French while Antoine Gendron, of full French ancestry, was seen as fully Ojibwe. The new American order, however, increasingly defined ones race according to the shade of his or her skin.
But there are never any easy narratives in the history of this area, and much can be missed if the story of American domination is only understood as strictly an Indian/White conflict. There are always misfits, and this area was full of them.
I recently found an example from the November 7, 1855 edition of the Western Reserve Chronicle in Warren, Ohio shows just how the suffocating paternalism directed toward the Ojibwe at the 1855 payment hit others as well:
A GENUINE IRISHMAN
A correspondent of the Home Journal relates the following characteristic incident of Irish tactic. He says:
Does the wide world contain another paradox that will compare with a real bona fide, unmitigated Irishman? Imagination and sensuality, poetry and cupidity, generosity and avarice, heroism and cowardice–and so on, to the end of the list; all colors, shades and degrees of character congregated together, and each in most intimate association with its intensest antithesis–a very Joseph’s coat, and yet, most marvelous of marvels! a perfect harmony pervading the whole.
Among the reminiscences of a month’s sojourn at La Pointe, Lake Superior, during the annual Indian payment of the last summer, I find the following truly ‘representative’ anecdote:
One day while Commissioner Monypenny was sitting in council with the chiefs, intelligence was brought to Mr. Gilbert (the Indian agent) that two or three Indians were drunk and fighting, at a certain wigwam. With his usual promptitude, Mr. Gilbert summoned one of his interpreters, and proceeded directly to the lodge, where he seized the parties and locked them in the little wooden jail of the village, having first ascertained from them where they obtained their liquor. He then went immediately to the house they had designated, which was a private dwelling, occupied by an Irishman and his wife, and demanded if they kept liquor to sell to the Indians.

Henry C. Gilbert was the Indian Agent during the Treaty of 1854 and oversaw the 1855 annuity payment along with Commissioner of Indian Affairs George Manypenny (Branch County Photographs).
Both the man and woman, with rational vehemence and volubility–and both at once, of course, utterly denied having ‘a dhrop in the house, more nor a little jug full, which we just kape by us, like, for saysonin’ the vittals, and sickness.’ But, unfortunately for the veracity of the parties, on searching the premises, the interpreter discovered, in a little back wood-shed, two barrels of whiskey, besides the ‘little jug’ which proved to be a two gallon one, and full.
Mr. Gilbert ordered some of his men to roll the barrels out on the green, where in the presence of the whole council, they knocked in head, and the jug broken. But the flow of whisky was as nothing compared with the Irish wife’s temper, meanwhile. I had never conceived it possible for a tongue to possess such leverage; it seemed literally to be ‘hung in the middle and to work both ways.’ However, mother Earth drank the whisky, and the abuse melted into ‘the circumambient air’–though one would not have suspected their volubility, they seemed to be such concrete masses of venom.
In the evening of the same day, as Col. Monypenny was walking out with a friend, he encountered and was accosted by, the Irish whisky vender.
‘The first star of the avenin’ to yees, Misther Commissioner! An’ sure it was a bad thrick ye were putting on a poor mon, this mornin’. Och, murther! to think how ye dissipayted the illegant whisky; but ye’ll not be doin’ less nor payin’ me the first cost of it, will ye?’
‘On the contrary,’ said the commissioner, ‘we are thinking of having you up in the morning, and fining you; and if we catch you selling another drop to the Indians, we shall forcibly remove you from the island.’
Quick as–but I despair of a simile, for surely there is no operation of nature or art that will furnish a parallel to the agility of an Irishman’s wit–his whole tone and manner changed, and dropping his voice to the pitch confidential, he said:
‘Wll, Misther Commissioner, an’ its truth I’m tellin’ ye–its mighty glad I was, intirely, to see the dirty barrels beheaded; sure I’d a done it meself, for the moral of the thing, ef it hadn’t been for the ould woman. Good avenin’ to ye, Misther Commissioner.’
It is hardly necessary to add that no further application was made for the ‘first cost of it.’
Very truly yours.
~ Western Reserve chronicle. (Warren, Ohio) November 07, 1855
(Library of Congress Chronicling America Historic Newspaper Collection)
The sale of alcohol was illegal at La Pointe at that time. However, the law was generally impossible to enforce and liquor flowed freely into and out of the island.
Admittedly I chuckled at the depiction of the Irish wit and the temper of the “Irish wife,” but as a descendant of immigrants who fled the Great Famine in the 1840s, it’s hard to read the condescending stereotypes my ancestors would have been subjected to.
That said, it’s important to note that the two or three Ojibwe people in this story were imprisoned without charges or trial for drinking, while the couple selling the illegal liquor only lost his stock and wasn’t fined. This is something those of us of European descent need to be careful of when trying to draw equivalencies.
So then who was the bona fide, unmitigated Irishman?
Hundreds of thousands of Irish immigrants came to America during the 1840s and ’50s. Inevitably, some of them ended up in this area. However, by 1855 it was only a handful.
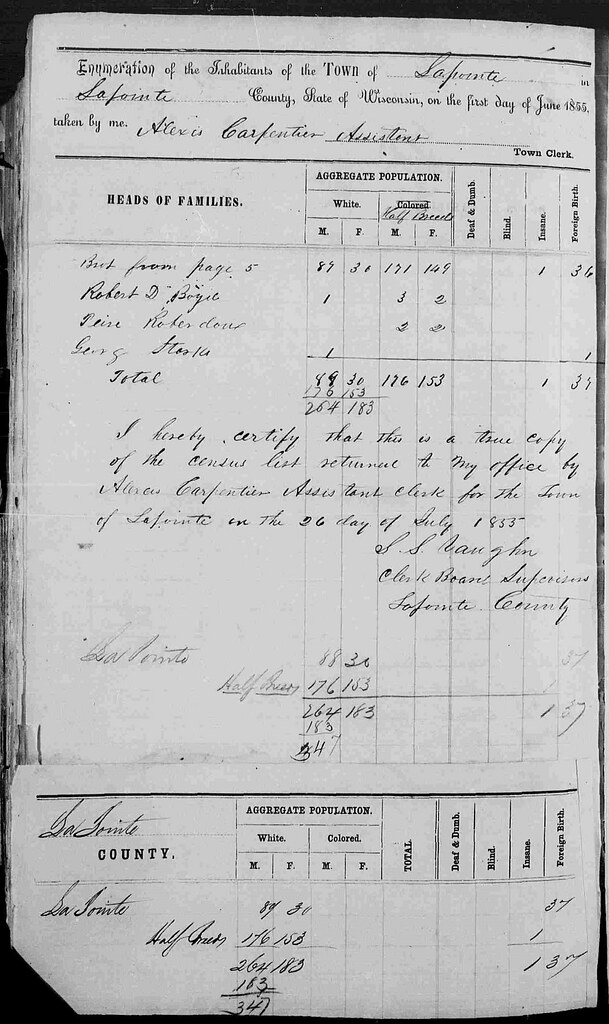
Just a few weeks prior to the payment, Alexis Carpentier, a former voyageur from a mixed French-Ojibwe family was charged with taking the Wisconsin State Census for La Pointe County. He found 37 residents of foreign birth. Most of these were French or mix-blooded men, born in Canada, who married into local Ojibwe and mix-blood families.
In only one household, more than one person is listed as being foreign-born. This was the home of Patric Sullivan. State censuses only listed the name of the head of household and do not list country of origin. However, in the 1860 Federal census, we find Patrick and Johanna Sullivan living with their three sons in La Pointe township. Both were born in Ireland.

Page 1 of 1855 Wisconsin State Census for La Pointe County (familysearch.org)

Pages 2 and 3. Patric Sullivan is fourth from the bottom on the right side. enlarge
Patrick Sullivan did not sign the LaPoint Agreement to Stop Whiskey Trade of September 10, 1855. In fact, I haven’t been able to find much information at all about Patrick and Johanna Sullivan in later years. It does appear the family stayed in the area and their children were still living in Ashland at the dawn of the 20th century.
Finally, since this post deals with the 1855 census and issues of race and identity, it’s worth noting another interesting fact. The state census had only two categories for race: “White” and “Colored.” As non-citizens, full-blooded Ojibwe people would not have been counted among the 447 names on the census. However, it seems that Carpentier and his boss, La Pointe town clerk Samuel S. Vaughn, were not sure how to categorize by race.
Carpentier crossed out the designation “Colored” and replaced it with “Half-Breed.” By their count, 329 “Half-Breeds” and 118 Whites (many of them in mixed families) lived in La Pointe County in 1855. Mix-bloods were considered Ojibwe tribal members under the Treaty of 1847. However, they traditionally had their own identity and were thought eligible for U.S. citizenship.
One wonders what conversations were had as the census was completed, but in the final compilation, all 447 names (including several core Red Cliff and Bad River families) were submitted to the state as “White” rather than “Colored.” Despite America’s best efforts to create a racial duality, which would only intensify following the Civil War, this region would continue to defy such categorization for the remainder of the 19th century.
Sources:
Kohl, J. G. Kitchi-Gami: Life among the Lake Superior Ojibway. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 1985. Print.
Miller, Kerby A. Emigrants and Exiles: Ireland and the Irish Exodus to North America. New York: Oxford UP, 1985. Print.
NOTES: Research originally featured on Chequamegon History is featured in the new Changing Currents exhibit opening today at the Chippewa Valley Museum in Eau Claire. I had a chance to preview the exhibit on Friday, and John Vanek and crew have created an incredibly well-done display of Ojibwe treaty and removal politics of the mid 1800s. See their website for more information. The research found in this exhibit, which extends into several topics, is very deep and does not shy away from uncomfortable topics. I highly recommend it.
There may be some exciting guest research featured on Chequamegon History in the coming months dealing with the aftermath of the 1854 Treaty and fraudulent land claims in the Penokee Iron Range. Stay tuned.




























!["For Plat of Townsite Odanah LaPointe Indian Reservation [...] See Large Plat Book [s]Next to last page[/s] Middle of Book" ~ Board of Commissioners of Public Lands](https://chequamegonhistory.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/1856-odanah-town-plat.jpg?w=460)