John Johnston Describes La Pointe (1807-09)
June 12, 2014

Susan Johnston, or Ozhaawashkodewekwe, the wife of John Johnston ( Chicago Newberry Library)
The name of John Johnston will be familiar to those who have read the works of his son-in-law Henry Schoolcraft. Johnston (1762-1828) was born into the Anglo-Protestant gentry of Northern Ireland and came to the Chequamegon region in 1791. After marrying Ozhaawashkodewekwe, the daughter of Waabojiig, he cemented his alliance with a prominent Ojibwe trading family. The Johnstons settled at Sault Ste. Marie, and their influence as a fur-trade power couple in the eastern part of Lake Superior parallels that of Michel and Madeline (Ikwezewe) Cadotte around La Pointe. The Johnstons played a key role in resistance to American encroachment in Lake Superior during the War of 1812 but later became centrally-connected to the United States Government efforts to establish a foothold in the northern country. A nice concise biography of John Johnston is available in the Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online.

Roderick MacKenzie (Wikimedia Commons)
In 1806, John Johnston was trading at the Soo for the North West Company when he received a printed request from Roderick MacKenzie, one of the heads of the Company. It called for information on the physical and cultural geography of the different parts of North America where the NWC traded. Johnston took it upon himself to describe the Lake Superior region and prepared An Account of Lake Superior, an 82-page manuscript.
By the end of the 19th century, the manuscript had found its way to Louis Rodrigue Masson (a grandson-in-law of MacKenzie) who edited it and published it in Les Bourgeois de la Compagnie du Nord-Ouest; recits de voyages, lettres et rapports inedits relatifs au Nord-Ouest Canadien (1889-90). The Masson archives were later donated to the McGill University Library in Montreal and are now digitized.
Much of Johnston’s account concerns the Sault and the eastern part of Lake Superior. However, he does include some information from his time at La Pointe, which is reproduced below. While it doesn’t say much about the political topics that I tend to focus on, this document is fascinating for its geographic toponyms and terminology, which is much more reflective of the 18th century than the 19th. Enjoy:
[Ojibwe names for geographic locations are taken from Gidakiiminaan: An Anishinaabe Atlas of the 1836 (Upper Michigan), 1837, and 1842 Treaty Ceded Territories (GLIFWC 2007)].
[pg. 49-56]
…The coast runs almost due West from the Kakewiching or Porcupine Mountain to the Montreal River a distance of fifteen leagues, and the beach is a shelving rock the same as the Mountain all the way with here and there a little gravelly strand. There is but one river, and that a very small one, from the Black to the Montreal River. This last takes its rise from the Wa[s]wagonnis or flambeau Lake about 80 leagues to the Southwest: it is one continued rapid from within ten leagues of its source, and a few hundred yards from the entrance has a fall of fifteen or twenty feet: – there are two high clay banks which distinguish the entrance. The lands tends to the Northwest and is a stiff clay for three leagues rent into deep gutters at short distances; it then gradually declines to a sandy beach for three leagues farther until you arrive at the Mouskissipi or bad river so called from its broad and shallow stream in which it is almost impossible to mount even an Indian Canoe.
It takes its rise from the Ottawa Lake about 125 leagues to the Westward: the Lake has its waters divided very partially as the chief part takes a southerly course and falls into the Mississipi and is called Ottawa River.
The Flambeau Lake has its waters also, the better part taking a southeasterly direction to the Mississipi and is called Ouisconsin or the medicine River. From the bad river the coast runs north four leagues to Chogowiminan or La Pointe; it is a fine strand all the way, behind which are sand hills covered with bent and sand cherry shrubs – and behind the hills there runs all the length a shallow bay which is a branch from the Bay of St Charles.
At Lapointe you are nearly opposite the Anse or Keegwagnan the distance I should conjecture to be twenty leagues in a straight line.
The Bay of St Charles runs southwest from La Pointe and is four leagues in depth and better than a league broad at the entrance. Opposite Lapointe to the Northeast is the Island of Montreal, one of the largest of those called the twelve Apostles. On the main land the Indians had once a Village amounting to 200 huts but since the Traders have multiplied, they no longer assemble at Netoungan or the sand beach, but remain in small bands near their hunting grounds. When you double the Point of Netoungan the coast tends nearly west and is composed of high rocky points of Basaltes with some freestone; there is one place in particular which is an humble imitation of the Portals but not near so high: it is about a leagues from La Pointe and is a projection from the highest mountain from Porcupine bay to fond du lac, a distance of more than 45 leagues. From the Summit of the Mountain; you can count twenty six Islands extending to the North and North east, Islands which has never been visited by the boldest Indians and lying out of the way of the N.W.Co’s Vessel: have a chance of never being better known. Of the Islands opposite La pointe ten or twelve have been visited by the Indians, some of which have a rich soil covered with oak and beech, and round all of them there is deep water and fine fishing for Trout. The Trout in this part of the Lake are equal to those of Mackinac in size & richness – I myself saw one taken off the Northeast end of Montreal Island that weighed fifty two Pounds. How many Islands this Archipelago actually contains will not be easily ascertained; but I take Carribou Island to be the eastern end of the chain. It lies a little to the Southward of the course of the Co’s Vessel, is about three miles round, has a flat shore and good anchorage, and is allowed to be half passage from Camanitiquia to St. Mary’s. However, no other land is seen from it by the Vessel; but that may be owing to the Islands being low and lying too much to the Southward of the course. It is to be observed this account of the number of Islands is upon Indian Authority, which though not the best, is still less apocryphal than that of the Canadians.
There are several rivers between Lapointe and Fond du Lac, the distance is allowed to be thirty leagues, and the breadth of the bay from a high Rocky point within a leagues of Netoungan to the roche deboute, or the upright rock, which is a lofty Mountain right opposite, cannot be less than twenty leagues.
The Metal River is within ten leagues of Fond du Lac; it is only remarkable from the Old Chief of Lapointe’s having once found a large piece of Silver ore in descending it. The Burnt river is three leagues to the Westward of Metal river; it issues from one of the Lakes of the little wild Oats Country about thirty leagues to the Southward, and is only navigable for small Canoes: it has several rapids and the Portages are dangerous, several of them lying along the edge of the river, and over precipices where one false step would be fatal. It empties itself into the Bay of Fond du Lac through a stiff Clay Bank which continues all along the shore until it joins the sands of Fond du Lac river.
About sixteen years ago, Wabogick, or the Whitefisher, the Chief of Lapointe, made his sugar on the skirt of a high mountain four days march from the entrance of the river to the south west, his eldest daughter then a girl of fourteen with a cousin of hers who was two or three years older, rambling one day up the eastern side of the Mountain came to a perpendicular Cliff, which exactly fronted the rising sun, and had an apparently artificial level before it, on which near the base of the Cliff they found a pieces of yellow metal as they called it, about eighteen inches long, a foot broad, and four inches thick; and perfectly Smooth: – it was so heavy that they could raise it with great difficulty: – after amusing themselves with examining it for some time, it occured to the eldest girl that it belonged to the Gitchi Manitou or the great spirit; upon which they abandoned the place with precipitation. As the Chipeways are not Idolators, it occurs to me that some of the Southern tribes must have once Migrated thus far to the North, and that the piece, either of copper or gold, is part of an alter dedicated to the sun. If my conjecture is right, the slab is most probably gold as the Mexicans have more of that Metal than they have of copper. I have often regretted the premature death of the Chief the same autumn that he told me the story, as he had promised to go and bring it to me if he recovered: and circumstances since have precluded my making any attempt to procure it.
The river of Fond du Lac is deep, wide and serpentine, but is only navigable for four or five leagues from its entrance. The Portages are many and different until you arrive at the sand Lake, where the tribe of Chipeways, called the Pillagers, reside. The furs from this country are the best assorted of any on the Continent; and the quantity would much increase were it possible to repress the mutual incursions of the Scieux and Chipeways, who caray on perpetual war. The tract of country lying between the two nations for near 150 leagues in length and from thirty to forty in breadth is only visited by stealth, and if peaceably hunted would be more productive than the richest mine of Peru…
[pg. 75-76]
…The wild Vine is not found at St Mary’s nor any where along the lake except at Lapointe, where however it is scarce. The wild Hop is very abundant at Lapointe but I do not recollect to have seen it elsewhere. There are three distinct species of Whortleberry. The blue or real whortleberry is by far the most wholesome and agreeable: the abundance of this fruit on the borders of Lake Superior is incredible; the Indians dry great quantities of them which they preserve during the winter, and which make an agreeable taste when repeatedly washed in warm water to take away the smoky taste from them. The black Whortleberry grows much higher than the blue; its seeds are very hard and astringent – the largest species the Indians call Hareberry; it grows to 2 or 3 feet high and bears a fruit as large as a cherry, but it is neither so agreeable nor so wholesome as either of the others…
 Poisson Blanc (whitefish), Broche (pike) and Truite Comune (Lake Trout) from the Codex Canadensis.
Poisson Blanc (whitefish), Broche (pike) and Truite Comune (Lake Trout) from the Codex Canadensis. (Photo: Wikimedia Images)
(Photo: Wikimedia Images) This is all for now on John Johnston, but this document is a potential jumping-off point for several potential research topics. Look for an upcoming post on the meaning of “La Pointe” and “La Pointe Band.”
Sources:
Armour, David A. “JOHNSTON, JOHN,” in Dictionary of Canadian Biography, vol. 6, University of Toronto/Université Laval, 2003–, accessed June 12, 2014, http://www.biographi.ca/en/bio/johnston_john_6E.html.
Gidakiiminaan = Our Earth. Odanah, WI: Great Lakes Indian Fish & Wildlife Commission, 2007. Print.
Masson, L. R. Les Bourgeois De La Compagnie Du Nord-Ouest: Recits De Voyages, Lettres Et Rapports Inedits Relatifs Au Nord-ouest Canadien. Québec: A. Côté, 1889. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe. Oneóta, or Characteristics of the Red Race of America. New York: Wiley & Putnam, 1845. Print
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe. The Indian in His Wigwam, Or, Characteristics of the Red Race of America from Original Notes and Manuscripts. New York: W.H. Graham, 1848. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Chief Buffalo’s Death and Conversion: A new perspective
April 18, 2014
By Leo Filipczak
Chief Buffalo died at La Pointe on September 7, 1855 amid the festivities and controversy surrounding that year’s annuity payment. Just before his death, he converted to the Catholic faith, and thus was buried inside the fence of the Catholic cemetery rather than outside with the Ojibwe people who kept traditional religious practices.
His death was noted by multiple written sources at the time, but none seemed to really dive into the motives and symbolism behind his conversion. This invited speculation from later scholars, and I’ve heard and proposed a number of hypotheses about why Buffalo became Catholic.
Now, a newly uncovered document, from a familiar source, reveals new information. And while it may diminish the symbolic impact of Buffalo’s conversion, it gives further insight into an important man whose legend sometimes overshadows his life.
Buffalo’s Obituary
The most well-known account of Buffalo’s death is from an obituary that appeared in newspapers across the country. It was also recorded in the essay, The Chippewas of Lake Superior, by Dr. Richard F. Morse, who was an eyewitness to the 1855 payment.
While it’s not entirely clear if it was Morse himself who wrote the obituary, he seems to be a likely candidate. Much like the rest of Chippewas of Lake Superior, the obituary is riddled with the inaccuracies and betrays an unfamiliarity with La Pointe society:


From Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin, Volume 3 (Digitized by Google Books)
It isn’t hard to understand how this obituary could invite several interpretations, especially when combined with other sources of the era and the biases of 20th and 21st-century investigators (myself included) who are always looking for a symbolic or political explanation.
Here, we will evaluate these interpretations.
Was Buffalo sending a message to the Ojibwe about the future?
The obituary states, “No tongue like Buffalo’s could control and direct the different bands.” An easy interpretation might suggest that he was trying to send a message that assimilation to white culture was the way of the future, and that all the Ojibwe should follow his lead. We do see suggestions in the writings of Henry Schoolcraft and William Warren that might support this conclusion.
The problem with this interpretation is that no Ojibwe leader, not even Buffalo, had that level of influence. Even if he wanted to, which would have been completely contrary to Ojibwe tolerance of religious pluralism, he could not have pulled a Henry VIII and converted his whole nation.
In fact, by 1855, Buffalo’s influence was at an all-time low. Recent scholarship has countered the image crafted by Benjamin Armstrong and others, of a chief whose trip to Washington and leadership through the Treaty of 1854 made him more powerful in his final years. Consider this 1852 depiction in Wagner and Scherzer’s Reisen in Nordamerika:
…Here we have the hereditary Chippewa chief, whose generations (totem) are carved in the ancient birch bark,** giving us profuse thanks for just a modest silver coin and a piece of dry cloth. What time can bring to a ruler!
So, did Buffalo decide in the last days of his life that Christianity was superior to traditional ways?
The reason why the obituary and other contemporary sources don’t go into the reasons for Buffalo’s conversion was because they hold the implicit assumption that Christianity is the one true religion. Few 19th-century American readers would be asking why someone would convert. It was a given. 160 years later, we don’t make this assumption anymore, but it should be explored whether or not this was purely a religious decision on Buffalo’s part.
I have a difficult time believing this. Buffalo had nearly 100 years to convert to Christianity if he’d wanted to. The traditional Ojibwe, in general, were extremely resistant to conversion, and there are several sources depicting Buffalo as a leader in the Midewiwin. This continuation of the above quote from Wagner and Scherzer shows Buffalo’s relationship to those who felt the Ojibwe needed Christianity.
Strangely, we later learned that the majestic Old Buffalo was violently opposed for years to the education and spiritual progress of the Indians. Probably, it’s because he suspected a better instructed generation would no longer obey. Presently, he tacitly accepts the existence of the school and even visits sometimes, where like ourselves, he has the opportunity to see the gains made in this school with its stubborn, fastidious look of an old German high council.
Accounts like this suggest a political rather than a spiritual motive.
So, did Buffalo’s convert for political rather than spiritual reasons?
Some have tied Buffalo’s conversion to a split in the La Pointe Band after the Treaty of 1854, and it’s important to remember all the heated factional divisions that rose up during the 1855 payment. Until recently, my personal interpretation would have been that Buffalo’s conversion represented a final break with Blackbird and the other Bad River chiefs. Perhaps Buffalo felt alienated from most of the traditional Ojibwe after he found himself in the minority over the issue of debt payments. His final speech was short, and reveals disappointment and exasperation on the part of the aged leader.
By the time of his death, most of his remaining followers, including the mix-blooded Ojibwe of La Pointe, and several of his children were Catholic, while most Ojibwe remained traditional. Perhaps there was additional jealousy over clauses in the treaty that gave Buffalo a separate reservation at Red Cliff and an additional plot of land. We see hints of this division in the obituary when an unidentified Ojibwe man blames the government for Buffalo’s death. This all could be seen as a separation forming between a Catholic Red Cliff and a traditional Bad River.
This interpretation would be perfect if it wasn’t grossly oversimplified. The division didn’t just happen in 1854. The La Pointe Band had always really been several bands. Those, like Buffalo’s, that were most connected to the mix-bloods and traders stayed on the Island more, and the others stayed at Bad River more. Still, there were Catholics at Bad River, and traditional Ojibwe on the Island. This dynamic and Buffalo’s place in it, were well-established. He did not have to convert to be with the “Catholic” faction. He had been in it for years.
Some have questioned whether Buffalo really converted at all. From a political point of view, one could say his conversion was really a show for Commissioner Manypenny to counter Blackbird’s pants (read this post if you don’t know what I’m talking about). I see that as overly cynical and out of character for Buffalo. I also don’t think he was ignorant of what conversion meant. He understood the gravity of what he was deciding, and being a ninety-year-old chief, I don’t think he would have felt pressured to please anyone.
So if it wasn’t symbolic, political, or religious zeal, why did Buffalo convert?
The Kohl article
As he documented the 1855 payment, Richard Morse’s ethnocentric values prevented any meaningful understanding of Ojibwe culture. However, there was another white outsider present at La Pointe that summer who did attempt to understand Ojibwe people as fellow human beings. He had come all the way from Germany.
The name of Johann Georg Kohl will be familiar to many readers who know his work Kitchi-Gami: Wanderings Around Lake Superior (1860). Kohl’s desire to truly know and respect the people giving him information left us with what I consider the best anthropological writing ever done on this part of the world.
My biggest complaint with Kohl is that he typically doesn’t identify people by name. Maangozid, Gezhiiyaash, and Zhingwaakoons show up in his work, but he somehow manages to record Blackbird’s speech without naming the Bad River chief. In over 100 pages about life at La Pointe in 1855, Buffalo isn’t mentioned at all.
So, I was pretty excited to find an untranslated 1859 article from Kohl on Google Books in a German-language weekly. The journal, Das Ausland, is a collection of writings that a would describe as ethnographic with a missionary bent.
I was even more excited as I put it through Google Translate and realized it discussed Buffalo’s final summer and conversion. It has to go out to the English-speaking world.
So without further ado, here is the first seven paragraphs of Remarks on the Conversion of the Canadian Indians and some Stories of Conversion by Johann Kohl. I apologize for any errors arising from the electronic translation. I don’t speak German and I can only hope that someone who does will see this and translate the entire article.

J. G. Kohl (Wikimedia Images)
Das Ausland.
Eine Wochenschrift
fur
Kunde des geistigen und sittlichen Lebens der Völker
[The Foreign Lands: A weekly for scholars of the moral and intellectual lives of foreign nations]
Nr. 2 8 January 1859
Remarks on the Conversion of the Canadian Indians and some Stories of Conversion
By J.G. Kohl
A few years ago, when I was on “La Pointe,” one of the so-called “Apostle Islands” in the western corner of the great Lake Superior, there still lived the old chief of the local Indians, the Chippeway or Ojibbeway people, named “Buffalo,” a man “of nearly a hundred years.” He himself was still a pagan, but many of his children, grandchildren and closest relatives, were already Christians.
I was told that even the aged old Buffalo himself “ébranlé [was shaking]”, and they told me his state of mind was fluctuating. “He thinks highly of the Christian religion,” they told me, “It’s not right to him that he and his family be of a different faith. He is afraid that he will be separated in death. He knows he will not be near them, and that not only his body should be brought to another cemetery, but also he believes his spirit shall go into another paradise away from his children.”
But Buffalo was the main representative of his people, the living embodiment, so to speak, of the old traditions and stories of his tribe, which once ranged over not only the whole group of the Apostle Islands, but also far and wide across the hunting grounds of the mainland of northern Wisconsin. His ancestors and his family, “the Totem of the Loons” (from the diver)* make claim to be the most distinguished chiefly family of the Ojibbeways. Indeed, they believe that from them and their village a far-reaching dominion once reached across all the tribes of the Ojibbeway Nation. In a word, a kind of monarchy existed with them at the center.
(*The Loon, or Diver, is a well-known large North American bird).
Old Buffalo, or Le Boeuf, as the French call him, or Pishiki, his Indian name, was like the last reflection of the long-vanished glory. He was stuck too deep in the old superstition. He was too intertwined with the Medä Order, the Wabanos, and the Jossakids, or priesthood, of his people. A conversion to Christianity would have destroyed his influence in a still mostly-pagan tribe. It would have been the equivalent of voluntarily stepping down from the throne he previously had. Therefore, in spite of his “doubting” state of mind, he could not decide to accept the act of baptism.
One evening, I visited old Buffalo in his bark lodge, and found in him grayed and stooped by the years, but nevertheless still quite a sprightly old man. Who knows what kind of fate he had as an old Indian chief on Lake Superior, passing his whole life near the Sioux, trading with the North West Company, with the British and later with the Americans. With the Wabanos and Jossakids (priests and sorcerers) he conjured for his people, and communed with the sky, but here people would call him an “old sinner.”
But still, due to his advanced age I harbored a certain amount of respect for him myself. He took me in, so kindly, and never forgot even afterwards, promising to remember my visit, as if it had been an honor for him. He told me much of the old glory of his tribe, of the origin of his people, and of his religion from the East. I gave him tobacco, and he, much more generously,gave me a beautiful fife. I later learned from the newspapers that my old host, being ill, and soon after my departure from the island, he departed from this earth. I was seized by a genuine sorrow and grieved for him. Those papers, however, reported a certain cause for consolation, in that Buffalo had said on his deathbed, he desired to be buried in a Christian way. He had therefore received Christianity and the Lord’s Supper, shortly before his death, from the Catholic missionaries, both with the last rites of the Church, and with a church funeral and burial in the Catholic cemetery, where in addition to those already resting, his family would be buried.
The story and the end of the old Buffalo are not unique. Rather, it was something rather common for the ancient pagan to proceed only on his death-bed to Christianity, and it starts not with the elderly adults on their deathbeds, but with their Indian families beginning with their young children. The parents are then won over by the children. For the children, while they are young and largely without religion, the betrayal of the old gods and laws is not so great. Therefore, the parents give allow it more easily. You yourself are probably already convinced that there is something fairly good behind Christianity, and that their children “could do quite well.” They desire for their children to attain the blessing of the great Christian God and therefore often lead them to the missionaries, although they themselves may not decide to give up their own ingrained heathen beliefs. The Christians, therefore, also prefer to first contact the youth, and know well that if they have this first, the parents will follow sooner or later because they will not long endure the idea that they are separated from their children in the faith. Because they believe that baptism is “good medicine” for the children, they bring them very often to the missionaries when they are sick…

Das Ausland: Wochenschrift für Länder- u. Völkerkunde, Volumes 31-32. Only about a quarter of the article is translated above. The remaining pages largely consist of Kohl’s observations on the successes and failures of missionary efforts based on real anecdotes.
Conclusion
According to Johann Kohl, who knew Buffalo, the chief’s conversion wasn’t based on politics or any kind of belief that Ojibwe culture and religion was inferior. Buffalo converted because he wanted to be united with his family in death. This may make the conversion less significant from a historical perspective, but it helps us understand the man himself. For that reason, this is the most important document yet about the end of the great chief’s long life.
Sources:
Armstrong, Benj G., and Thomas P. Wentworth. Early Life among the Indians: Reminiscences from the Life of Benj. G. Armstrong : Treaties of 1835, 1837, 1842 and 1854 : Habits and Customs of the Red Men of the Forest : Incidents, Biographical Sketches, Battles, &c. Ashland, WI: Press of A.W. Bowron, 1892. Print.
Kohl, J. G. Kitchi-Gami: Wanderings round Lake Superior. London: Chapman and Hall, 1860. Print.
Loew, Patty. Indian Nations of Wisconsin: Histories of Endurance and Renewal. Madison: Wisconsin Historical Society, 2001. Print.
McElroy, Crocket. “An Indian Payment.” Americana v.5. American Historical Company, American Historical Society, National Americana Society Publishing Society of New York, 1910 (Digitized by Google Books) pages 298-302.
Morse, Richard F. “The Chippewas of Lake Superior.” Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin. Ed. Lyman C. Draper. Vol. 3. Madison: State Historical Society of Wisconsin, 1857. 338-69. Print.
Paap, Howard D. Red Cliff, Wisconsin: A History of an Ojibwe Community. St. Cloud, MN: North Star, 2013. Print.
Satz, Ronald N. Chippewa Treaty Rights: The Reserved Rights of Wisconsin’s Chippewa Indians in Historical Perspective. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters, 1991. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and times of an Ojibwe Leader. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2007. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe, and Seth Eastman. Historical and Statistical Information Respecting the History, Condition, and Prospects of the Indian Tribes of the United States: Collected and Prepared under the Direction of the Bureau of Indian Affairs per Act of Congress of March 3rd, 1847. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo, 1851. Print.
Wagner, Moritz, and Karl Von Scherzer. Reisen in Nordamerika in Den Jahren 1852 Und 1853. Leipzig: Arnold, 1854. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Perrault, Curot, Nelson, and Malhoit
March 8, 2014
I’ve been getting lazy, lately, writing all my posts about the 1850s and later. It’s easy to find sources about that because they are everywhere, and many are being digitized in an archival format. It takes more work to write a relevant post about the earlier eras of Chequamegon History. The sources are sparse, scattered, and the ones that are digitized or published have largely been picked over and examined by other researchers. However, that’s no excuse. Those earlier periods are certainly as interesting as the mid-19th Century. I needed to just jump in and do a project of some sort.
I’m someone who needs to know the names and personalities involved to truly wrap my head around a history. I’ve never been comfortable making inferences and generalizations unless I have a good grasp of the specific. This doesn’t become easy in the Lake Superior country until after the Cass Expedition in 1820.
But what about a generation earlier?
The dawn of the 19th-century was a dynamic time for our region. The fur trade was booming under the British North West Company. The Ojibwe were expanding in all directions, especially to west, and many of familiar French surnames that are so common in the area arrived with Canadian and Ojibwe mix-blooded voyageurs. Admittedly, the pages of the written record around 1800 are filled with violence and alcohol, but that shouldn’t make one lose track of the big picture. Right or wrong, sustainable or not, this was a time of prosperity for many. I say this from having read numerous later nostalgic accounts from old chiefs and voyageurs about this golden age.
We can meet some of the bigger characters of this era in the pages of William W. Warren and Henry Schoolcraft. In them, men like Mamaangazide (Mamongazida “Big Feet”) and Michel Cadotte of La Pointe, Beyazhig (Pay-a-jick “Lone Man) of St. Croix, and Giishkiman (Keeshkemun “Sharpened Stone”) of Lac du Flambeau become titans, covered with glory in trade, war, and influence. However, there are issues with these accounts. These two authors, and their informants, are prone toward glorifying their own family members. Considering that Schoolcraft’s (his mother-in law, Ozhaawashkodewike) and Warren’s (Flat Mouth, Buffalo, Madeline and Michel Cadotte Jr., Jean Baptiste Corbin, etc.) informants were alive and well into adulthood by 1800, we need to keep things in perspective.
The nature of Ojibwe leadership wasn’t different enough in that earlier era to allow for a leader with any more coercive power than that of the chiefs in 1850s. Mamaangazide and his son Waabojiig may have racked up great stories and prestige in hunting and war, but their stature didn’t get them rich, didn’t get them out of performing the same seasonal labors as the other men in the band, and didn’t guarantee any sort of power for their descendants. In the pages of contemporary sources, the titans of Warren and Schoolcraft are men.
Finally, it should be stated that 1800 is comparatively recent. Reading the journals and narratives of the Old North West Company can make one feel completely separate from the American colonization of the Chequamegon Region in the 1840s and ’50s. However, they were written at a time when the Americans had already claimed this area for over a decade. In fact, the long knife Zebulon Pike reached Leech Lake only a year after Francois Malhoit traded at Lac du Flambeau.
The Project
I decided that if I wanted to get serious about learning about this era, I had to know who the individuals were. The most accessible place to start would be four published fur-trade journals and narratives: those of Jean Baptiste Perrault (1790s), George Nelson (1802-1804), Michel Curot (1803-1804), and Francois Malhoit (1804-1805).
The reason these journals overlap in time is that these years were the fiercest for competition between the North West Company and the upstart XY Company of Sir Alexander MacKenzie. Both the NWC traders (such as Perrault and Malhoit) and the XY traders (Nelson and Curot) were expected to keep meticulous records during these years.
I’d looked at some of these journals before and found them to be fairly dry and lacking in big-picture narrative history. They mostly just chronicle the daily transactions of the fur posts. However, they do frequently mention individual Ojibwe people by name, something that can be lacking in other primary records. My hope was that these names could be connected to bands and villages and then be cross-referenced with Warren and Schoolcraft to fill in some of the bigger story. As the project took shape, it took the form of a map with lots of names on it. I recorded every Ojibwe person by name and located them in the locations where they met the traders, unless they are mentioned specifically as being from a particular village other than where they were trading.
I started with Perrault’s Narrative and tried to record all the names the traders and voyageurs mentioned as well. As they were mobile and much less identified with particular villages, I decided this wasn’t worth it. However, because this is Chequamegon History, I thought I should at least record those “Frenchmen” (in quotes because they were British subjects, some were English speakers, and some were mix-bloods who spoke Ojibwe as a first language) who left their names in our part of the world. So, you’ll see Cadotte, Charette, Corbin, Roy, Dufault (DeFoe), Gauthier (Gokee), Belanger, Godin (Gordon), Connor, Bazinet (Basina), Soulierre, and other familiar names where they were encountered in the journals. I haven’t tried to establish a complete genealogy for either, but I believe Perrault (Pero) and Malhoit (Mayotte) also have names that are still with us.
For each of the names on the map, I recorded the narrative or journal they appeared in:
JBP= Jean Baptiste Perrault
GN= George Nelson
MC= Michel Curot
FM= Francois Malhoit

Red Lake-Pembina area: By this time, the Ojibwe had started to spread far beyond the Lake Superior forests and into the western prairies. Perrault speaks of the Pillagers (Leech Lake Band) being absent from their villages because they had gone to hunt buffalo in the west. Vincent Roy Sr. and his sons later settled at La Pointe, but their family maintained connections in the Canadian borderlands. Jean Baptiste Cadotte Jr. was the brother of Michel Cadotte (Gichi-Mishen), the famous La Pointe trader.

Leech Lake and Sandy Lake area: The names that jump out at me here are La Brechet or Gaa-dawaabide (Broken Tooth), the great Loon-clan chief from Sandy Lake (son of Bayaaswaa mentioned in this post) and Loon’s Foot (Maangozid). The Maangozid we know as the old speaker and medicine man from Fond du Lac (read this post) was the son of Gaa-dawaabide. He would have been a teenager or young man at the time Perrault passed through Sandy Lake.

Fond du Lac and St. Croix: Augustin Belanger and Francois Godin had descendants that settled at La Pointe and Red Cliff. Jean Baptiste Roy was the father of Vincent Roy Sr. I don’t know anything about Big Marten and Little Marten of Fond du Lac or Little Wolf of the St. Croix portage, but William Warren writes extensively about the importance of the Marten Clan and Wolf Clan in those respective bands. Bayezhig (Pay-a-jick) is a celebrated warrior in Warren and Giishkiman (Kishkemun) is credited by Warren with founding the Lac du Flambeau village. Buffalo of the St. Croix lived into the 1840s. I wrote about his trip to Washington in this post.

Lac Courte Oreilles and Chippewa River: Many of the men mentioned at LCO by Perrault are found in Warren. Little (Petit) Michel Cadotte was a cousin of the La Pointe trader, Big (Gichi/La Grande) Michel Cadotte. The “Red Devil” appears in Schoolcraft’s account of 1831. The old, respected Lac du Flambeau chief Giishkiman appears in several villages in these journals. As the father of Keenestinoquay and father-in-law of Simon Charette, a fur-trade power couple, he traded with Curot and Nelson who worked with Charette in the XY Company.

La Pointe: Unfortunately, none of the traders spent much time at La Pointe, but they all mention Michel Cadotte as being there. The family of Gros Pied (Mamaangizide, “Big Feet”) the father of Waabojiig, opened up his lodge to Perrault when the trader was waylaid by weather. According to Schoolcraft and Warren, the old war chief had fought for the French on the Plains of Abraham in 1759.

Lac du Flambeau: Malhoit records many of the same names in Lac du Flambeau that Nelson met on the Chippewa River. Simon Charette claimed much of the trade in this area. Mozobodo and “Magpie” (White Crow), were his brothers-in-law. Since I’ve written so much about chiefs named Buffalo, I should point out that there’s an outside chance Le Taureau (presumably another Bizhiki) could be the famous Chief Buffalo of La Pointe.

L’Anse, Ontonagon, and Lac Vieux Desert: More Cadottes and Roys, but otherwise I don’t know much about these men.

At Mackinac and the Soo, Perrault encountered a number of names that either came from “The West,” or would find their way there in later years. “Cadotte” is probably Jean Baptiste Sr., the father of “Great” Michel Cadotte of La Pointe.

Malhoit meets Jean Baptiste Corbin at Kaministiquia. Corbin worked for Michel Cadotte and traded at Lac Courte Oreilles for decades. He was likely picking up supplies for a return to Wisconsin. Kaministiquia was the new headquarters of the North West Company which could no longer base itself south of the American line at Grand Portage.
Initial Conclusions
There are many stories that can be told from the people listed in these maps. They will have to wait for future posts, because this one only has space to introduce the project. However, there are two important concepts that need to be mentioned. Neither are new, but both are critical to understanding these maps:
1) There is a great potential for misidentifying people.
Any reading of the fur-trade accounts and attempts to connect names across sources needs to consider the following:
- English names are coming to us from Ojibwe through French. Names are mistranslated or shortened.
- Ojibwe names are rendered in French orthography, and are not always transliterated correctly.
- Many Ojibwe people had more than one name, had nicknames, or were referenced by their father’s names or clan names rather than their individual names.
- Traders often nicknamed Ojibwe people with French phrases that did not relate to their Ojibwe names.
- Both Ojibwe and French names were repeated through the generations. One should not assume a name is always unique to a particular individual.
So, if you see a name you recognize, be careful to verify it’s reall the person you’re thinking of. Likewise, if you don’t see a name you’d expect to, don’t assume it isn’t there.
2) When talking about Ojibwe bands, kinship is more important than physical location.
In the later 1800s, we are used to talking about distinct entities called the “St. Croix Band” or “Lac du Flambeau Band.” This is a function of the treaties and reservations. In 1800, those categories are largely meaningless. A band is group made up of a few interconnected families identified in the sources by the names of their chiefs: La Grand Razeur’s village, Kishkimun’s Band, etc. People and bands move across large areas and have kinship ties that may bind them more closely to a band hundreds of miles away than to the one in the next lake over.
I mapped here by physical geography related to trading posts, so the names tend to group up. However, don’t assume two people are necessarily connected because they’re in the same spot on the map.
On a related note, proximity between villages should always be measured in river miles rather than actual miles.
Going Forward
I have some projects that could spin out of these maps, but for now, I’m going to set them aside. Please let me know if you see anything here that you think is worth further investigation.
Sources:
Curot, Michel. A Wisconsin Fur Trader’s Journal, 1803-1804. Edited by Reuben Gold Thwaites. Wisconsin Historical Collections, vol. XX: 396-472, 1911.
Malhoit, Francois V. “A Wisconsin Fur Trader’s Journal, 1804-05.” Collections of the State Historical Society of Wisconsin. Ed. Reuben Gold Thwaites. Vol. 19. Madison: State Historical Society of Wisconsin, 1910. 163-225. Print.
Nelson, George, Laura L. Peers, and Theresa M. Schenck. My First Years in the Fur Trade: The Journals of 1802-1804. St. Paul, MN: Minnesota Historical Society, 2002. Print.
Perrault, Jean Baptiste. Narrative of The Travels And Adventures Of A Merchant Voyager In The Savage Territories Of Northern America Leaving Montreal The 28th of May 1783 (to 1820) ed. and Introduction by, John Sharpless Fox. Michigan Pioneer and Historical Collections. vol. 37. Lansing: Wynkoop, Hallenbeck, Crawford Co., 1900.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe. Information Respecting The History,Condition And Prospects OF The Indian Tribes Of The United States. Illustrated by Capt. S. Eastman. Published by the Authority of Congress. Part III. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo & Company, 1953.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe, and Philip P. Mason. Expedition to Lake Itasca; the Discovery of the Source of the Mississippi. East Lansing: Michigan State UP, 1958. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Reconstructing the “Martell” Delegation through Newspapers
November 2, 2013

Symbolic Petition of the Chippewa Chiefs: This pictographic petition was brought to Washington D.C. by a delegation of Ojibwe chiefs and their interpreter J.B. Martell. This one, representing the band of Chief Oshkaabewis, is the most famous, but their were several others copied from birch bark by Seth Eastman and published in the works of Henry Schoolcraft. For more, follow this link.
Henry Schoolcraft. William W. Warren. George Copway. These names are familiar to any scholar of mid-19th-century Ojibwe history. They are three of the most referenced historians of the era, and their works provide a great deal of historical material that is not available in any other written sources. Copway was Ojibwe, Warren was a mix-blood Ojibwe, and Schoolcraft was married to the granddaughter of the great Chequamegon chief Waabojiig, so each is seen, to some extent, as providing an insider’s point of view. This could lead one to conclude that when all three agree on something, it must be accurate. However, there is a danger in over-relying on these early historians in that we forget that they were often active participants in the history they recorded.
This point was made clear to me once again as I tried to sort out my lingering questions about the 1848-49 “Martell” Delegation to Washington. If you are a regular reader, you may remember that this delegation was the subject of the first post on this website. You may also remember from this post, that the group did not have money to get to Washington and had to reach out to the people they encountered along the way.
The goal of the Martell Delegation was to get the United States to cede back title to the lands surrounding the major Lake Superior Ojibwe villages. The Ojibwe had given this land up in the Treaty of 1842 with the guarantee that they could remain on it. However, by 1848 there were rumors of removal of all the bands east of the Mississippi to unceded land in Minnesota. That removal was eventually attempted, in 1850-51, in what is now called the Sandy Lake Tragedy.
The Martell Delegation remains a little-known part of the removal story, although the pictographs remain popular. Those petitions are remembered because they were published in Henry Schoolcrafts’ Historical and statistical information respecting the history, condition, and prospects of the Indian tribes of the United States (1851) along with the most accessible primary account of the delegation:
In the month of January, 1849, a delegation of eleven Chippewas, from Lake Superior, presented themselves at Washington, who, amid other matters not well digested in their minds, asked the government for a retrocession of some portion of the lands which the nation had formerly ceded to the United States, at a treaty concluded at Lapointe, in Lake Superior, in 1842. They were headed by Oshcabawiss, a chief from a part of the forest-country, called by them Monomonecau, on the head-waters of the River Wisconsin. Some minor chiefs accompanied them, together with a Sioux and two boisbrules, or half-breeds, from the Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan. The principal of the latter was a person called Martell, who appeared to be the master-spirit and prime mover of the visit, and of the motions of the entire party. His motives in originating and conducting the party, were questioned in letters and verbal representations from persons on the frontiers. He was freely pronounced an adventurer, and a person who had other objects to fulfil, of higher interest to himself than the advancement of the civilization and industry of the Indians. Yet these were the ostensible objects put forward, though it was known that he had exhibited the Indians in various parts of the Union for gain, and had set out with the purpose of carrying them, for the same object, to England. However this may be, much interest in, and sympathy for them, was excited. Officially, indeed, their object was blocked up. The party were not accredited by their local agent. They brought no letter from the acting Superintendent of Indian Affairs on that frontier. The journey had not been authorized in any manner by the department. It was, in fine, wholly voluntary, and the expenses of it had been defrayed, as already indicated, chiefly from contributions made by citizens on the way, and from the avails of their exhibitions in the towns through which they passed; in which, arrayed in their national costume, they exhibited their peculiar dances, and native implements of war and music. What was wanting, in addition to these sources, had been supplied by borrowing from individuals.
Martell, who acted as their conductor and interpreter, brought private letters from several persons to members of Congress and others, which procured respect. After a visit, protracted through seven or eight weeks, an act was passed by Congress to defray the expenses of the party, including the repayment of the sums borrowed of citizens, and sufficient to carry them back, with every requisite comfort, to their homes in the north-west. While in Washington, the presence of the party at private houses, at levees, and places of public resort, and at the halls of Congress, attracted much interest; and this was not a little heightened by their aptness in the native ceremonies, dancing, and their orderly conduct and easy manners, united to the attraction of their neat and well-preserved costume, which helped forward the object of their mission.
The visit, although it has been stated, from respectable sources, to have had its origin wholly in private motives, in the carrying out of which the natives were made to play the part of mere subordinates, was concluded in a manner which reflects the highest credit on the liberal feelings and sentiments of Congress. The plan of retrocession of territory, on which some of the natives expressed a wish to settle and adopt the modes of civilized life, appeared to want the sanction of the several states in which the lands asked for lie. No action upon it could therefore be well had, until the legislatures of these states could be consulted (pg. 414-416, pictographic plates follow).
I have always had trouble with Schoolcraft’s interpretation of these events. It wasn’t that I had evidence to contradict his argument, but rather that I had a hard time believing that all these chiefs would make so weighty a decision as to go to Washington simply because their interpreter was trying to get rich. The petitions asked for a permanent homeland in the traditional villages east of the Mississippi. This was the major political goal of the Lake Superior Ojibwe leadership at that time and would remain so in all the years leading up to 1854. Furthermore, chiefs continued to ask for, or go “uninvited” on, diplomatic missions to the president in the years that followed.
I explored some of this in the post about the pictograph, but a number of lingering questions remained:
What route did this group take to Washington?
Who was Major John Baptiste Martell?
Did he manipulate the chiefs into working for him, or was he working for them?
Was the Naaganab who went with this group the well-known Fond du Lac chief or the warrior from Lake Chetek with the same name?
Did any chiefs from the La Pointe band go?
Why was Martell criticized so much? Did he steal the money?
What became of Martell after the expedition?
How did the “Martell Expedition” of 1848-49 impact the Ojibwe removal of 1850-51?
Lacking access to the really good archives on this subject, I decided to focus on newspapers, and since this expedition received so much attention and publicity, this was a good choice. Enjoy:


Indiana Palladium. Vevay, IN. Dec. 2, 1848
Capt. Seth Eastman of the U.S. Army took note of the delegation as it traveled down the Mississippi from Fort Snelling to St. Louis. Eastman, a famous painter of American Indians, copied the birch bark petitions for publication in the works of his collaborator Henry Schoolcraft. At least one St. Louis paper also noticed these unique pictographic documents.
 Lafayette Courier. Lafayette, IN. Dec. 8, 1848.
Lafayette Courier. Lafayette, IN. Dec. 8, 1848.
The delegation made its way up the Ohio River to Cincinnati, where Gezhiiyaash’s illness led to a chance encounter with some Ohio Freemasons. I won’t repeat it here, but I covered this unusual story in this post from August.
At Cincinnati, they left the river and headed toward Columbus. Just east of that city, on the way to Pittsburgh, one of the Ojibwe men offered some sound advice to the women of Hartford, Ohio, but he received only ridicule in return.

Madison Weekly Courier. Madison, IN. Jan. 24, 1849

It’s unclear how quickly reports of the delegation came back to the Lake Superior country. William Warren’s letter to his cousin George, written in March after the delegation had already left Washington, still spoke of St. Louis:
William W. Warren (Wikimedia Images)
“…About Martells Chiefs. They were according to last accounts dancing the pipe dance at St. Louis. They have been making monkeys of themselves to fill the pockets of some cute Yankee who has got hold of them. Black bird returned from Cleveland where he caught scarlet fever and clap. He has behaved uncommon well since his return…” (Schenck, pg. 49)
From this letter, we learn that Blackbird, the La Pointe chief, was originally part of the group. In evaluating Warren’s critical tone, we must remember that he was working closely with the very government officials who withheld their permission. Of the La Pointe chiefs, Blackbird was probably the least accepting of American colonial power. However, we see in the obituary of Naaganab, Blackbird’s rival at the 1855 annuity payment, that the Fond du Lac chief was also there.
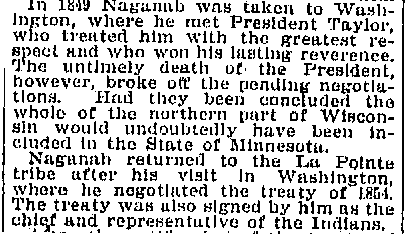
New York World. New York. July 22, 1894
Before finding this obituary, I had thought that the Naaganab who signed the petition was more likely the headman from Lake Chetek. Instead, this information suggests it was the more famous Fond du Lac chief. This matters because in 1848, Naaganab was considered the speaker for his cousin Zhingob, the leading chief at Fond du Lac. Blackbird, according to his son James, was the pipe carrier for Buffalo. While these chiefs had their differences with each other, it seems likely that they were representing their bands in an official capacity. This means that the support for this delegation was not only from “minor chiefs” as Schoolcraft described them, or “Martells Chiefs” as Warren did, from Lac du Flambeau and Michigan. I would argue that the presence of Blackbird and Naaganab suggests widespread support from the Lake Superior bands. I would guess that there was much discussion of the merits of a Washington delegation by Buffalo and others during the summer of 1848, and that the trip being a hasty money-making scheme by Martell seems much less likely.

Madison Daily Banner. Madison, IN. Jan. 3, 1849.
From Pittsburgh, the delegation made it to Philadelphia, and finally Washington. They attracted a lot of attention in the nation’s capital. Some of their adventures and trials: Oshkaabewis and his wife Pammawaygeonenoqua losing an infant child, the group hunting rabbits along the Potomac, and the chiefs taking over Congress, are included this post from March, so they aren’t repeated here.

Adams Sentinel. Gettysburg, PA. Feb. 5, 1849.
According to Ronald Satz, the delegation was received by both Congress and President Polk with “kindly feelings” and the expectation of “good treatment in the future” if they “behaved themselves (Satz 51).” Their petition was added to the Congressional Record, but the reservations were not granted at the time. However, Congress did take up the issue of paying for the debts accrued by the Ojibwe along the way.


George Copway (Wikimedia Commons)
Kah-Ge-Ga-Gah-Bowh (George Copway), a Mississauga Ojibwe and Methodist missionary, was the person “belonging to one of the Canada Bands of Chippewas,” who wrote the anti-Martell letter to Indian Commissioner William Medill. This is most likely the letter Schoolcraft referred to in 1851. In addition to being upset about the drinking, Copway was against reservations in Wisconsin. He wanted the government to create a huge pan-Indian colony at the headwaters of the Missouri River.

William Medill (Wikimedia Commons)

Iowa State Gazette. Burlington, IA. April 4, 1849
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
 Weekly Wisconsin. Milwaukee. Feb. 28, 1849.
Weekly Wisconsin. Milwaukee. Feb. 28, 1849.
With $6000 (or did they only get $5000?), a substantial sum for the antebellum Federal Government, the group prepared to head back west with the ability to pay back their creditors.
It appears the chiefs returned to their villages by going back though the Great Lakes to Green Bay and then overland.
The Chippewa Delegation, who have been on a visit to see their “great fathers” in Washington, passed through this place on Saturday last, on their way to their homes near Lake Superior. From the accounts of the newspapers, they have been lionized during their whole journey, and particularly in Washington, where many presents were made them, among the most substantial of which was six boxed of silver ($6,000) to pay their expenses. They were loaded with presents, and we noticed one with a modern style trunk strapped to his back. They all looked well and in good spirits (qtd. in Paap, pg. 205).
Green Bay Gazette. April 4, 1849
So, it hardly seems that the Ojibwe chiefs returned to their villages feeling ripped off by their interpreter. Martell himself returned to the Soo, and found a community about to be ravaged by a epidemic of cholera.

Weekly Wisconsin. Milwaukee. Sep. 5, 1849.
Martell appears in the 1850 census on the record of those deceased in the past year. Whether he was a major in the Mexican War, whether he was in the United States or Canadian military, or whether it was even a real title, remains a mystery. His death record lists his birthplace as Minnesota, which probably connects him to the Martells of Red Lake and Red River, but little else is known about his early years. And while we can’t say for certain whether he led the group purely out of self-interest, or whether he genuinely supported the cause, John Baptiste Martell must be remembered as a key figure in the struggle for a permanent Ojibwe homeland in Wisconsin and Michigan. He didn’t live to see his fortieth birthday, but he made the 1848-49 Washington delegation possible.
So how do we sort all this out?
To refresh, my unanswered questions from the other posts about this delegation were:
1) What route did this group take to Washington?
2) Who was Major John Baptiste Martell?
3) Did he manipulate the chiefs into working for him, or was he working for them?
4) Was the Naaganab who went with this group the well-known Fond du Lac chief or the warrior from Lake Chetek with the same name?
5) Did any chiefs from the La Pointe band go?
6) Why was Martell criticized so much? Did he steal the money?
7) What became of Martell after the expedition?
8) How did the “Martell Expedition” of 1848-49 impact the Ojibwe removal of 1850-51?
We’ll start with the easiest and work our way to the hardest. We know that the primary route to Washington was down the Brule, St. Croix, and Mississippi to St. Louis, and from there up the Ohio. The return trip appears to have been via the Great Lakes.
We still don’t know how Martell became a major, but we do know what became of him after the diplomatic mission. He didn’t survive to see the end of 1849.
The Fond du Lac chief Naaganab, and the La Pointe chief Blackbird, were part of the group. This indicates that a wide swath of the Lake Superior Ojibwe leadership supported the delegation, and casts serious doubt on the notion that it was a few minor chiefs in Michigan manipulated by Martell.
Until further evidence surfaces, there is no reason to support Schoolcraft’s accusations toward Martell. Even though these allegations are seemingly validated by Warren and Copway, we need to remember how these three men fit into the story. Schoolcraft had moved to Washington D.C. by this point and was no longer Ojibwe agent, but he obviously supported the power of the Indian agents and favored the assimilation of his mother-in-law’s people. Copway and Warren also worked closely with the Government, and both supported removal as a way to separate the Ojibwe from the destructive influences of the encroaching white population. These views were completely opposed to what the chiefs were asking for: permanent reservations at the traditional villages. Because of this, we need to consider that Schoolcraft, Warren, and Copway would be negatively biased toward this group and its interpreter.
Finally there’s the question Howard Paap raises in Red Cliff, Wisconsin. How did this delegation impact the political developments of the early 1850s? In one sense the chiefs were clearly pleased with the results of the trip. They made many friends in Congress, in the media, and in several American cities. They came home smiling with gifts and money to spread to their people. However, they didn’t obtain their primary goal: reservations east of the Mississippi, and for this reason, the following statement in Schoolcraft’s account stands out:
The plan of retrocession of territory, on which some of the natives expressed a wish to settle and adopt the modes of civilized life, appeared to want the sanction of the several states in which the lands asked for lie. No action upon it could therefore be well had, until the legislatures of these states could be consulted.
“Kindly feelings” from President Polk didn’t mean much when Zachary Taylor and a new Whig administration were on the way in. Meanwhile, Congress and the media were so wrapped up in the national debate over slavery that they forgot all about the concerns of the Ojibwes of Lake Superior. This allowed a handful of Indian Department officials, corrupt traders, and a crooked, incompetent Minnesota Territorial governor named Alexander Ramsey to force a removal in 1850 that resulted in the deaths of 400 Ojibwe people in the Sandy Lake Tragedy.
It is hard to know how the chiefs felt about their 1848-49 diplomatic mission after Sandy Lake. Certainly their must have been a strong sense that they were betrayed and abandoned by a Government that had indicated it would support them, but the idea of bypassing the agents and territorial officials and going directly to the seat of government remained strong. Another, much more famous, “uninvited” delegation brought Buffalo and Oshogay to Washington in 1852, and ultimately the Federal Government did step in to grant the Ojibwe the reservations. Almost all of the chiefs who made the journey, or were shown in the pictographs, signed the Treaty of 1854 that made them.
Sources:
McClurken, James M., and Charles E. Cleland. Fish in the Lakes, Wild Rice, and Game in Abundance: Testimony on Behalf of Mille Lacs Ojibwe Hunting and Fishing Rights / James M. McClurken, Compiler ; with Charles E. Cleland … [et Al.]. East Lansing, MI: Michigan State UP, 2000. Print.
Paap, Howard D. Red Cliff, Wisconsin: A History of an Ojibwe Community. St. Cloud, MN: North Star, 2013. Print.
Satz, Ronald N. Chippewa Treaty Rights: The Reserved Rights of Wisconsin’s Chippewa Indians in Historical Perspective. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters, 1991. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and times of an Ojibwe Leader. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2007. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe, and Seth Eastman. Historical and Statistical Information Respecting the History, Condition, and Prospects of the Indian Tribes of the United States: Collected and Prepared under the Direction of the Bureau of Indian Affairs per Act of Congress of March 3rd, 1847. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo, 1851. Print.
CAUTION: This translation was made using Google Translate by someone who neither speaks nor reads German. It should not be considered accurate by scholarly standards.
Americans love travelogues. From de Tocqueville’s Democracy in America, to Twain’s Roughing It, to Steinbeck’s Travels with Charley, a few pages of a well-written travelogue by a random interloper can often help a reader picture a distant society more clearly than volumes of documents produced by actual members of the community. And while travel writers often misinterpret what they see, their works remain popular long into the future. When you think about it, this isn’t surprising. The genre is built on helping unfamiliar readers interpret a place that is different, whether by space or time, from the one they inhabit. The travel writer explains everything in a nice summary and doesn’t assume the reader knows the subject.
You can imagine, then, my excitement when I accidentally stumbled upon a largely-unknown and untranslated travelogue from 1852 that devotes several pages to to the greater Chequamegon region.
I was playing around on Google Books looking for variants of Chief Buffalo’s name from sources in the 1850s. Those of you who read regularly know that the 1850s were a decade of massive change in this area, and the subject of many of my posts. I was surprised to see one of the results come back in German. The passage clearly included the words Old Buffalo, Pezhickee, La Pointe, and Chippewa, but otherwise, nothing. I don’t speak any German, and I couldn’t decipher all the letters of the old German font.

Karl (Carl) Ritter von Scherzer (1821-1903) (Wikimedia Images)
The book was Reisen in Nordamerika in den Jahren 1852 und 1853 (Travels in North America in the years 1852 and 1853) by the Austrian travel writers Dr. Moritz Wagner and Dr. Carl Scherzer. These two men traveled throughout the world in the mid 19th-century and became well-known figures in Europe as writers, government officials, and scientists. In America, however, Reisen in Nordamerika never caught on. It rests in a handful of libraries, but as far as I can find, it has never been translated into English.
Chapter 21, From Ontonagon to the Mouth of the Bois-brule River, was the chapter I was most interested in. Over the course of a couple of weeks, I plugged paragraphs into Google Translate, about 50 pages worth.
Here is the result (with the caveat that it was e-translated, and I don’t actually know German). Normally I clog up my posts with analysis, but I prefer to let this one stand on its own. Enjoy:
XXI
From Ontonagon to the mouth of the Bois-brule River–Canoe ride to Magdalen Island–Porcupine Mountains–Camping in the open air–A dangerous canoe landing at night–A hospitable Jewish family–The island of La Pointe–The American Fur Company–The voyageurs or courriers de bois–Old Buffalo, the 90 year-old Chippewa chief–A schoolhouse and an examination–The Austrian Franciscan monk–Sunday mass and reflections on the Catholic missions–Continuing the journey by sail–Nous sommes degrades–A canoeman and apostle of temperance–Fond du lac–Sauvons-nous!
On September 15th, we were under a cloudless sky with the thermometer showing 37°F. In a birch canoe, we set out for Magdalene Island (La Pointe). Our intention was to drive up the great Lake Superior to its western end, then up the St. Louis and Savannah Rivers, to Sandy Lake on the eastern bank of the Mississippi River. Our crew consisted of a young Frenchman of noble birth and education and a captain of the U.S. Navy. Four French Canadians were the leaders of the canoes. Their trustworthy, cheerful, sprightly, and fearless natures carried us so bravely against the thundering waves, that they probably could have even rowed us across the river Styx.
Upon embarkation, an argument broke out between passengers and crew over the issue of overloading the boat. It was only conditioned to hold our many pieces of baggage and the provisions to be acquired along the way. However, our mercenary pilot produced several bags and packages, for which he could be well paid, by carrying them Madeline Island as freight.
Shortly after our exit, the weather hit us and a strong north wind obliged us to pull to shore and make Irish camp, after we had only covered four English miles to the Attacas (Cranberry) Rive,r one of the numerous mountain streams that pour into Lake Superior. We brought enough food from Ontonagon to provide for us for approximately 14 days of travel. The settlers of La Pointe, which is the last point on the lake where whites live, provided for themselves only scanty provisions. A heavy bag of ship’s biscuit was at the end of one canoe, and a second sack contained tea, sugar, flour, and some rice. A small basket contained our cooking and dining utensils.
The captain believed that all these supplies would be unecessary because the bush and fishing would provide us with the richest delicacies. But already in the next lunch hour, when we caught sight of no wild fowl, he said that we must prepare the rice. It was delicious with sugar. Dry wood was collected and a merry flickering fire prepared. An iron kettle hung from birch branches crossed akimbo, and the water soon boiled and evaporated. The sea air was fresh, and the sun shone brightly. The noise of the oncoming waves sounded like martial music to the unfinished ear, so we longed for the peaceful quiet lake. The shore was flat and sandy, but the main attraction of the scenery was in the gigantic forest trees and the richness of their leafy ornaments.
At a quarter to 3 o’clock, we left the bivouac as there was no more wind, and by 3 o’clock, with our camp still visible, the water became weaker and weaker and soon showed tree and cloud upon its smooth surface. We passed the Porcupine Mountains, a mountain range made of trapp geological formation. We observed that some years ago, a large number of inexperienced speculators sunk shafts and made a great number of investments in anticipation of a rich copper discovery. Now everything is destroyed and deserted and only the green arbor vitae remain on the steep trap rocks.
Our night was pretty and serene, so we went uninterrupted until 1 o’clock in the morning. Our experienced boatmen did not trust the deceptive smoothness of the lake, however, and they uttered repeated fears that storms would interrupt our trip. It happens quite often that people who travel in late autumn for pleasure or necessity from Ontonagon to Magdalene Island, 70 miles away, are by sea storms prevented from travelling that geographically-small route for as many as 6 or 8 days.
Used to the life of the Indians in the primeval forests, for whom even in places of civilization prefer the green carpet under the open sky to the soft rug and closed room, the elements could not dampen the emotion of the paddlers of the canoe or force out the pleasure of the chase.* But for Europeans, all sense of romantic adventure is gone when in such a forest for days without protection from the heavy rain and without shelter from the cold eeriness for his shivering limbs.
(*We were accompanied on our trip throughout the lakes of western Canada by half-Indians who had paternal European blood in their veins. Yet so often, a situation would allow us to spend a night inside rather than outdoors, but they always asked us to choose to Irish camp outside with the Indians, who lived at the various places. Although one spoke excellent English, and they were both drawn more to the great American race, they thought, felt, and spoke—Indian!)
It is amazing the carelessness with which the camp is set near the sparks of the crackling fire. An overwhelming calm is needed to prevent frequent accidents, or even loss of human life, from falling on the brands. As we were getting ready to continue our journey early in the morning, we found the front part of our tent riddled with a myriad of flickering sparks.
16 September (50° Fahrenheit)*) Black River, seven miles past Presque Isle. Gradually the shore area becomes rolling hills around Black River Mountain, which is about 100 feet in height. Frequently, immense masses of rock protrude along the banks and make a sudden landing impossible. This difficulty to reach shore, which can stretch for several miles long, is why a competent captain will only risk a daring canoe crossing on a fairly calm lake.
(*We checked the thermometer regularly every morning at 7 o’clock, and when travel conditions allowed it, at noon and evening.)
At Little Girl’s Point, a name linked to a romantic legend, we prepared lunch from the unfinished bread from the day before. We had rice, tea, and the remains of the bread we brought from a bakery in Ontonagon from our first days.
In the afternoon, we met at a distance a canoe with two Indians and a traveler going in an easterly direction. We got close enough to ask some short questions in telegraph style. We asked, “Where do you go? How is the water in the St. Louis and Savannah River?”
We were answered in the same brevity that they were from Crow Wing going to Ontonagon, and that the rivers were almost dried from a month-long lack of rain.
The last information was of utmost importance to us for it changed, all of a sudden, the fibers of our entire itinerary. With the state of the rivers, we would have to do most of the 300-mile long route on foot which neither the advanced season of the year, nor the sandy steppes invited. If we had been able to extend our trip, we could have visited Itasca Lake, the cradle of the Mississippi, where only a few historically-impressive researchers and travelers have passed near: Pike, Cass, Schoolcraft, Nicollet, and to our knowledge, no Austrian.
However, this was impossible considering our lack of necessary academic preparation and in consideration of the economy of our travel plan. We do not like the error, we would almost say vice, of so many travelers who rush in hasty discontent, supported by modern transport, through wonderful parts of creation without gaining any knowledge of the land’s physical history and the fate of its inhabitants.*
(*We were told here recently of such a German tourist who traveled through Mexico in only a fortnight– i.e. 6 days from Veracruz to the capital and 6 days back with only two days in the capital!)
While driving, the boatmen sang alternately. They were, for the most part, frivolous love songs and not of the least philological or ethnographic interest.
After 2 o’clock, we passed the rocks of the Montreal River. They run for about six miles with a long drag reaching up to an altitude of 100 feet. There are layers of shale and red sandstone, all of which run east to west. By weathering, they have obtained such a dyed-painting appearance, that you can see in their marbled colors something resembling a washed-out image.
The Montreal* is a major tributary of Lake Superior. About 300 steps up from where it empties into the lake, it forms a very pretty waterfall surrounded by an impressive pool. Rugged cliffs form the 80’ falls over a vertical sandstone layer and form a lovely valley. The width of the Montreal is 10’, and it also forms the border between the states of Michigan and Wisconsin.
(*Indian: Ka-wa’-si-gi-nong sepi, the white flowing falls.)
We stayed in this cute little bay for over an hour as our frail canoes had begun to take on a questionable amount of water as the result of some wicked stone wounds.
Up from Montreal River heading towards La Pointe, the earlier red sandstone formation starts again, and the rich shaded hills and rugged cliffs disappear suddenly. Around 6 o’clock, we rested for half an hour at the mouth of the Bad River of Lake Superior. We quickly prepared our evening snack as the possibility of reaching Magdalene Island that same night was still in contention.
Across from us, on the western shore of Bad River*, we saw Indians by a warm fire. One of the boatmen suspected they’d come back from catching fish, and he called in a loud voice across the river asking if they wanted to come over and sell us some. We took their response, and soon shy Indian women (squaws) appeared. Lacking a male, they dreaded to get involved in trading with Whites, and did not like the return we offered.
(*On Bad River, a Methodist Mission was founded in 1841. It consists of the missionary, his wife, and a female teacher. Their sphere of influence is limited to dispensing divine teaching only to those wandering tribes of Chippewa Indians that come here every year during the season of fishing, to divest the birch tree of its bark, and to build it into a shelter).
A part of our nightly trip was spent fantastically in blissful contemplation of the wonders above us and next to us. Night sent the cool fragrance of the forest to our lonely rocking boat, and the sky was studded with stars that sparkled through the green branches of the woods. Soon, luminous insects appeared on the tops of the trees in equally brilliant bouquets.
At 11 o’clock at night, we saw a magnificent aurora borealis, which left such a bright scent upon the dark blue sky. However, the theater soon changed scene, and a fierce south wind moved in incredibly fast. What had just been a quietly slumbering lake, as if inhabited by underwater ghosts, struck the alarm and suddenly tumultuous waves approached the boat. With the faster waves wanting to forestall the slower, a raging tumult arose resembling the dirt thrown up by great wagon wheels.
We were directly in the middle of that powerful watery surface, about one and one half miles from the mainland and from the nearest south bank of the island. It would have been of no advantage to reverse course as it required no more time to reach the island as to go back. At the outbreak of this dangerous storm, our boatmen were still determined to reach La Pointe.
But when several times the beating waves began to fill our boat from all sides with water, the situation became much more serious. As if to increase our misery, at almost the same moment a darkness concealed the sky and gloomy clouds veiled the stars and northern lights, and with them went our cheerful countenance.
Now singing, our boatmen spoke with anxious gestures and an unintelligible patois to our fellow traveler. The captain said jokingly, that they took counsel to see who should be thrown in the water first should the danger increase. We replied in a like manner that it was never our desire to be first and that we felt the captain should keep that honor. Fortunately, all our concern soon ended as we landed at La Pointe (Chegoimegon).
To be continued…
CAUTION: This translation was made using Google Translate by someone who neither speaks nor reads German. It should not be considered accurate by scholarly standards.
Oshogay
August 12, 2013
At the most recent count, Chief Buffalo is mentioned in over two-thirds of the posts here on Chequamegon History. That’s the most of anyone listed so far in the People Index. While there are more Buffalo posts on the way, I also want to draw attention to some of the lesser known leaders of the La Pointe Band. So, look for upcoming posts about Dagwagaane (Tagwagane), Mizay, Blackbird, Waabojiig, Andeg-wiiyas, and others. I want to start, however, with Oshogay, the young speaker who traveled to Washington with Buffalo in 1852 only to die the next year before the treaty he was seeking could be negotiated.
I debated whether to do this post, since I don’t know a lot about Oshogay. I don’t know for sure what his name means, so I don’t know how to spell or pronounce it correctly (in the sources you see Oshogay, O-sho-ga, Osh-a-ga, Oshaga, Ozhoge, etc.). In fact, I don’t even know how many people he is. There were at least four men with that name among the Lake Superior Ojibwe between 1800 and 1860, so much like with the Great Chief Buffalo Picture Search, the key to getting Oshogay’s history right is dependent on separating his story from those who share his name.
In the end, I felt that challenge was worth a post in its own right, so here it is.
Getting Started
According to his gravestone, Oshogay was 51 when he died at La Pointe in 1853. That would put his birth around 1802. However, the Ojibwe did not track their birthdays in those days, so that should not be considered absolutely precise. He was considered a young man of the La Pointe Band at the time of his death. In my mind, the easiest way to sort out the information is going to be to lay it out chronologically. Here it goes:
1) Henry Schoolcraft, United States Indian Agent at Sault Ste. Marie, recorded the following on July 19, 1828:
Oshogay (the Osprey), solicited provisions to return home. This young man had been sent down to deliver a speech from his father, Kabamappa, of the river St. Croix, in which he regretted his inability to come in person. The father had first attracted my notice at the treaty of Prairie du Chien, and afterwards received a small medal, by my recommendation, from the Commissioners at Fond du Lac. He appeared to consider himself under obligations to renew the assurance of his friendship, and this, with the hope of receiving some presents, appeared to constitute the object of his son’s mission, who conducted himself with more modesty and timidity before me than prudence afterwards; for, by extending his visit to Drummond Island, where both he and his father were unknown, he got nothing, and forfeited the right to claim anything for himself on his return here.
I sent, however, in his charge, a present of goods of small amount, to be delivered to his father, who has not countenanced his foreign visit.
Oshogay is a “young man.” A birth year of 1802 would make him 26. He is part of Gaa-bimabi’s (Kabamappa’s) village in the upper St. Croix country.
2) In June of 1834, Edmund Ely and W. T. Boutwell, two missionaries, traveled from Fond du Lac (today’s Fond du Lac Reservation near Cloquet) down the St. Croix to Yellow Lake (near today’s Webster, WI) to meet with other missionaries. As they left Gaa-bimabi’s (Kabamappa’s) village near the head of the St. Croix and reached the Namekagon River on June 28th, they were looking for someone to guide them the rest of the way. An old Ojibwe man, who Boutwell had met before at La Pointe, and his son offered to help. The man fed the missionaries fish and hunted for them while they camped a full day at the mouth of the Namekagon since the 29th was a Sunday and they refused to travel on the Sabbath. On Monday the 30th, the reembarked, and Ely recorded in his journal:
The man, whose name is “Ozhoge,” and his son embarked with us about 1/2 past 9 °clk a.m. The old man in the bow and myself steering. We run the rapids safely. At half past one P. M. arrived at the mouth of Yellow River…
Ozhoge is an “old man” in 1834, so he couldn’t have been born in 1802. He is staying on the Namekagon River in the upper St. Croix country between Gaa-bimabi and the Yellow Lake Band. He had recently spent time at La Pointe.
3) Ely’s stay on the St. Croix that summer was brief. He was stationed at Fond du Lac until he eventually wore out his welcome there. In the 1840s, he would be stationed at Pokegama, lower on the St. Croix. During these years, he makes multiple references to a man named Ozhogens (a diminutive of Ozhoge). Ozhogens is always found above Yellow River on the upper St. Croix.
Ozhogens has a name that may imply someone older (possibly a father or other relative) lives nearby with the name Ozhoge. He seems to live in the upper St. Croix country. A birth year of 1802 would put him in his forties, which is plausible.

Ke-che-wask keenk (Gichi-weshki) is Chief Buffalo. Gab-im-ub-be (Gaa-bimabi) was the chief Schoolcraft identified as the father of Oshogay. Ja-che-go-onk was a son of Chief Buffalo.
4) On August 2, 1847, the United States and the Mississippi and Lake Superior Ojibwe concluded a treaty at Fond du Lac. The US Government wanted Ojibwe land along the nation’s border with the Dakota Sioux, so it could remove the Ho-Chunk people from Wisconsin to Minnesota.
Among the signatures, we find O-sho-gaz, a warrior from St. Croix. This would seem to be the Ozhogens we meet in Ely.
Here O-sho-gaz is clearly identified as being from St. Croix. His identification as a warrior would probably indicate that he is a relatively young man. The fact that his signature is squeezed in the middle of the names of members of the La Pointe Band may or may not be significant. The signatures on the 1847 Treaty are not officially grouped by band, but they tend to cluster as such.
5) In 1848 and 1849 George P. Warren operated the fur post at Chippewa Falls and kept a log that has been transcribed and digitized by the University of Wisconsin Eau Claire. He makes several transactions with a man named Oshogay, and at one point seems to have him employed in his business. His age isn’t indicated, but the amount of furs he brings in suggests that he is the head of a small band or large family. There were multiple Ojibwe villages on the Chippewa River at that time, including at Rice Lake and Lake Shatac (Chetek). The United States Government treated with them as satellite villages of the Lac Courte Oreilles Band.
Based on where he lives, this Oshogay might not be the same person as the one described above.
6) In December 1850, the Wisconsin Supreme Court ruled in the case Oshoga vs. The State of Wisconsin, that there were a number of irregularities in the trial that convicted “Oshoga, an Indian of the Chippewa Nation” of murder. The court reversed the decision of the St. Croix County circuit court. I’ve found surprisingly little about this case, though that part of Wisconsin was growing very violent in the 1840s as white lumbermen and liquor salesmen were flooding the country.

Pg 56 of Containing cases decided from the December term, 1850, until the organization of the separate Supreme Court in 1853: Volume 3 of Reports of Cases Argued and Determined in the Supreme Court of the State of Wisconsin: With Tables of the Cases and Principal Matters, and the Rules of the Several Courts in Force Since 1838, Wisconsin. Supreme Court Authors: Wisconsin. Supreme Court, Silas Uriah Pinney (Google Books).
The man killed, Alexander Livingston, was a liquor dealer himself.
Alexander Livingston, a man who in youth had had excellent advantages, became himself a dealer in whisky, at the mouth of Wolf creek, in a drunken melee in his own store was shot and killed by Robido, a half-breed. Robido was arrested but managed to escape justice.
~From Fifty Years in the Northwest by W.H.C Folsom
Several pages later, Folsom writes:
At the mouth of Wolf creek, in the extreme northwestern section of this town, J. R. Brown had a trading house in the ’30s, and Louis Roberts in the ’40s. At this place Alex. Livingston, another trader, was killed by Indians in 1849. Livingston had built him a comfortable home, which he made a stopping place for the weary traveler, whom he fed on wild rice, maple sugar, venison, bear meat, muskrats, wild fowl and flour bread, all decently prepared by his Indian wife. Mr. Livingston was killed by an Indian in 1849.
Folsom makes no mention of Oshoga, and I haven’t found anything else on what happened to him or Robido (Robideaux?).
It’s hard to say if this Oshoga is the Ozhogen’s of Ely’s journals or the Oshogay of Warren’s. Wolf Creek is on the St. Croix, but it’s not far from the Chippewa River country either, and the Oshogay of Warren seems to have covered a lot of ground in the fur trade. Warren’s journal, linked in #4, contains a similar story of a killing and “frontier justice” leading to lynch mobs against the Ojibwe. To escape the violence and overcrowding, many Ojibwe from that part of the country started to relocate to Fond du Lac, Lac Courte Oreilles, or La Pointe/Bad River. La Pointe is also where we find the next mention of Oshogay.
7) From 1851 to 1853, a new voice emerged loudly from the La Pointe Band in the aftermath of the Sandy Lake Tragedy. It was that of Buffalo’s speaker Oshogay (or O-sho-ga), and he spoke out strongly against Indian Agent John Watrous’ handling of the Sandy Lake payments (see this post) and against Watrous’ continued demands for removal of the Lake Superior Ojibwe. There are a number of documents with Oshogay’s name on them, and I won’t mention all of them, but I recommend Theresa Schenck’s William W. Warren and Howard Paap’s Red Cliff, Wisconsin as two places to get started.
Chief Buffalo was known as a great speaker, but he was nearing the end of his life, and it was the younger chief who was speaking on behalf of the band more and more. Oshogay represented Buffalo in St. Paul, co-wrote a number of letters with him, and most famously, did most of the talking when the two chiefs went to Washington D.C. in the spring of 1852 (at least according to Benjamin Armstrong’s memoir). A number of secondary sources suggest that Oshogay was Buffalo’s son or son-in-law, but I’ve yet to see these claims backed up with an original document. However, all the documents that identify by band, say this Oshogay was from La Pointe.
The Wisconsin Historical Society has digitized four petitions drafted in the fall of 1851 and winter of 1852. The petitions are from several chiefs, mostly of the La Pointe and Lac Courte Oreilles/Chippewa River bands, calling for the removal of John Watrous as Indian Agent. The content of the petitions deserves its own post, so for now we’ll only look at the signatures.

November 6, 1851 Letter from 30 chiefs and headmen to Luke Lea, Commissioner of Indian Affairs: Multiple villages are represented here, roughly grouped by band. Kijiueshki (Buffalo), Jejigwaig (Buffalo’s son), Kishhitauag (“Cut Ear” also associated with the Ontonagon Band), Misai (“Lawyerfish”), Oshkinaue (“Youth”), Aitauigizhik (“Each Side of the Sky”), Medueguon, and Makudeuakuat (“Black Cloud”) are all known members of the La Pointe Band. Before the 1850s, Kabemabe (Gaa-bimabi) and Ozhoge were associated with the villages of the Upper St. Croix.

November 8, 1851, Letter from the Chiefs and Headmen of Chippeway River, Lac Coutereille, Puk-wa-none, Long Lake, and Lac Shatac to Alexander Ramsey, Superintendent of Indian Affairs: This letter was written from Sandy Lake two days after the one above it was written from La Pointe. O-sho-gay the warrior from Lac Shatac (Lake Chetek) can’t be the same person as Ozhoge the chief unless he had some kind of airplane or helicopter back in 1851.

Undated (Jan. 1852?) petition to “Our Great Father”: This Oshoga is clearly the one from Lake Chetek (Chippewa River).

Undated (Jan. 1852?) petition: These men are all associated with the La Pointe Band. Osho-gay is their Speaker.
In the early 1850s, we clearly have two different men named Oshogay involved in the politics of the Lake Superior Ojibwe. One is a young warrior from the Chippewa River country, and the other is a rising leader among the La Pointe Band.

Washington Delegation July 22, 1852 This engraving of the 1852 delegation led by Buffalo and Oshogay appeared in Benjamin Armstrong’s Early Life Among the Indians. Look for an upcoming post dedicated to this image.
8) In the winter of 1853-1854, a smallpox epidemic ripped through La Pointe and claimed the lives of a number of its residents including that of Oshogay. It had appeared that Buffalo was grooming him to take over leadership of the La Pointe Band, but his tragic death left a leadership vacuum after the establishment of reservations and the death of Buffalo in 1855.
Oshogay’s death is marked in a number of sources including the gravestone at the top of this post. The following account comes from Richard E. Morse, an observer of the 1855 annuity payments at La Pointe:
The Chippewas, during the past few years, have suffered extensively, and many of them died, with the small pox. Chief O-SHO-GA died of this disease in 1854. The Agent caused a suitable tomb-stone to be erected at his grave, in La Pointe. He was a young chief, of rare promise and merit; he also stood high in the affections of his people.
Later, Morse records a speech by Ja-be-ge-zhick or “Hole in the Sky,” a young Ojibwe man from the Bad River Mission who had converted to Christianity and dressed in “American style.” Jabegezhick speaks out strongly to the American officials against the assembled chiefs:
…I am glad you have seen us, and have seen the folly of our chiefs; it may give you a general idea of their transactions. By the papers you have made out for the chiefs to sign, you can judge of their ability to do business for us. We had but one man among us, capable of doing business for the Chippewa nation; that man was O-SHO-GA, now dead and our nation now mourns. (O-SHO-GA was a young chief of great merit and much promise; he died of small-pox, February 1854). Since his death, we have lost all our faith in the balance of our chiefs…
This O-sho-ga is the young chief, associated with the La Pointe Band, who went to Washington with Buffalo in 1852.
9) In 1878, “Old Oshaga” received three dollars for a lynx bounty in Chippewa County.
Report of the Wisconsin Office of the Secretary of State, 1878; pg. 94 (Google Books)
It seems quite possible that Old Oshaga is the young man that worked with George Warren in the 1840s and the warrior from Lake Chetek who signed the petitions against Agent Watrous in the 1850s.
10) In 1880, a delegation of Bad River, Lac Courte Oreilles, and Lac du Flambeau chiefs visited Washington D.C. I will get into their purpose in a future post, but for now, I will mention that the chiefs were older men who would have been around in the 1840s and ’50s. One of them is named Oshogay. The challenge is figuring out which one.

Ojibwe Delegation c. 1880 by Charles M. Bell. [Identifying information from the Smithsonian] Studio portrait of Anishinaabe Delegation posed in front of a backdrop. Sitting, left to right: Edawigijig; Kis-ki-ta-wag; Wadwaiasoug (on floor); Akewainzee (center); Oshawashkogijig; Nijogijig; Oshoga. Back row (order unknown); Wasigwanabi; Ogimagijig; and four unidentified men (possibly Frank Briggs, top center, and Benjamin Green Armstrong, top right). The men wear European-style suit jackets and pants; one man wears a peace medal, some wear beaded sashes or bags or hold pipes and other props.(Smithsonian Institution National Museum of the American Indian).
- Upper row reading from the left.
- 1. Vincent Conyer- Interpreter 1,2,4,5 ?, includes Wasigwanabi and Ogimagijig
- 2. Vincent Roy Jr.
- 3. Dr. I. L. Mahan, Indian Agent Frank Briggs
- 4. No Name Given
- 5. Geo P. Warren (Born at LaPointe- civil war vet.
- 6. Thad Thayer Benjamin Armstrong
- Lower row
- 1. Messenger Edawigijig
- 2. Na-ga-nab (head chief of all Chippewas) Kis-ki-ta-wag
- 3. Moses White, father of Jim White Waswaisoug
- 4. No Name Given Akewainzee
- 5. Osho’gay- head speaker Oshawashkogijig or Oshoga
- 6. Bay’-qua-as’ (head chief of La Corrd Oreilles, 7 ft. tall) Nijogijig or Oshawashkogijig
- 7. No name given Oshoga or Nijogijig
The Smithsonian lists Oshoga last, so that would mean he is the man sitting in the chair at the far right. However, it doesn’t specify who the man seated on the right on the floor is, so it’s also possible that he’s their Oshoga. If the latter is true, that’s also who the unknown writer of the library caption identified as Osho’gay. Whoever he is in the picture, it seems very possible that this is the same man as “Old Oshaga” from number 9.
11) There is one more document I’d like to include, although it doesn’t mention any of the people we’ve discussed so far, it may be of interest to someone reading this post. It mentions a man named Oshogay who was born before 1860 (albeit not long before).
For decades after 1854, many of the Lake Superior Ojibwe continued to live off of the reservations created in the Treaty of La Pointe. This was especially true in the St. Croix region where no reservation was created at all. In the 1910s, the Government set out to document where various Ojibwe families were living and what tribal rights they had. This process led to the creation of the St. Croix and Mole Lake reservations. In 1915, we find 64-year-old Oshogay and his family living in Randall, Wisconsin which may suggest a connection to the St. Croix Oshogays. As with number 6 above, this creates some ambiguity because he is listed as enrolled at Lac Courte Oreilles, which implies a connection to the Chippewa River Oshogay. For now, I leave this investigation up to someone else, but I’ll leave it here for interest.

United States. Congress. House. Committee on Indian Affairs. Indian Appropriation Bill: Supplemental Hearings Before a Subcommittee. 1919 (Google Books).
This is not any of the Oshogays discussed so far, but it could be a relative of any or all of them.
In the final analysis
These eleven documents mention at least four men named Oshogay living in northern Wisconsin between 1800 and 1860. Edmund Ely met an old man named Oshogay in 1834. He is one. A 64-year old man, a child in the 1850s, was listed on the roster of “St. Croix Indians.” He is another. I believe the warrior from Lake Chetek who traded with George Warren in the 1840s could be one of the chiefs who went to Washington in 1880. He may also be the one who was falsely accused of killing Alexander Livingston. Of these three men, none are the Oshogay who went to Washington with Buffalo in 1852.
That leaves us with the last mystery. Is Ozhogens, the young son of the St. Croix chief Gaa-bimabi, the orator from La Pointe who played such a prominent role in the politics of the early 1850s? I don’t have a smoking gun, but I feel the circumstantial evidence strongly suggests he is. If that’s the case, it explains why those who’ve looked for his early history in the La Pointe Band have come up empty.
However, important questions remain unanswered. What was his connection to Buffalo? If he was from St. Croix, how was he able to gain such a prominent role in the La Pointe Band, and why did he relocate to La Pointe anyway? I have my suspicions for each of these questions, but no solid evidence. If you do, please let me know, and we’ll continue to shed light on this underappreciated Ojibwe leader.
Sources:
Armstrong, Benj G., and Thomas P. Wentworth. Early Life among the Indians: Reminiscences from the Life of Benj. G. Armstrong : Treaties of 1835, 1837, 1842 and 1854 : Habits and Customs of the Red Men of the Forest : Incidents, Biographical Sketches, Battles, &c. Ashland, WI: Press of A.W. Bowron, 1892. Print.
Ely, Edmund Franklin, and Theresa M. Schenck. The Ojibwe Journals of Edmund F. Ely, 1833-1849. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2012. Print.
Folsom, William H. C., and E. E. Edwards. Fifty Years in the Northwest. St. Paul: Pioneer, 1888. Print.
KAPPLER’S INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES. Ed. Charles J. Kappler. Oklahoma State University Library, n.d. Web. 12 August 2013. <http:// digital.library.okstate.edu/Kappler/>.
Nichols, John, and Earl Nyholm. A Concise Dictionary of Minnesota Ojibwe. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota, 1995. Print.
Paap, Howard D. Red Cliff, Wisconsin: A History of an Ojibwe Community. St. Cloud, MN: North Star, 2013. Print.
Redix, Erik M. “The Murder of Joe White: Ojibwe Leadership and Colonialism in Wisconsin.” Diss. University of Minnesota, 2012. Print.
Schenck, Theresa M. The Voice of the Crane Echoes Afar: The Sociopolitical Organization of the Lake Superior Ojibwa, 1640-1855. New York: Garland Pub., 1997. Print.
———–William W. Warren: The Life, Letters, and times of an Ojibwe Leader. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2007. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe. Personal Memoirs of a Residence of Thirty Years with the Indian Tribes on the American Frontiers: With Brief Notices of Passing Events, Facts, and Opinions, A.D. 1812 to A.D. 1842. Philadelphia, [Pa.: Lippincott, Grambo and, 1851. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
This post is on of several that seeks to determine how many images exist of Great Buffalo, the famous La Pointe Ojibwe chief who died in 1855. To learn why this is necessary, read this post introducing the Great Chief Buffalo Picture Search.
Today’s post looks at two paintings from the 1820s of Ojibwe men named Bizhiki (Buffalo). The originals are lost forever, but the images still exist in the lithographs that follow.

Pee-che-kir: A Chippewa Chief Lithograph from McKenney and Hall’s History of the Indian Tribes of North America based on destroyed original by Charles Bird King; 1824. (Wikimedia Images)

Pe-shick-ee: A Celebrated Chippeway Chief from the Aboriginal Port-Folio by James Otto Lewis. The original painting was done by Lewis at Prairie du Chien or Fond du Lac of Lake Superior in 1825 or 1826 (Wisconsin Historical Society).
1824 Delegation to Washington
Chronologically, the first known image to show an Ojibwe chief named Buffalo appeared in the mid-1820s at time when the Ojibwe and the United States government were still getting to know each other. Prior to the 1820s, the Americans viewed the Ojibwe as a large and powerful nation. They had an uncomfortably close history with the British, who were till lurking over the border in Canada, but they otherwise inhabited a remote country unfit for white settlement. To the Ojibwe, the Americans were chimookomaan, “long knives,” in reference to the swords carried by the military officers who were the first Americans to come into their country. It was one of these long knives, Thomas McKenney, who set in motion the gathering of hundreds of paintings of Indians. Two of these showed men named Buffalo (Bizhiki).

Charles Bird King: Self portrait 1815 (Wikimedia Images)
McKenney was appointed the first Superintendent of Indian Affairs in 1824. Indian Affairs was under the Department of War at that time, and McKenneyʼs men in the West were mostly soldiers. He, like many in his day, believed that the Indian nations of North America were destined for extinction within a matter of decades. To preserve a record of these peoples, he commissioned over 100 portraits of various Indian delegates who came to Washington from all over the U.S. states and territories. Most of the painting work fell to Charles Bird King, a skilled Washington portrait artist. Beginning in 1822, King painted Indian portraits for two decades. He would paint famous men like Black Hawk, Red Jacket, Joseph Brandt, and Major Ridge, but Kingʼs primary goal was not to record the stories of important individuals so much as it was to capture the look of a vanishing race.

No-tin copied from 1824 Charles Bird King original by Henry Inman. Noodin (Wind) was a prominent chief from the St. Croix country. King’s painting of Buffalo from St. Croix was probably also copied by Inman, but its location is unknown (Wikimedia Images).
In July of 1824, William Clark, the famous companion of Meriwether Lewis, brought a delegation of Sauks, Foxes, and Ioways to Washington to negotiate land cessions. Lawrence Taliaferro, the Indian agent at Fort St. Anthony (now Minneapolis), brought representatives of the Sioux, Menominee, and Ojibwe to observe the treaty process. The St. Croix chiefs Buffalo and Noodin (Wind) represented the Ojibwe.

Charles Bird King painted portraits of most of the Indians listed here in the the 1824 Washington group by Niles’ Weekly Register, July 31, 1824. (Google Books)
The St. Croix chiefs were treated well: taken to shows, and to visit the sights of the eastern cities. However, there was a more sinister motivation behind the governmentʼs actions. McKenney made sure the chiefs saw the size and scope of the U.S. Military facilities in Washington, the unspoken message being that resistance to American expansion was impossible. This message seems to have resonated with Buffalo and Noodin of St. Croix as it is referred to repeatedly in the official record. McKenney pointed Buffalo out as a witness to American power at the Treaty of Fond du Lac (1826). Schoolcraft and Allen mention Buffalo’s trip in their own ill-fated journey up the St. Croix in 1832 (see it in this post), and Noodin talks about the soldiers he saw in Washington in the treaty deliberations in the 1837 Treaty of St. Peters.
While in Washington, Buffalo, Noodin, and most of the other Indians in the group sat with King for portraits in oil. Buffalo was shown wearing a white shirt and cloak, holding a pipe, with his face painted red. The paintings were hung in the offices of the Department of War, and the chiefs returned to their villages.
James Otto Lewis
The following summer, St. Croix Buffalo and Noodin joined chiefs from villages throughout the Ojibwe country, as well as from the Sioux, Sac and Fox, Menominee, Ho-Chunk, Ioway, Ottawa, and Potawatomi at Prairie du Chien. The Americans had called them there to sign a treaty to establish firm borders between their nations. The stated goal was to end the wars between the Sioux and Ojibwe, but it also provided the government an opportunity to assert its authority over the country and to set the stage for future land cessions.
McKenney did not attend the Treaty of Prairie du Chien leaving it to Clark and Lewis Cass to act as commissioners. A quick scan of the Ojibwe signatories shows “Pee-see- ker or buffalo, St. Croix Band,” toward the bottom. Looking up to the third signature, we see “Gitspee Waskee, or le boeuf of la pointe lake Superior,” so both the St. Croix and La Pointe Buffalos were present among the dozens of signatures. One of the government witnesses listed was an artist from Philadelphia named James Otto Lewis. Over the several days of negotiation, Lewis painted scenes of the treaty grounds as well as portraits of various chiefs. These were sent back to Washington, some were copied and improved by King or other artists, and they were added to the collection of the War Department.
The following year, 1826, McKenney himself traveled to Fond du Lac at the western end of Lake Superior to make a new treaty with the Ojibwe concerning mineral exploration on the south shore. Lewis accompanied him and continued to create images. At some point in these two years, a Lewis portrait of an Ojibwe chief named Pe-schick-ee (Bizhiki) appeared in McKenneyʼs growing War Department collection.
Lithographs
By 1830, McKenney had been dismissed from his position and turned his attention to publishing a portfolio of lithographs from the paintings in the War Department collection. Hoping to cash in his own paintings by beating McKenney to the lithograph market, Lewis released The Aboriginal Port Folio in May of 1835. It included 72 color plates, one of which was Pe-schick-ee: A Celebrated Chippeway Chief.

Pencil sketch of Pee-che-kir by Charles Bird King. King made these sketches after his original paintings to assist in making copies. (Herman J. Viola, The Indian Legacy of Charles Bird King.)
Due to financial issues The History of the Indian Tribes of North America, by McKenney with James Hall, would not come out in full release until the mid 1840s. The three-volume work became a bestseller and included color plates of 120 Indians, 95 of which are accompanied by short biographies. Most of the lithographs were derived from works by King, but some were from Lewis and other artists. Kingʼs portrait of Pee-Che-Kir: A Chippewa Chief was included among them, unfortunately without a biography. However, we know its source as the painting of the St. Croix Buffalo in 1824. Noodin and several others from that delegation also made it into lithograph form. The original War Department paintings, including both Pee-Che-Kir and Pe-schick-ee were sent to the Smithsonian, where they were destroyed in a fire in 1858. Oil copies of some of the originals, including Henry Inmanʼs copy of Kingʼs portrait of Noodin, survive, but the lithographs remain the only known versions of the Buffalo portraits other than a pencil sketch of the head of Pee-Che-Kir done by King.
The man in the Lewis lithograph is difficult to identify. The only potential clue we get from the image itself is the title of “A Celebrated Chippeway Chief,” and information that it was painted at Prairie du Chien in 1825. To many, “celebrated” would indicate Buffalo from La Pointe, but in 1825, he was largely unknown to the Americans while the St. Croix Buffalo had been to Washington. In the 1820s, La Pointe Buffaloʼs stature was nowhere near what it would become. However, he was a noted speaker from a prominent family and his signature is featured prominently in the treaty. Any assumptions about which chief was more “celebrated” are difficult.
In dress and pose, the man painted by Lewis resembles the King portrait of St. Croix Buffalo. This has caused some to claim that the Lewis is simply the original version of the King. King did copy and improve several of Lewisʼ works, but the copies tended to preserve in some degree the grotesque, almost cartoonish, facial features that are characteristic of the self-taught Lewis (see this post for another Lewis portrait). The classically-trained King painted highly realistic faces, and side-by-side comparison of the lithographs shows very little facial resemblance between Kingʼs Pee-Che-Kir and Lewisʼ Pe-schick-ee.

Thomas L. McKenney painted in 1856 by Charles Loring Elliott (Wikimedia Images)
Of the 147 War Department Indian portraits cataloged by William J. Rhees of the Smithsonian prior to the fire, 26 are described as being painted by “King from Lewis,” all of which are from 1826 or after. Most of the rest are attributed solely to King. Almost all the members of the 1824 trip to Washington are represented in the catalog. “Pee-che-ker, Buffalo, Chief of the Chippeways.” does not have an artist listed, but Noodin and several of the others from the 1824 group are listed as King, and it is safe to assume Buffalo’s should be as well. The published lithograph of Pee-che-kir was attributed solely to King, and not “King from Lewis” as others are. This further suggests that the two Buffalo lithographs are separate portraits from separate sittings, and potentially of separate chiefs.
Even without all this evidence, we can be confident that the King is not a copy of the Lewis because the King portrait was painted in 1824, and the Lewis was painted no earlier than 1825. There is, however, some debate about when the Lewis was painted. From the historical record, we know that Lewis was present at both Prairie du Chien and Fond du Lac along with both the La Pointe Buffalo and the St. Croix Buffalo. When Pe- schick-ee was released, Lewis identified it as being painted at Prairie du Chien. However, the work has also been placed at Fond du Lac.
The modern identification of Pee-che-kir as a copy of Pe-schick-ee seems to have originated with the work of James D. Horan. In his 1972 book, The McKenney-Hall Portrait Gallery of American Indians, he reproduces all the images from History of the Indian Tribes, and adds his own analysis. On page 206, he describes the King portrait of Pee-che-kir with:
“Peechekir (or Peechekor, Buffalo) was “a solid, straight formed Indian,” Colonel McKenney recalled many years after the Fond du Lac treaty where he had met the chief. Apparently the Chippewa played a minor role at the council.
Original by James Otto Lewis, Fond du Lac council, 1826, later copied in Washington by Charles Bird King.”
Presumably, the original he refers to would be the Lewis portrait of Pe-schick-ee. However, Horanʼs statement that McKenney met St. Croix Buffalo at Fond du Lac is false. As we already know, the two men met in 1824 in Washington. It is puzzling how Horan did not know this considering he includes the following account on page 68:
The first Indian to step out of the closely packed lines of stone-faced red men made McKenney feel at home; it was a chief he had met a few years before in Washington. The Indian held up his hand in a sign of peace and called out:
“Washigton [sic]… Washington… McKenney shook hands with the chief and nodded to Lewis but the artist had already started to sketch.”
McKenneyʼs original account identifies this chief as none other than St. Croix Buffalo:
In half an hour after, another band came in who commenced, as did the others, by shaking hands, followed, of course, by smoking. In this second band I recognized Pee-che-kee, or rather he recognized me–a chief who had been at Washington, and whose likeness hangs in my office there. I noticed that his eye was upon me, and that he smiled, and was busily employed speaking to an Indian who sat beside him, and no doubt about me. His first word on coming up to speak to me was, “Washington”–pointing to the east. The substance of his address was, that he was glad to see me–he felt his heart jump when he first saw me–it made him think of Washington, of his great father, of the good living he had when he visited us–how kind we all were to him, and that he should never forget any of it.
From this, Horan should have known not only that the two men knew each other, but also that a portrait of the chief (Kingʼs) already was part of the War Department collection and therefore existed before the Lewis portrait. Horanʼs description of Lewis already beginning his sketch does not appear in McKenneyʼs account and seems to invented. This is not the only instance where Horan confuses facts or takes wide license with Ojibwe history. His statement quoted above that the Ojibwe “played a minor role” in the Treaty of Fond du Lac, when they were the only Indian nation present and greatly outnumbered the Americans, should disqualify Horan from being treated as any kind of authority on the topic. However, he is not the only one to place the Lewis portrait of Pe-schick-ee at Fond du Lac rather than Prairie du Chien.
Between, 1835 and 1838 Lewis released 80 lithographs, mostly of individual Indians, in a set of ten installments. He had intended to include an eleventh with biographies. However, a dispute with the publisher prevented the final installment from coming out immediately. His London edition, released in 1844 by another publisher, included a few short biographies but none for Pe-schick-ee. Most scholars assumed that he never released the promised eleventh installment. However, one copy of a self-published 1850 pamphlet donated by Lewisʼs grandson exists in the Free Library of Philadelphia. In it are the remaining biographies. Number 30 reads:
No. 30. Pe-shisk-Kee. A Chippewa warrior from Lake Huron, noted for his attachment to the British, with whom he always sided. At the treaty held at Fond du Lac, when the Council opened, he appeared with a British medal of George the III. on his breast, and carrying a British flag, which Gen. Cass, one of the Commissioners, promptly and indignantly placed under his feet, and pointing to the stars and stripes, floating above them, informed him that that was the only one permitted to wave there.
The Chief haughtily refused to participate in the business of the Council, until, by gifts, he became partly conciliated, when he joined in their deliberations. Painted at Fond du Lac, in 1826.
This new evidence further clouds the story. Initially, this description does not seem to fit what we know about either the La Pointe or the St. Croix Buffalo, as both were born near Lake Superior and lived in Wisconsin. Both men were also inclined to be friendly toward the American government. The St. Croix Buffalo had recently been to Washington, and the La Pointe Buffalo frequently spoke of his desire for good relations with the United States in later years. It is also troubling that Lewis contradicts his earlier identification of the location of the portrait at Prairie du Chien.
It is unlikely that Pe-schick-ee depicts a third chief given that no men named Buffalo other than the two mentioned signed the Treaty of Fond du Lac, and the far-eastern bands of Ojibwe from Lake Huron were not part of treaty councils with the Lake Superior bands. One can speculate that perhaps Lewis, writing 25 years after the original painting, mistook the story of Pe-schick-ee with that one of the many other chiefs he met in his travels, but there are some suggestions that it might, in fact, be La Pointe Buffalo.
The La Pointe Band traded with the British in the other side of Lake Superior for years after the War of 1812 supposedly confirmed Chequamegon as American territory. If you’ve read this post, you’ll know that Buffalo from La Pointe was a follower of Tenskwatawa, whose brother Tecumseh fought beside the British. On July 22, 1822, Schoolcraft writes:
At that place [Chequamegon] lived, in comparatively modern times, Wabojeeg and Andaigweos, and there still lives one of their descendants in Gitchee Waishkee, the Great First-born, or, as he is familiarly called, Pezhickee, or the Buffalo, a chief decorated with British insignia. His band is estimated at one hundred and eighteen souls, of whom thirty-four are adult males, forty-one females, and forty-three children.
It’s possible that it was La Pointe Buffalo with the British flag. Archival research into the Treaty of Fond du Lac could potentially clear this up. If I stumble across any, I’ll be sure to add it here. For now, we can’t say one way or the other which Buffalo is in the Lewis portrait.
The Verdict

Not Chief Buffalo from La Pointe: This is Chief Buffalo from St. Croix.

Inconclusive: This could be Buffalo from La Pointe or Buffalo from St. Croix.
Sources:
Horan, James David, and Thomas Loraine McKenney. The McKenney-Hall Portrait Gallery of American Indians. New York, NY: Bramhall House, 1986. Print.
KAPPLER’S INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES. Ed. Charles J. Kappler. Oklahoma State University Library, n.d. Web. 21 June 2012. <http:// digital.library.okstate.edu/Kappler/>.
Lewis, James O., The Aboriginal Port-Folio: A Collection of Portraits of the Most Celebrated Chiefs of the North American Indians. Philadelphia: J.O. Lewis, 1835-1838. Print.
———– Catalogue of the Indian Gallery,. New York: J.O. Lewis, 1850. Print.
Loew, Patty. Indian Nations of Wisconsin: Histories of Endurance and Renewal.
Madison: Wisconsin Historical Society, 2001. Print.
McKenney, Thomas Loraine. Sketches of a Tour to the Lakes of the Character and Customs of the Chippeway Indians, and of Incidents Connected with the Treaty of Fond Du Lac. Baltimore: F. Lucas, Jun’r., 1827. Print.
McKenney, Thomas Loraine, and James Hall. Biographical Sketches and Anecdotes of Ninety-five of 120 Principal Chiefs from the Indian Tribes of North America. Washington: U.S. Dept. of the Interior, Bureau of Indian Affairs, 1967. Print.
Moore, Robert J. Native Americans: A Portrait : The Art and Travels of Charles Bird King, George Catlin, and Karl Bodmer. New York: Stewart, Tabori & Chang, 1997. Print.
Niles, Hezekiah, William O. Niles, Jeremiah Hughes, and George Beatty, eds. “Indians.” Niles’ Weekly Register [Baltimore] 31 July 1824, Miscellaneous sec.: 363. Print.
Rhees, William J. An Account of the Smithsonian Institution. Washington: T. McGill, 1859. Print.
Satz, Ronald N. Chippewa Treaty Rights: The Reserved Rights of Wisconsin’s Chippewa Indians in Historical Perspective. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Academy of Sciences, Arts and Letters, 1991. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe, and Philip P. Mason. Expedition to Lake Itasca; the Discovery of the Source of the Mississippi,. [East Lansing]: Michigan State UP, 1958. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry R. Personal Memoirs of a Residence of Thirty Years with the Indian Tribes on the American Frontiers: With Brief Notices of Passing Events, Facts, and Opinions, A.D. 1812 to A.D. 1842. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo and, 1851. Print.
Viola, Herman J. The Indian Legacy of Charles Bird King. Washington: Smithsonian Institution, 1976. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Special thanks to Theresa Schenck of the University of Wisconsin and Charles Lippert for helping me work through this information, and to Michael Edmonds of the Wisconsin Historical Society, and Alice Cornell (formerly of the University of Cincinnati) for tracking down the single copy of the unpublished James Otto Lewis catalog.
Note: This is the final post of four about Lt. James Allen, his ten American soldiers and their experiences on the St. Croix and Brule rivers. They were sent from Sault Ste. Marie to accompany the 1832 expedition of Indian Agent Henry Schoolcraft to the source of the Mississippi River. Each of the posts gives some general information about the expedition and some pages from Allen’s journal.
On the night of August 1, 1831, the section of the Michigan Territory that would become the state of Wisconsin, was a scene of stark contrasts regarding the United States Army’s ability to force its will on Indian people. In the south, American forces had caught up and skirmished with the starving followers of Black Hawk near the mouth of the Bad Axe River in present-day Vernon County. The next morning, with the backing of the steamboat Warrior, the soldiers would slaughter dozens of men, women, and children as they tried to retreat across the Mississippi. The massacre at Bad Axe was the end of the Black Hawk War, the last major military resistance from the Indian nations of the Old Northwest.
Less than 300 miles upstream, Lieutenant James Allen had his bread stolen right out of his fire as he slept. Presumably, it was taken by Ojibwe youths from the Yellow River village on the St. Croix. Earlier that day, he had been unable to get convince any members of the Yellow River band to guide him up to the Brule River portage. The next morning, (the same day as the Battle of Bad Axe), Allen was able to buy a new bark canoe to take some load off his leaky fleet. However, the Ojibwe family that sold it to him was able to take advantage of supply and demand to get twice the amount of flour from the soldiers that they would’ve gotten from the local traders. Later that day, the well-known chief Gaa-bimabi (Kabamappa), from the upper St. Croix, brought him a desperately-needed map, so not all of his interactions with the Ojibwe that day were negative. However, each of these encounters showed clearly that the Ojibwe were neither cowed nor intimidated by the presence of American soldiers in their country.
In fact, Allen’s detachment must have been a miserable sight. They had fallen several days behind the voyageur-paddled canoes carrying Schoolcraft, the interpreter, and the doctor. Their canoes were leaking badly and they were running out of gum (pitch) to seal them up. Their feet were torn up from wading up the rapids, and one man was too injured to walk. They were running low on food, didn’t know how to find the Brule, and their morale was running dangerously low. If the War Department’s plan was for Allen to demonstrate American power to the Ojibwe, the plan had completely backfired.
The journey down the Brule was even more difficult for the soldiers than the trip up the St. Croix. I won’t repeat it all here because it’s in the posted pages of Allen’s journal in these four posts, but in the end, it was our old buddy Maangozid (see 4/14/13 post) and some other Fond du Lac Ojibwe who rescued the soldiers from their ordeal.
Allen’s journal entry after finally reaching Lake Superior is telling:
“[T]he management of bark canoes, of any size, in rapid rivers, is an art which it takes years to acquire; and, in this country, it is only possessed by Canadians [mix-blooded voyageurs] and Indians, whose habits of life have taught them but little else. The common soldiers of the army have no experience of this kind, and consequently, are not generally competent to transport themselves in this way; and whenever it is required to transport troops, by means of bark canoes, two Canadian voyageurs ought to be assigned to each canoe, one in the bow, and another in the stern; it will then be the safest and most expeditious method that can be adopted in this country.”
The 1830s were the years of Indian Removal throughout the United States, but at that time, the American government had no hope of conquering and subduing the Ojibwe militarily. When the Ojibwe did surrender their lands (in 1837 and 1842 for the Wisconsin parts), it was due to internal politics and economics rather than any serious threat of American invasion. Rather than proving the strength of the United States, Allen’s expedition revealed a serious weakness.
The Ojibwe weren’t overconfident or ignorant. The very word for Americans, chimookomaan (long knife), referred to soldiers. A handful of Ojibwe and mix-blooded warriors had fought the United States in the War of 1812 and earlier in the Ohio country. Bizhiki and Noodin, two chiefs whose territory Allen passed through on his ill-fated journey, had been to Washington in 1824 and saw the army firsthand. The next year, many more chiefs got to see the long knives in person at the Treaty of Prairie du Chien. Finally, the removal of their Ottawa and Potawatomi cousins and other nations to Indian Territory in the 1830s was a well-known topic of concern in Ojibwe villages. They knew the danger posed by American soldiers, but the reality of the Lake Superior Country in 1832 was that American power was very limited.
The journal picks up from part 3 with Allen and crew on the Brule River with their canoes in rapidly-deteriorating condition. They’ve made contact with the Fond du Lac villagers camped at the mouth, but there are still several obstacles to overcome.

Doc. 323, pg. 66
Allen’s journal is part of Phillip P. Mason’s edition of Schoolcraft’s Expedition to Lake Itasca: The Discovery of the Source of the Mississippi (1958). However, these Google Books pages come from the original publication as part of the United States Congress Serial Set.

James Allen (1806-1846)
Collections of the Iowa Historical Society
Allen and all of his men survived the ordeal of the 1832 expedition. He returned to La Pointe on August 11 and left the next day with Dr. Houghton. The two men returned to the Soo together, stopping at the great copper rock on the Ontonagon River along the way.
On September 13, 1832, he wrote Alexander Macomb, his commander at Fort Brady. The letter officially complained about Schoolcraft “unnecessarily and injuriously” leaving the soldiers behind at the mouth of the St. Croix. When the New York American published its review of Schoolcraft’s Narrative on July 19, 1834, it expressed “indignation and dismay” at the “un-Christianlike” behavior of the agent for abandoning the soldiers in the “enemy’s country.” The resulting controversy forced Schoolcraft to defend himself in the Detroit Journal and Michigan Advertiser where he pointed out Allen’s map’s importance to the Narrative. He also reminded the public that the Ojibwe and the United States were considered allies.
James Allen went on to serve in Chicago and at the Sac and Fox agency in Iowa Territory. After the Mexican War broke out in 1846, he traveled to Utah and organized a Mormon Battalion to fight on the American side. He died on his way back east on August 23, 1846. He was only forty years old. (John Lindquist has great website about the career of James Allen with much more information about his post-1832 life).
Sources:
Ely, Edmund Franklin, and Theresa M. Schenck. The Ojibwe Journals of Edmund F. Ely, 1833-1849. Lincoln: University of Nebraska, 2012. Print.
Loew, Patty. Indian Nations of Wisconsin: Histories of Endurance and Renewal. Madison: Wisconsin Historical Society, 2001. Print.
Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe, and Philip P. Mason. Expedition to Lake Itasca; the Discovery of the Source of the Mississippi,. [East Lansing]: Michigan State UP, 1958. Print.
Warren, William W., and Theresa M. Schenck. History of the Ojibway People. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2009. Print.
Witgen, Michael J. An Infinity of Nations: How the Native New World Shaped Early North America. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania, 2012. Print.
Note: This is the third of four posts about Lt. James Allen, his ten American soldiers and their experiences on the St. Croix and Brule rivers. They were sent from Sault Ste. Marie to accompany the 1832 expedition of Indian Agent Henry Schoolcraft to the source of the Mississippi River. Each of the posts will give some general information about the expedition and some pages from Allen’s journal.

Douglass Houghton (1809-1845) was the naturalist and physician for the expedition. While traveling with Schoolcraft’s lead group, he expressed frequent concern for Allen and the soldiers as they fell behind (painted by Alva Bradish, 1850; Wikimedia Commons).
Schoolcraft’s original book takes up the first quarter of the pages in the 1958 edition of Narrative of an Expedition, edited by Phillip P. Mason. The rest of the pages are six appendixes including the journals of Douglass Houghton the surgeon and geologist, W.T. Boutwell the missionary, and Allen. Of the four, Schoolcraft’s provides the blandest reading. His positive, official spin on everything offers little glimpse into his psyche. In contrast, Houghton gives us a unique account of smallpox vaccinations, botany, and geology. Boutwell gives us detailed descriptions of Ojibwe religious practices through his zealous missionary filter. His frequent complaints about mosquitoes, profane soldiers, Indian drumming, and voyageur gambling ruining his Sabbaths are very humorous to those who aren’t sympathetic to his mission.
Allen’s journal is fascinating. He was sent by the War Department to record information about the geography of the country and its people for military purposes. Officially the Ojibwe and the United States were friendly. Schoolcraft, being married into a prominent Ojibwe family at the Sault, promoted this idea. However, a sense of future military confrontation looms over the narrative. The Indian Removal Act was only two years old, and Black Hawk’s War broke out just as the expedition was starting out. In 1832, lasting peace between the Ojibwe and the United States was not automatically guaranteed.
The journal reads, at times, like a post-modern anti-colonial novel complete with Allen as the villainous narrator looking to get rich off Lake Superior copper and making war plans against Leech Lake. However, Allen’s writing style allows the reader in as Schoolcraft’s doesn’t, and he shows himself to be thoughtful and observant.
Allen’s primary objective was to protect Schoolcraft and show the Ojibwe that the United States could easily deliver soldiers to their remotest villages. This mission proved difficult from the beginning. Once they left Lake Superior and reached the Fond du Lac portages, it became evident that Allen’s soldiers had no canoe experience and could not keep up with Schoolcraft’s mix-blooded voyageurs. Schoolcraft never seems overly concerned about this, and much of Allen’s narrative is about his men painfully trying to catch up while the Ojibwe and mix-blooded guides laugh at their floundering techniques for getting through rapids.
Through all the hardship, though, Allen did complete the journey to Elk Lake (Itasca) and back down the Mississippi to Fort Snelling. His map of the trip was praised back east as a great contribution to world geography, and Schoolcraft used it to illustrate the published narrative. However, it was the final stretch through the St. Croix and Brule, after Schoolcraft had already declared the expedition a success, where things really got bad for the soldiers.
Continued from Part 2:

Section of Allen’s map showing the St. Croix to Brule portage. Note Gaa-bimabi’s (Keppameppa’s) village on Whitefish Lake near present-day Gordon, Wisconsin. (Reproduced by John Lindquist).
At this point, Allen and his men have fallen multiple days behind Schoolcraft. They have no knowledge of the country save a few rough maps and descriptions. Their canoes are falling apart, and they are physically beaten from their difficult journey up the St. Croix. In theory, the portage over the hill to the Brule should be an easy one given the fact they have little food and supplies left to carry. However, the men are demoralized and ready to quit. Little do they know, the darkest days of their journey are still to come.

Doc. 323, pg. 63
Allen’s journal is part of Phillip P. Mason’s edition of Schoolcraft’s Expedition to Lake Itasca: The Discovery of the Source of the Mississippi (1958). However, these Google Books pages come from the original publication as part of the United States Congress Serial Set.





















